Central Rice Research Institute Annual report...2011-12
Central Rice Research Institute Annual report...2011-12
Central Rice Research Institute Annual report...2011-12
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Breeding for Resistance/Tolerance to Biotic, Abiotic and Environmental Stresses<br />
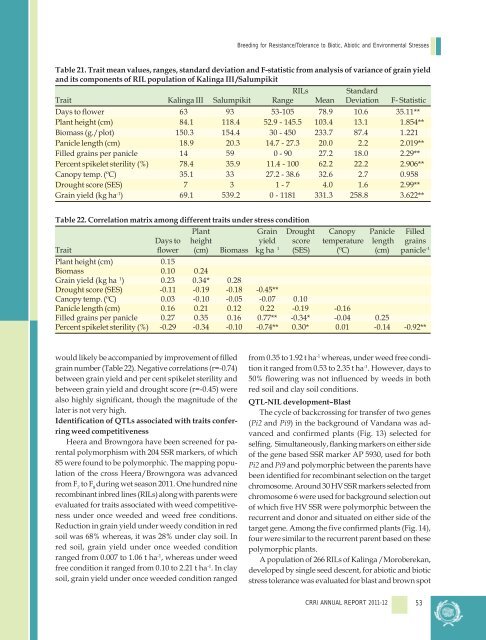
Table 21. Trait mean values, ranges, standard deviation and F-statistic from analysis of variance of grain yield<br />
and its components of RIL population of Kalinga III /Salumpikit<br />
RILs Standard<br />
Trait Kalinga III Salumpikit Range Mean Deviation F- Statistic<br />
Days to flower 63 93 53-105 78.9 10.6 35.11**<br />
Plant height (cm) 84.1 118.4 52.9 - 145.5 103.4 13.1 1.854**<br />
Biomass (g./plot) 150.3 154.4 30 - 450 233.7 87.4 1.221<br />
Panicle length (cm) 18.9 20.3 14.7 - 27.3 20.0 2.2 2.019**<br />
Filled grains per panicle 14 59 0 - 90 27.2 18.0 2.29**<br />
Percent spikelet sterility (%) 78.4 35.9 11.4 - 100 62.2 22.2 2.906**<br />
Canopy temp. (ºC) 35.1 33 27.2 - 38.6 32.6 2.7 0.958<br />
Drought score (SES) 7 3 1 - 7 4.0 1.6 2.99**<br />
Grain yield (kg ha -1 ) 69.1 539.2 0 - 1181 331.3 258.8 3.622**<br />
Table 22. Correlation matrix among different traits under stress condition<br />
Plant Grain Drought Canopy Panicle Filled<br />
Days to height yield score temperature length grains<br />
Trait flower (cm) Biomass kg ha 1 (SES) (ºC) (cm) panicle -1<br />
Plant height (cm) 0.15<br />
Biomass 0.10 0.24<br />
Grain yield (kg ha 1 ) 0.23 0.34* 0.28<br />
Drought score (SES) -0.11 -0.19 -0.18 -0.45**<br />
Canopy temp. (ºC) 0.03 -0.10 -0.05 -0.07 0.10<br />
Panicle length (cm) 0.16 0.21 0.<strong>12</strong> 0.22 -0.19 -0.16<br />
Filled grains per panicle 0.27 0.35 0.16 0.77** -0.34* -0.04 0.25<br />
Percent spikelet sterility (%) -0.29 -0.34 -0.10 -0.74** 0.30* 0.01 -0.14 -0.92**<br />
would likely be accompanied by improvement of filled<br />
grain number (Table 22). Negative correlations (r=-0.74)<br />
between grain yield and per cent spikelet sterility and<br />
between grain yield and drought score (r=-0.45) were<br />
also highly significant, though the magnitude of the<br />
later is not very high.<br />
Identification of QTLs associated with traits conferring<br />
weed competitiveness<br />
Heera and Browngora have been screened for parental<br />
polymorphism with 204 SSR markers, of which<br />
85 were found to be polymorphic. The mapping population<br />
of the cross Heera/Browngora was advanced<br />
from F 7<br />
to F 8<br />
during wet season 2011. One hundred nine<br />
recombinant inbred lines (RILs) along with parents were<br />
evaluated for traits associated with weed competitiveness<br />
under once weeded and weed free conditions.<br />
Reduction in grain yield under weedy condition in red<br />
soil was 68% whereas, it was 28% under clay soil. In<br />
red soil, grain yield under once weeded condition<br />
ranged from 0.007 to 1.06 t ha -1 , whereas under weed<br />
free condition it ranged from 0.10 to 2.21 t ha -1 . In clay<br />
soil, grain yield under once weeded condition ranged<br />
from 0.35 to 1.92 t ha -1 whereas, under weed free condition<br />
it ranged from 0.53 to 2.35 t ha -1 . However, days to<br />
50% flowering was not influenced by weeds in both<br />
red soil and clay soil conditions.<br />
QTL-NIL development–Blast<br />
The cycle of backcrossing for transfer of two genes<br />
(Pi2 and Pi9) in the background of Vandana was advanced<br />
and confirmed plants (Fig. 13) selected for<br />
selfing. Simultaneously, flanking markers on either side<br />
of the gene based SSR marker AP 5930, used for both<br />
Pi2 and Pi9 and polymorphic between the parents have<br />
been identified for recombinant selection on the target<br />
chromosome. Around 30 HV SSR markers selected from<br />
chromosome 6 were used for background selection out<br />
of which five HV SSR were polymorphic between the<br />
recurrent and donor and situated on either side of the<br />
target gene. Among the five confirmed plants (Fig. 14),<br />
four were similar to the recurrent parent based on these<br />
polymorphic plants.<br />
A population of 266 RILs of Kalinga /Moroberekan,<br />
developed by single seed descent, for abiotic and biotic<br />
stress tolerance was evaluated for blast and brown spot<br />
CRRI ANNUAL REPORT 2011-<strong>12</strong><br />
53