NSH-566 Modularized 24 (100Base-FX) + 2G Access Switch
NSH-566 Modularized 24 (100Base-FX) + 2G Access Switch
NSH-566 Modularized 24 (100Base-FX) + 2G Access Switch
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Modularized</strong> <strong>24</strong>+<strong>2G</strong> <strong>Switch</strong><br />
information, please refer to IEEE 802.3ad.<br />
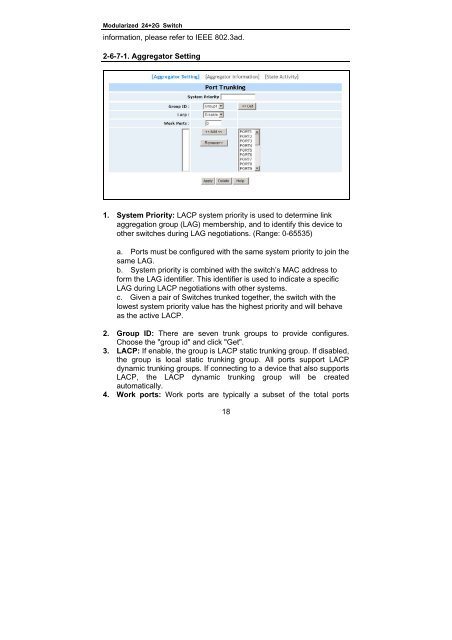
2-6-7-1. Aggregator Setting<br />
1. System Priority: LACP system priority is used to determine link<br />
aggregation group (LAG) membership, and to identify this device to<br />
other switches during LAG negotiations. (Range: 0-65535)<br />
a. Ports must be configured with the same system priority to join the<br />
same LAG.<br />
b. System priority is combined with the switch’s MAC address to<br />
form the LAG identifier. This identifier is used to indicate a specific<br />
LAG during LACP negotiations with other systems.<br />
c. Given a pair of <strong>Switch</strong>es trunked together, the switch with the<br />
lowest system priority value has the highest priority and will behave<br />
as the active LACP.<br />
2. Group ID: There are seven trunk groups to provide configures.<br />
Choose the "group id" and click "Get".<br />
3. LACP: If enable, the group is LACP static trunking group. If disabled,<br />
the group is local static trunking group. All ports support LACP<br />
dynamic trunking groups. If connecting to a device that also supports<br />
LACP, the LACP dynamic trunking group will be created<br />
automatically.<br />
4. Work ports: Work ports are typically a subset of the total ports<br />
18