Introduction to Digital Signal and System Analysis - Tutorsindia
Introduction to Digital Signal and System Analysis - Tutorsindia
Introduction to Digital Signal and System Analysis - Tutorsindia
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Introduction</strong> <strong>to</strong> <strong>Digital</strong> <strong>Signal</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>System</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
Time-domain <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
4<br />
a) Unit impulse<br />
4<br />
b) Impulse response<br />
2<br />
2<br />
0<br />
0<br />
-2<br />
-2<br />
4<br />
0 5 10<br />
c) input 1<br />
4<br />
0 5 10<br />
d) response 1<br />
2<br />
2<br />
0<br />
0<br />
-2<br />
-2<br />
4<br />
0 5 10<br />
e) input 2<br />
4<br />
0 5 10<br />
f) response 2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
0<br />
0<br />
-2<br />
-2<br />
4<br />
0 5 10<br />
g) input 3<br />
4<br />
0 5 10<br />
h) response 3<br />
2<br />
2<br />
0<br />
0<br />
-2<br />
-2<br />
4<br />
0 5 10<br />
i) <strong>to</strong>tal input x[n]<br />
4<br />
0 5 10<br />
j) <strong>to</strong>tal response y[n]<br />
2<br />
2<br />
0<br />
0<br />
-2<br />
-2<br />
0 5 10<br />
n<br />
0 5 10<br />
n<br />
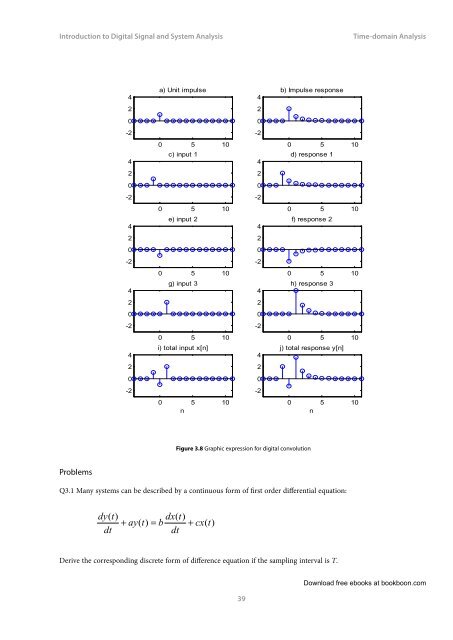
Figure 3.8 Graphic expression for digital convolution<br />
Problems<br />
Q3.1 Many systems can be described by a continuous form of first order differential equation:<br />
dy(<br />
t)<br />
dx(<br />
t)<br />
+ ay(<br />
t)<br />
= b + cx(<br />
t)<br />
dt<br />
dt<br />
Derive the corresponding discrete form of difference equation if the sampling interval is T.<br />
39<br />
Download free ebooks at bookboon.com