Compendium of Potato Diseases - (PDF, 101 mb) - USAID
Compendium of Potato Diseases - (PDF, 101 mb) - USAID
Compendium of Potato Diseases - (PDF, 101 mb) - USAID
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Selected Reference brown to bronze areas, later becoming necrotic, may develop on<br />
leaves near the middle <strong>of</strong> the plant and later involve all leaves.<br />
MIIGI.EY. A. R., and 1). F. I)IINKII. 1940. Ihe cause and nature Brownish spots may develop on petioles and stems.<br />
<strong>of</strong> oserliming injury. VI Agric. Exp. Stin. Bull. 460. 22 pp. Zn deficieney in recently developed land. alkaline soils, or<br />
soils with excessivcly high1P results in severe stunting, leaf<br />
Zinc malformation, and indistinct bron/ing or yellowi ng around leaf<br />
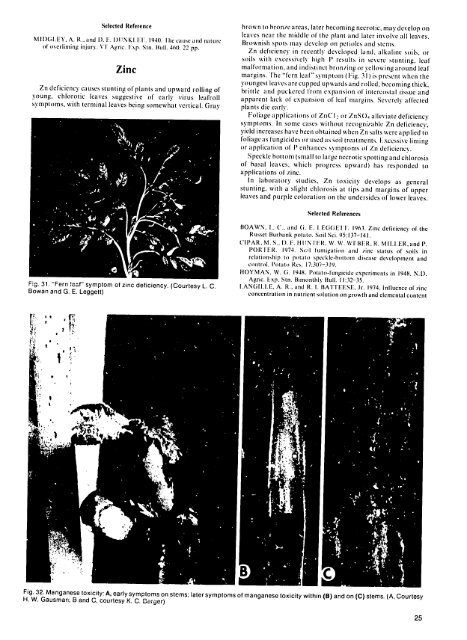
margins. The "fern leaf" sympton (Fig. 31 ) is present when the<br />
youngest leaves are cupped upwards and rolled, becoming thick,<br />
Zn deficiency causes stunting <strong>of</strong> plants and upward rolling <strong>of</strong> brittle and puckered from expansion <strong>of</strong> intercostal tissue and<br />
young. chlorotic leaves suggestive <strong>of</strong> early virus leafroll apparent lack <strong>of</strong> expansion <strong>of</strong> leaf margins. Severely affected<br />
symptoms, with terminal leaves being somewhat vertical. Gray plants die early.<br />
Foliage applications <strong>of</strong> ZnC I : or ZnS0 4 alleviate deficiency<br />
symptoms. In some cases without recogni/able Zn deficiency.<br />
yield increases have been obtained when Zn salts were applied to<br />
foliage as fungicides or used as soil treatments. Excessive liming<br />
or application <strong>of</strong> 1)enhlnces symptoms <strong>of</strong> Zn deficiency.<br />
Speckle bottom (small to large necrotic spotting and chlorosis<br />
<strong>of</strong> basal leaves, which progress upward) has responded to<br />
applications <strong>of</strong> zinc.<br />
In laboratory studies, Zn toxicity develops as general<br />
stunting, with a slight chlorosis at tips and margins <strong>of</strong> upper<br />
leaves and purple coloration on the undersides <strong>of</strong> lower leaves.<br />
Selected References<br />
HOAWN, I.. C., and (i. lECGE'. 1963. Zinc deficiency <strong>of</strong> the<br />
Russet Burbank potato. Soil Sci. 95:137-141.<br />
CIPAR. M.S., D. E. ItUN IR. W. W. WE1IR. R. MII.1.ER.and P.<br />
PORIER. 1974. Soil fumigation and /inc stattus <strong>of</strong> soils in<br />
relationship to potato speckle-hottom disease de\elopment and<br />
control. <strong>Potato</strong> Res. 17:30'/-319.<br />
HOYMAN. W. G. 1948. <strong>Potato</strong>-lungicide experiments in 1948. N.D.<br />
Agric. Exp. Stn. IBimonthly Bull. 11:32-35.<br />
Fig. 31. "Fern leaf" symptom <strong>of</strong> zinc deficiency. (Courtesy L. C. I.ANGII.E, A. I.. and R. I. IATlEESE, Jr. 1974. Influence <strong>of</strong> inc<br />
Bowan and G. E. Leggett) concentration in nutrient solution on growth and elemental content<br />
• |<br />
..,<br />
' 4l'<br />
Fig. 32. Manganese toxicity: A, early symptoms on stems; later symptoms <strong>of</strong> manganese toxicity within (B) and on (C) stems. (A, Courtesy<br />
H. W. Gausman; B and C, courtesy K. C. Darger)<br />
25