Gene regulation in Streptococcus pneumoniae - RePub - Erasmus ...
Gene regulation in Streptococcus pneumoniae - RePub - Erasmus ...
Gene regulation in Streptococcus pneumoniae - RePub - Erasmus ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
GlnR-regulon and pneumococcal virulence<br />
Contribution of the GlnR-regulon to bacteremia<br />
In the bacteremia model, <strong>in</strong>fection of the blood stream is followed for 36h, allow<strong>in</strong>g<br />
track<strong>in</strong>g of bacterial survival and growth with<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>dividual mice. Moreover, comparison of<br />
results obta<strong>in</strong>ed with the blood compartment <strong>in</strong> the pneumonia model enabled us to<br />
discrim<strong>in</strong>ate between attenuation <strong>in</strong> bacterial survival <strong>in</strong> blood or <strong>in</strong> the capability to<br />
dissem<strong>in</strong>ate from the lungs to the blood component. As a measure of disease potential, we<br />
compared the mean survival times of mice <strong>in</strong>fected with the different stra<strong>in</strong>s.<br />
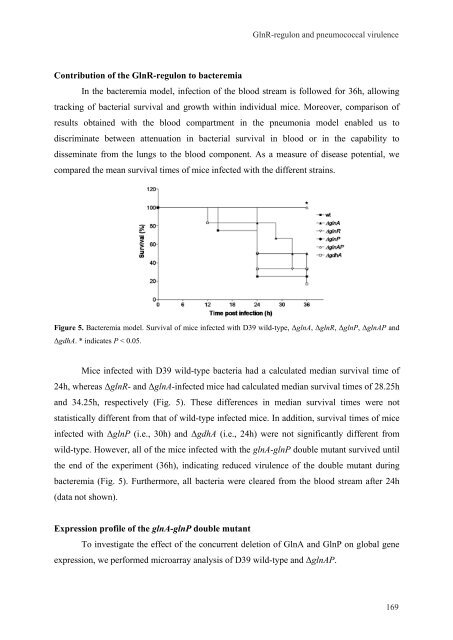
Figure 5. Bacteremia model. Survival of mice <strong>in</strong>fected with D39 wild-type, ΔglnA, ΔglnR, ΔglnP, ΔglnAP and<br />
ΔgdhA. * <strong>in</strong>dicates P < 0.05.<br />
Mice <strong>in</strong>fected with D39 wild-type bacteria had a calculated median survival time of<br />
24h, whereas ΔglnR- and ΔglnA-<strong>in</strong>fected mice had calculated median survival times of 28.25h<br />
and 34.25h, respectively (Fig. 5). These differences <strong>in</strong> median survival times were not<br />
statistically different from that of wild-type <strong>in</strong>fected mice. In addition, survival times of mice<br />
<strong>in</strong>fected with ΔglnP (i.e., 30h) and ΔgdhA (i.e., 24h) were not significantly different from<br />
wild-type. However, all of the mice <strong>in</strong>fected with the glnA-glnP double mutant survived until<br />
the end of the experiment (36h), <strong>in</strong>dicat<strong>in</strong>g reduced virulence of the double mutant dur<strong>in</strong>g<br />
bacteremia (Fig. 5). Furthermore, all bacteria were cleared from the blood stream after 24h<br />
(data not shown).<br />
Expression profile of the glnA-glnP double mutant<br />
To <strong>in</strong>vestigate the effect of the concurrent deletion of GlnA and GlnP on global gene<br />
expression, we performed microarray analysis of D39 wild-type and ΔglnAP.<br />
169<br />
169