Gene regulation in Streptococcus pneumoniae - RePub - Erasmus ...
Gene regulation in Streptococcus pneumoniae - RePub - Erasmus ...
Gene regulation in Streptococcus pneumoniae - RePub - Erasmus ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Chapter 5<br />
repression of glnA expression <strong>in</strong> the wild-type already at a relatively low concentration (0.25<br />
mM). A higher glutam<strong>in</strong>e concentration did not lead to stronger repression <strong>in</strong> the wild-type.<br />
However, when besides glutam<strong>in</strong>e ammonium was <strong>in</strong>cluded, glnA expression could be further<br />
repressed. The comb<strong>in</strong>ation of glutamate and ammonium also gave rise to repression of glnA<br />
expression <strong>in</strong> the wild-type. None of the above comb<strong>in</strong>ations caused repression of glnA<br />
expression <strong>in</strong> the glnR mutant. GlnA enzymatic activity is regulated <strong>in</strong> the same way (Fig.<br />
2B).<br />
140<br />
140<br />
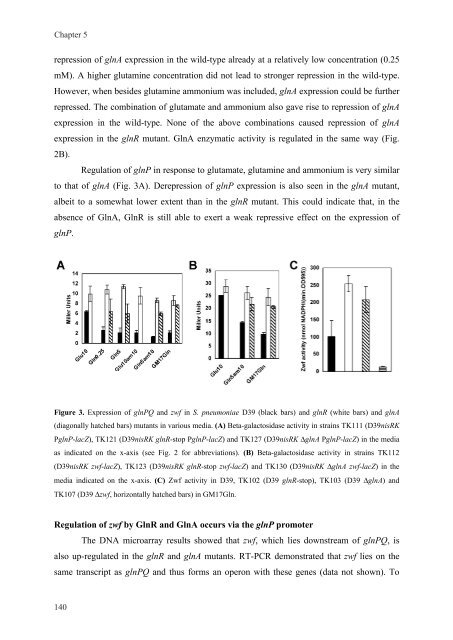
Regulation of glnP <strong>in</strong> response to glutamate, glutam<strong>in</strong>e and ammonium is very similar<br />
to that of glnA (Fig. 3A). Derepression of glnP expression is also seen <strong>in</strong> the glnA mutant,<br />
albeit to a somewhat lower extent than <strong>in</strong> the glnR mutant. This could <strong>in</strong>dicate that, <strong>in</strong> the<br />
absence of GlnA, GlnR is still able to exert a weak repressive effect on the expression of<br />
glnP.<br />
Figure 3. Expression of glnPQ and zwf <strong>in</strong> S. <strong>pneumoniae</strong> D39 (black bars) and glnR (white bars) and glnA<br />
(diagonally hatched bars) mutants <strong>in</strong> various media. (A) Beta-galactosidase activity <strong>in</strong> stra<strong>in</strong>s TK111 (D39nisRK<br />
PglnP-lacZ), TK121 (D39nisRK glnR-stop PglnP-lacZ) and TK127 (D39nisRK ΔglnA PglnP-lacZ) <strong>in</strong> the media<br />
as <strong>in</strong>dicated on the x-axis (see Fig. 2 for abbreviations). (B) Βeta-galactosidase activity <strong>in</strong> stra<strong>in</strong>s TK112<br />
(D39nisRK zwf-lacZ), TK123 (D39nisRK glnR-stop zwf-lacZ) and TK130 (D39nisRK ΔglnA zwf-lacZ) <strong>in</strong> the<br />
media <strong>in</strong>dicated on the x-axis. (C) Zwf activity <strong>in</strong> D39, TK102 (D39 glnR-stop), TK103 (D39 ΔglnA) and<br />
TK107 (D39 Δzwf, horizontally hatched bars) <strong>in</strong> GM17Gln.<br />
Regulation of zwf by GlnR and GlnA occurs via the glnP promoter<br />
The DNA microarray results showed that zwf, which lies downstream of glnPQ, is<br />
also up-regulated <strong>in</strong> the glnR and glnA mutants. RT-PCR demonstrated that zwf lies on the<br />
same transcript as glnPQ and thus forms an operon with these genes (data not shown). To