Introduction to Digital Signal and System Analysis - Tutorsindia
Introduction to Digital Signal and System Analysis - Tutorsindia
Introduction to Digital Signal and System Analysis - Tutorsindia
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Introduction</strong> <strong>to</strong> <strong>Digital</strong> <strong>Signal</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>System</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
Time-domain <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
s[3]= h[0]+h[1]+h[2]+h[3]=1+0.6+0.6´0.6+0.6´0.6´0.6<br />
1<br />
s[∞]=1+0.6+0.6´0.6+0.6´0.6´0.6+… = = 2. 5 ,<br />
1−<br />
0.6<br />
where the following series summation formula is applied.<br />
2 3 1<br />
1+ a + a + a + ... =<br />
a<br />
1−<br />
a<br />
< 1<br />
(3.13)<br />
3.5 Convolution<br />
In order <strong>to</strong> derive the convolution formula based on clear underst<strong>and</strong>ing, a signal is expressed by impulse functions as<br />
following:<br />
For a signal x [ n],<br />
−∞ < n < ∞ , using the rules of the signal shifting <strong>and</strong> scaling described Section 2.3, it is decomposed<br />
in<strong>to</strong> a series of unit impulses scaled by the sample values:<br />
x[ n]<br />
= ... + x[<br />
−2]<br />
d[<br />
n + 2] + x[<br />
−1]<br />
d[<br />
n + 1] + x[0]<br />
d[<br />
n]<br />
+ x[1]<br />
d[<br />
n − 1] + x[2]<br />
d[<br />
n − 2] + ...<br />
or<br />
∑ ∞<br />
k = −∞<br />
x [ n]<br />
= x[<br />
k]<br />
d[<br />
n − k]<br />
(3.14)<br />
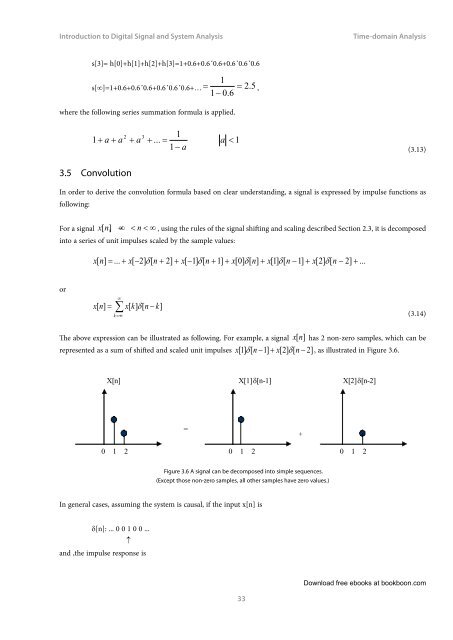
The above expression can be illustrated as following. For example, a signal x [n]<br />
has 2 non-zero samples, which can be<br />
represented as a sum of shifted <strong>and</strong> scaled unit impulses x[ 1] d [ n −1]<br />
+ x[2]<br />
d[<br />
n − 2]<br />
, as illustrated in Figure 3.6.<br />
X[n]<br />
X[1]d[n-1]<br />
X[2]d[n-2]<br />
=<br />
+<br />
0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2<br />
Figure 3.6 A signal can be decomposed in<strong>to</strong> simple sequences.<br />
(Except those non-zero samples, all other samples have zero values.)<br />
In general cases, assuming the system is causal, if the input x[n] is<br />
δ[n]: ... 0 0 1 0 0 ...<br />
↑<br />
<strong>and</strong> ,the impulse response is<br />
33<br />
Download free ebooks at bookboon.com