X-ray Study of Low-mass Young Stellar Objects in the ρ Ophiuchi ...
X-ray Study of Low-mass Young Stellar Objects in the ρ Ophiuchi ...
X-ray Study of Low-mass Young Stellar Objects in the ρ Ophiuchi ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
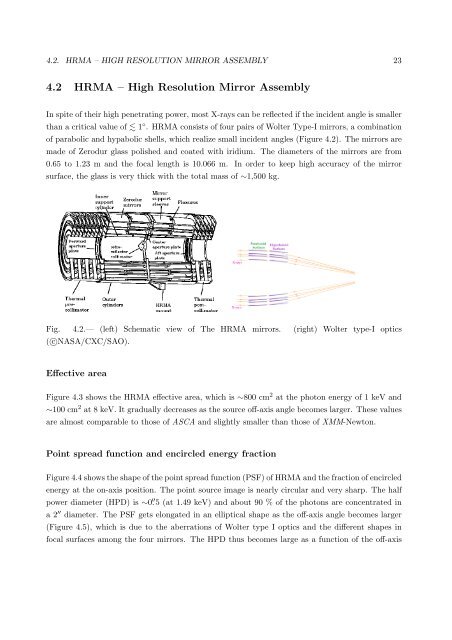
4.2. HRMA – HIGH RESOLUTION MIRROR ASSEMBLY 234.2 HRMA – High Resolution Mirror AssemblyIn spite <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>ir high penetrat<strong>in</strong>g power, most X-<strong>ray</strong>s can be reflected if <strong>the</strong> <strong>in</strong>cident angle is smallerthan a critical value <strong>of</strong> 1 ◦ . HRMA consists <strong>of</strong> four pairs <strong>of</strong> Wolter Type-I mirrors, a comb<strong>in</strong>ation<strong>of</strong> parabolic and hypabolic shells, which realize small <strong>in</strong>cident angles (Figure 4.2). The mirrors aremade <strong>of</strong> Zerodur glass polished and coated with iridium. The diameters <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> mirrors are from0.65 to 1.23 m and <strong>the</strong> focal length is 10.066 m. In order to keep high accuracy <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> mirrorsurface, <strong>the</strong> glass is very thick with <strong>the</strong> total <strong>mass</strong> <strong>of</strong> ∼1,500 kg.Fig. 4.2.— (left) Schematic view <strong>of</strong> The HRMA mirrors. (right) Wolter type-I optics( c○NASA/CXC/SAO).Effective areaFigure 4.3 shows <strong>the</strong> HRMA effective area, which is ∼800 cm 2 at <strong>the</strong> photon energy <strong>of</strong> 1 keV and∼100 cm 2 at 8 keV. It gradually decreases as <strong>the</strong> source <strong>of</strong>f-axis angle becomes larger. These valuesare almost comparable to those <strong>of</strong> ASCA and slightly smaller than those <strong>of</strong> XMM-Newton.Po<strong>in</strong>t spread function and encircled energy fractionFigure 4.4 shows <strong>the</strong> shape <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> po<strong>in</strong>t spread function (PSF) <strong>of</strong> HRMA and <strong>the</strong> fraction <strong>of</strong> encircledenergy at <strong>the</strong> on-axis position. The po<strong>in</strong>t source image is nearly circular and very sharp. The halfpower diameter (HPD) is ∼0. ′′ 5 (at 1.49 keV) and about 90 % <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> photons are concentrated <strong>in</strong>a 2 ′′ diameter. The PSF gets elongated <strong>in</strong> an elliptical shape as <strong>the</strong> <strong>of</strong>f-axis angle becomes larger(Figure 4.5), which is due to <strong>the</strong> aberrations <strong>of</strong> Wolter type I optics and <strong>the</strong> different shapes <strong>in</strong>focal surfaces among <strong>the</strong> four mirrors. The HPD thus becomes large as a function <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>of</strong>f-axis