International Summer School PROGRAM - Laboratoire d'Infochimie ...
International Summer School PROGRAM - Laboratoire d'Infochimie ...
International Summer School PROGRAM - Laboratoire d'Infochimie ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Cationic amphiphilic calixarenes:<br />
self-assembling in water solutions and virus-sized DNA nanoparticles<br />
Rodik, R.V., a Jain, N., b Miroshnichenko, S.I., a Richert, L., b Kalchenko, V.I., a Mely,<br />
Y., b Klymchenko, A. S. b<br />
a Institute of Organic Chemistry National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine;<br />
Murmanska str.,5 02660, Kyiv-94, Ukraine E-mail: manli@ioch.kiev.ua<br />
b Laboratory of Biophotonics and Pharmacology, Faculty of Pharmacy, University<br />
of Strasbourg; 74, route du Rhin BP 60024 F-67401 Illkirch Cedex, France<br />
E-mail: aklymchenko@pharma.u-strasbg.fr<br />
The highly diverse biomedical applications of calixarene now include antibacterial,<br />
anticancer, antiviral, selective enzyme blocking and mimicking, as well as protein<br />
complexation 1 . On the other hand macro cycles (including calixarenes) were recently<br />
used as scaffolds for the synthesis cationic agents for gene delivery. However, only a<br />
few reports describe the interaction of cationic calix[4]arenes with DNA for gene<br />
delivery applications 2 .<br />
In this report, we present synthesis of cationic calixarenes and investigation of their<br />
self-assembly in aqueous solutions. Moreover, DNA binding experiments were carried<br />
out and good gene transfection properties of calixarenes were evidenced.<br />
Cl<br />
+<br />
N<br />
N+ N +<br />
N +<br />
OH<br />
OHCl HO<br />
HO<br />
Cl<br />
Cl<br />
O O O O<br />
1 2 2<br />
R R R R<br />
1<br />
CX3 1 R= 2 R= C3 H 7 -n<br />
CX6 1 R= 2 R=C 6 H 13 -n<br />
CX8 1 R= 2 R=C 8 H 17 -n<br />
CX12-8 1 R= C 12 H 25 -n, 2 R= C 8 H 17 -n<br />
CX12 1 R= 2 R=C 12 H 25 -n<br />
CX16 1 R= 2 R=C 16 H 33 -n<br />
Cl<br />
Cl Cl<br />
O O O O<br />
1 2 2<br />
R R 1 R R<br />
Cl<br />
Cl<br />
NH2 H N<br />
NH2<br />
2 H2N<br />
Cl +<br />
+ + Cl<br />
N N Cl +<br />
N<br />
N<br />
O O O O<br />
1 2 2 1<br />
R R R R<br />
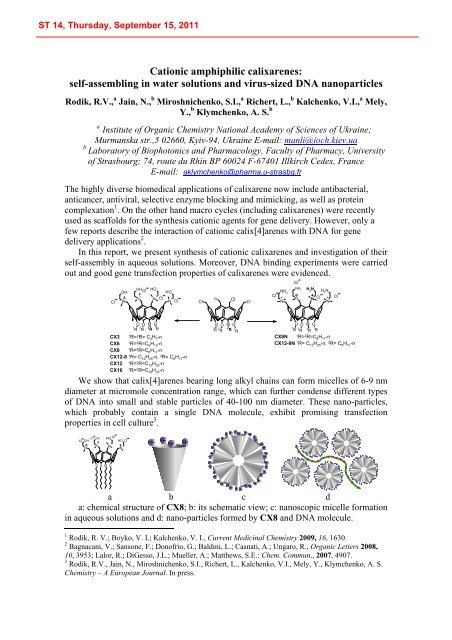
CX8N 1R= 2R=C8H17-n CX12-8N 1R= C12H25-n, 2R= C8H17-n We show that calix[4]arenes bearing long alkyl chains can form micelles of 6-9 nm<br />
diameter at micromole concentration range, which can further condense different types<br />
of DNA into small and stable particles of 40-100 nm diameter. These nano-particles,<br />
which probably contain a single DNA molecule, exhibit promising transfection<br />
properties in cell culture 3 .<br />
+<br />
N<br />
N+ N +<br />
N +<br />
Cl OH<br />
Cl OH<br />
HO<br />
Cl<br />
HO<br />
Cl<br />
O O O O<br />
+ + +<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+ + +<br />
+ + + + + +<br />
++<br />
++<br />
+ + + + +<br />
+ +<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+ +<br />
+<br />
+ + +<br />
+ + + +<br />
++<br />
++<br />
-<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+ ++<br />
+ ++ ++ + + + +<br />
+ +<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
- +<br />
+ + +<br />
+ - + + +<br />
+ + + +<br />
- - -<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+ + + +<br />
+ +<br />
- - - - - +<br />
-<br />
+ + + +<br />
++<br />
++<br />
+<br />
+ +<br />
+<br />
+ + +<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+ + +<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+ + +<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+ +<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+ + +<br />
++<br />
++<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
-<br />
-<br />
-<br />
-<br />
-<br />
a b c d<br />
a: chemical structure of CX8; b: its schematic view; c: nanoscopic micelle formation<br />
in aqueous solutions and d: nano-particles formed by CX8 and DNA molecule.<br />
1<br />
Rodik, R. V.; Boyko, V. I.; Kalchenko, V. I., Current Medicinal Chemistry 2009, 16, 1630.<br />
2<br />
Bagnacani, V.; Sansone, F.; Donofrio, G.; Baldini, L.; Casnati, A.; Ungaro, R., Organic Letters 2008,<br />
10, 3953; Lalor, R.; DiGesso, J.L.; Mueller, A.; Matthews, S.E.: Chem. Commun., 2007, 4907.<br />
3<br />
Rodik, R.V., Jain, N., Miroshnichenko, S.I., Richert, L., Kalchenko, V.I., Mely, Y., Klymchenko, A. S.<br />
Chemistry – A European Journal. In press.<br />
+ + +<br />
+ +<br />
+ + + + ++ ++<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+ + + +<br />
+ +