view - Department of Reproduction, Obstetrics and Herd Health
view - Department of Reproduction, Obstetrics and Herd Health
view - Department of Reproduction, Obstetrics and Herd Health
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
CHAPTER 2<br />
Burr, 1930). Specific long chain fatty acids (LCFA), such as 18:2n-6 <strong>and</strong> 18:3n-3 <strong>and</strong> not<br />
fat per se, have ever since gained general recognition as being essential for reproduction<br />
in all mammalian species as well, being necessary precursors for metabolic regulation<br />
<strong>and</strong> cell membrane function (Staples <strong>and</strong> Thatcher, 2005).<br />
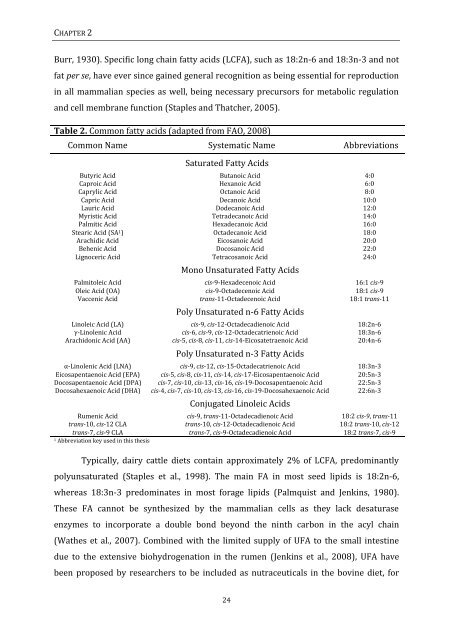
Table 2. Common fatty acids (adapted from FAO, 2008)<br />
Common Name Systematic Name Abbreviations<br />
Saturated Fatty Acids<br />
Butyric Acid Butanoic Acid 4:0<br />
Caproic Acid Hexanoic Acid 6:0<br />
Caprylic Acid Octanoic Acid 8:0<br />
Capric Acid Decanoic Acid 10:0<br />
Lauric Acid Dodecanoic Acid 12:0<br />
Myristic Acid Tetradecanoic Acid 14:0<br />
Palmitic Acid Hexadecanoic Acid 16:0<br />
Stearic Acid (SA 1 ) Octadecanoic Acid 18:0<br />
Arachidic Acid Eicosanoic Acid 20:0<br />
Behenic Acid Docosanoic Acid 22:0<br />
Lignoceric Acid Tetracosanoic Acid 24:0<br />
Mono Unsaturated Fatty Acids<br />
Palmitoleic Acid cis-9-Hexadecenoic Acid 16:1 cis-9<br />
Oleic Acid (OA) cis-9-Octadecenoic Acid 18:1 cis-9<br />
Vaccenic Acid trans-11-Octadecenoic Acid 18:1 trans-11<br />
Poly Unsaturated n-6 Fatty Acids<br />
Linoleic Acid (LA) cis-9, cis-12-Octadecadienoic Acid 18:2n-6<br />
γ-Linolenic Acid cis-6, cis-9, cis-12-Octadecatrienoic Acid 18:3n-6<br />
Arachidonic Acid (AA) cis-5, cis-8, cis-11, cis-14-Eicosatetraenoic Acid 20:4n-6<br />
Poly Unsaturated n-3 Fatty Acids<br />
α-Linolenic Acid (LNA) cis-9, cis-12, cis-15-Octadecatrienoic Acid 18:3n-3<br />
Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) cis-5, cis-8, cis-11, cis-14, cis-17-Eicosapentaenoic Acid 20:5n-3<br />
Docosapentaenoic Acid (DPA) cis-7, cis-10, cis-13, cis-16, cis-19-Docosapentaenoic Acid 22:5n-3<br />
Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) cis-4, cis-7, cis-10, cis-13, cis-16, cis-19-Docosahexaenoic Acid 22:6n-3<br />
Conjugated Linoleic Acids<br />
Rumenic Acid cis-9, trans-11-Octadecadienoic Acid 18:2 cis-9, trans-11<br />
trans-10, cis-12 CLA trans-10, cis-12-Octadecadienoic Acid 18:2 trans-10, cis-12<br />
trans-7, cis-9 CLA trans-7, cis-9-Octadecadienoic Acid 18:2 trans-7, cis-9<br />
1<br />
Abbreviation key used in this thesis<br />
Typically, dairy cattle diets contain approximately 2% <strong>of</strong> LCFA, predominantly<br />
polyunsaturated (Staples et al., 1998). The main FA in most seed lipids is 18:2n-6,<br />
whereas 18:3n-3 predominates in most forage lipids (Palmquist <strong>and</strong> Jenkins, 1980).<br />
These FA cannot be synthesized by the mammalian cells as they lack desaturase<br />
enzymes to incorporate a double bond beyond the ninth carbon in the acyl chain<br />
(Wathes et al., 2007). Combined with the limited supply <strong>of</strong> UFA to the small intestine<br />
due to the extensive biohydrogenation in the rumen (Jenkins et al., 2008), UFA have<br />
been proposed by researchers to be included as nutraceuticals in the bovine diet, for<br />
24