Compendium of Potato Diseases - (PDF, 101 mb) - USAID
Compendium of Potato Diseases - (PDF, 101 mb) - USAID
Compendium of Potato Diseases - (PDF, 101 mb) - USAID
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
humidity, photoperiod, and host plant condition) to which the Where winter conditions are severe, most potato-infesting<br />
aphid or its mother is exposed. Thus. the life cycle <strong>of</strong> any aphids overwinter as sexually produced eggs laid on the rough<br />
particular species riaN not be the same in different parts <strong>of</strong>the bark <strong>of</strong> a woody host or on the crown and leaves <strong>of</strong> an<br />
world. Aphids may he winged (alate) or wingless (apterous), herbaceous biennial or perennial plant. A female nymph<br />
male or emale. Females may he o%iparous (sexually producing hatches from each egg in the spring, feeds on the expanding<br />
fertili/ed oxer%%intering eggs) or parthenogenetic and viviparous foliage, and after molting four times, develops into a nature,<br />
(asexually producing living young, called nymphs), wingless, parthenogenetic female. She gives birth to female<br />
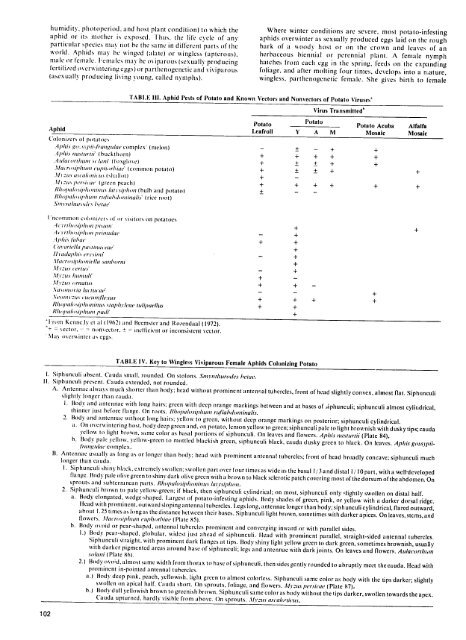
TABLE i11.Aphid Pests <strong>of</strong> <strong>Potato</strong> and Known Vectors and Nonvectors <strong>of</strong> <strong>Potato</strong> Viruses'<br />
Virus Transmitted"<br />
Aphid<br />
<strong>Potato</strong><br />
Leafroll Y<br />
<strong>Potato</strong><br />
A M<br />
<strong>Potato</strong> Acuba<br />
Mosaic<br />
Alfalfa<br />
Mosaic<br />
Coloni/ers ol potatoes<br />
,.lphi. iA..rpii-fI;'at/ae. cornplex' (melon)<br />
.-IIhi. na.turtif buckthorn)<br />
.Aulacorthui. lani' (Ioxgloye)<br />
.t/a(rophtint euirhiae'(conmmon potato)<br />
./it: atcalon 'io (shallot)<br />
.1/ii. per.%iat' (green peach)<br />
lIhopahemiiphonimi lati.hsipion(bulb and potato)<br />
Ihoah.oiphumruiabtdominali. (rice root<br />
-<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
_<br />
+<br />
_<br />
-<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
'Smri ihio 'he Icuj<br />
I'rconiniton ctloniicrs <strong>of</strong> or visitors on potatoes<br />
,-I(irhin il)hito pt.uttm'<br />
.. i rthoipio pri t/ac<br />
Aphi. /ia'at<br />
("avariella '<br />
i,%tiliateae<br />
lit dto eri.knit<br />
.lacro.ilhontiilla .%an/orni<br />
r ttro.<br />
.Ilizt.u hiuoitl<br />
+<br />
_<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
-<br />
+<br />
_<br />
+<br />
. rnala s + + _<br />
.\m'o:Ii 4ctil//t',ilds<br />
Rhohinu,,s '.itmiia tialhrleaeta/ipaelhts<br />
Rholi wmpntm pad,<br />
I-rm Kennel\ cit a 11962) and Beemsier and Ro/endaal (1972).<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+ = \ector. -- -- nonector, I<br />
Ma o\crinter as eggs.<br />
incficient or inconsistent vector.<br />
TABLE IV. Key to Wingless Viviparous Female Aphids Colonizing <strong>Potato</strong><br />
I. Siphunculi absent. Cauda small, rounded. On stolons. Smynithurodes hetae.<br />
II. Siphunculi present. Cauda extended, not rounded.<br />
A. Antennae always much shorter than body: head without prominent anten,;al tubercles, front <strong>of</strong> head slightly convex, almost flat. Siphunculi<br />
slightly longer than cauda.<br />
I. Body and antennae with long hairs; green with deep orange markings between and at bases <strong>of</strong> ,iphunculi; siphunculi almost cylindrical,<br />
thinner iust before flange. On roots. R/opalosilium ruflahdotoinalis.<br />
2. Hody and antennae without long hairs; yellow to green, without deep orange markings on posterior; siphunculi cylindrical.<br />
a. On overwi nteri ng host, bodydeep green and, on potato, lemon yellow to green; siphunculi pale to light brownish with dusky tips; cauda<br />
y'clloss to light brown. same color as basal portions <strong>of</strong> siphunculi. On leaves and flowers. Aphis nasturtii (Plate 84),<br />
b. Body pah: yellow, yellow-green to mottled blackish green, siphunculi black, cauda dusky green to black. On leaves. Aphis gossl'fi<br />
/ani.dae'complex.<br />
B. Antennae usually as long as or longer than bodv: head with prominent antennal tubercles; front <strong>of</strong> head broadly concave; siphunculi much<br />
102<br />
longer than cauda.<br />
I. Siphunculi shiny black, cxtremely swollen: swollen part over four times as wide as the basal 1/3and distal I / 10 part, with a well-developed<br />
flange. Body pale olivc green to shiny dark olive green with a brown to black sclerotic patch covering most <strong>of</strong> the dorsum <strong>of</strong> the abdomen. On<br />
sprouts and subterranean parts. Rholao.silgto/nin. lahiyrp/ton.<br />
2. SiphunCuli brown to pale yellow-green: if black, then siphunculi cylindrical; on most, siphunculi only slightly swollen on distal half.<br />
a. Body clongated. wedge-shaped. Largest <strong>of</strong> potato-infesting aphids. Body shades <strong>of</strong> green, pink, or yellow with a darker dorsal ridge.<br />
[lead with prominent, outward sloping antennal tubercles. l.egs long, antennae longer than body; siphunculi cylindrical, flared outward,<br />
about 1.25 times as longas the distance between their bases. Siphunculi light brown, sometimes with darkerapices. On leaves, stcms,and<br />
flowers. .1facro.ip/tium euphorhiae(Plate 85).<br />
b. Body ovoid or pear-shaped, antennal tubercles prominent and converging inward or with parallel sides.<br />
1.) Body pear-shaped. globular. widest just ahead <strong>of</strong> siphunculi. flead with prominent parallel, straight-sided antennal tubercles.<br />
Siphunculi straight, with prominent dark flanges at tips. Body shiny light yellow green to dark green, sometimes brownish, usually<br />
with darker pigmented areas around base <strong>of</strong> siphunculi: legs and antennae with dark joints. On leaves and flowers. Aulacorth,o<br />
.oltani (Plate 861.<br />
2.) Body ovoid, almost same width from thorax to base <strong>of</strong> siphunculi. then sides gently rounded to abruptly meet thecauda. Head with<br />
prominent in-pointed antennal tubercles.<br />
a.) Body deep pink, peach, yellowish, light green to almost colorless. Siphunculi same color as body with the tips darker; slightly<br />
swollen on apical half. Cauda short. On sprouts, foliage, and flowers. iaus persicae(Plate 87).<br />
b.) Body dull yellowish brown to greenish brown. Siphunculi same coloras body without the tips darker, swollen towards the apex.<br />
Cauda upturned, hardly visible from above. On sprouts. M v:us a.calo'tiCus.<br />
+