Gene regulation in Streptococcus pneumoniae - RePub - Erasmus ...
Gene regulation in Streptococcus pneumoniae - RePub - Erasmus ...
Gene regulation in Streptococcus pneumoniae - RePub - Erasmus ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Chapter 7<br />
severely affected <strong>in</strong> their ability to adhere to human epithelial Detroit 562 cells. These<br />
mutants are also severely reduced <strong>in</strong> the ability to colonize the mur<strong>in</strong>e nasopharynx (17).<br />
192<br />
192<br />
In a recent paper, the transcriptional response of S. <strong>pneumoniae</strong> upon contact with<br />
human epithelial cells was described (48). In this study, microarray analysis revealed that the<br />
transcriptional activity of many genes is changed when pneumococcal cells <strong>in</strong>teract with<br />
epithelial cells. Interest<strong>in</strong>gly, some pronounced CodY targets were among these genes. For<br />
example, the genes ilvB, ilvE, and asd (encod<strong>in</strong>g acetolactate synthase, branched cha<strong>in</strong> am<strong>in</strong>o<br />
acid am<strong>in</strong>otransferase, and aspartate semi-aldehyde dehydrogenase, respectively), were<br />
strongly downregulated. This is <strong>in</strong> agreement with our observations that the codY mutant is<br />
severely affected <strong>in</strong> its ability to adhere to the Detroit 562 epithelial cells (17). In the codY<br />
mutant, ilvB, ilvE, and asd, were strongly upregulated dur<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> vitro growth. This<br />
up<strong>regulation</strong> might have had a negative effect on the adherence ability.<br />
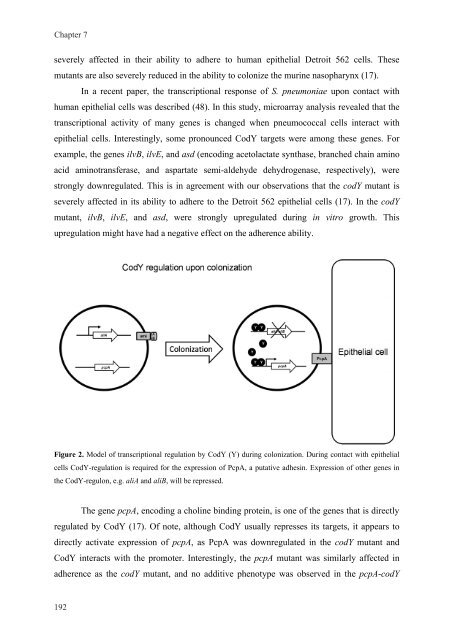
Figure 2. Model of transcriptional <strong>regulation</strong> by CodY (Y) dur<strong>in</strong>g colonization. Dur<strong>in</strong>g contact with epithelial<br />
cells CodY-<strong>regulation</strong> is required for the expression of PcpA, a putative adhes<strong>in</strong>. Expression of other genes <strong>in</strong><br />
the CodY-regulon, e.g. aliA and aliB, will be repressed.<br />
The gene pcpA, encod<strong>in</strong>g a chol<strong>in</strong>e b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g prote<strong>in</strong>, is one of the genes that is directly<br />
regulated by CodY (17). Of note, although CodY usually represses its targets, it appears to<br />
directly activate expression of pcpA, as PcpA was downregulated <strong>in</strong> the codY mutant and<br />
CodY <strong>in</strong>teracts with the promoter. Interest<strong>in</strong>gly, the pcpA mutant was similarly affected <strong>in</strong><br />
adherence as the codY mutant, and no additive phenotype was observed <strong>in</strong> the pcpA-codY