Gene regulation in Streptococcus pneumoniae - RePub - Erasmus ...
Gene regulation in Streptococcus pneumoniae - RePub - Erasmus ...
Gene regulation in Streptococcus pneumoniae - RePub - Erasmus ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Chapter 6<br />
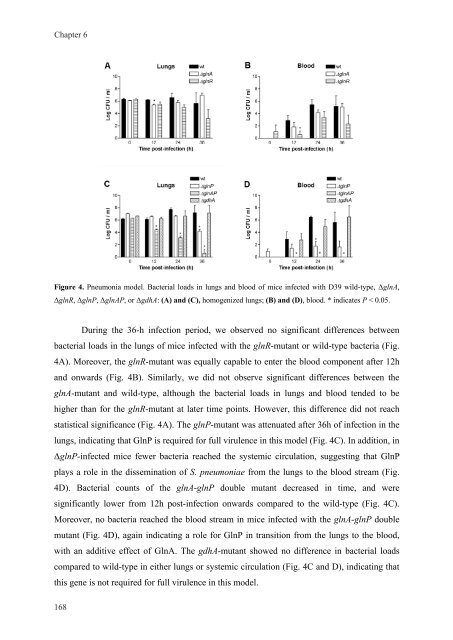
Figure 4. Pneumonia model. Bacterial loads <strong>in</strong> lungs and blood of mice <strong>in</strong>fected with D39 wild-type, ΔglnA,<br />
ΔglnR, ΔglnP, ΔglnAP, or ΔgdhA: (A) and (C), homogenized lungs; (B) and (D), blood. * <strong>in</strong>dicates P < 0.05.<br />
Dur<strong>in</strong>g the 36-h <strong>in</strong>fection period, we observed no significant differences between<br />
bacterial loads <strong>in</strong> the lungs of mice <strong>in</strong>fected with the glnR-mutant or wild-type bacteria (Fig.<br />
4A). Moreover, the glnR-mutant was equally capable to enter the blood component after 12h<br />
and onwards (Fig. 4B). Similarly, we did not observe significant differences between the<br />
glnA-mutant and wild-type, although the bacterial loads <strong>in</strong> lungs and blood tended to be<br />
higher than for the glnR-mutant at later time po<strong>in</strong>ts. However, this difference did not reach<br />
statistical significance (Fig. 4A). The glnP-mutant was attenuated after 36h of <strong>in</strong>fection <strong>in</strong> the<br />
lungs, <strong>in</strong>dicat<strong>in</strong>g that GlnP is required for full virulence <strong>in</strong> this model (Fig. 4C). In addition, <strong>in</strong><br />
ΔglnP-<strong>in</strong>fected mice fewer bacteria reached the systemic circulation, suggest<strong>in</strong>g that GlnP<br />
plays a role <strong>in</strong> the dissem<strong>in</strong>ation of S. <strong>pneumoniae</strong> from the lungs to the blood stream (Fig.<br />
4D). Bacterial counts of the glnA-glnP double mutant decreased <strong>in</strong> time, and were<br />
significantly lower from 12h post-<strong>in</strong>fection onwards compared to the wild-type (Fig. 4C).<br />
Moreover, no bacteria reached the blood stream <strong>in</strong> mice <strong>in</strong>fected with the glnA-glnP double<br />
mutant (Fig. 4D), aga<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>dicat<strong>in</strong>g a role for GlnP <strong>in</strong> transition from the lungs to the blood,<br />
with an additive effect of GlnA. The gdhA-mutant showed no difference <strong>in</strong> bacterial loads<br />
compared to wild-type <strong>in</strong> either lungs or systemic circulation (Fig. 4C and D), <strong>in</strong>dicat<strong>in</strong>g that<br />
this gene is not required for full virulence <strong>in</strong> this model.<br />
168<br />
168