Presentation Outline ICHP Annual Meeting September 13-15
Presentation Outline ICHP Annual Meeting September 13-15
Presentation Outline ICHP Annual Meeting September 13-15
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
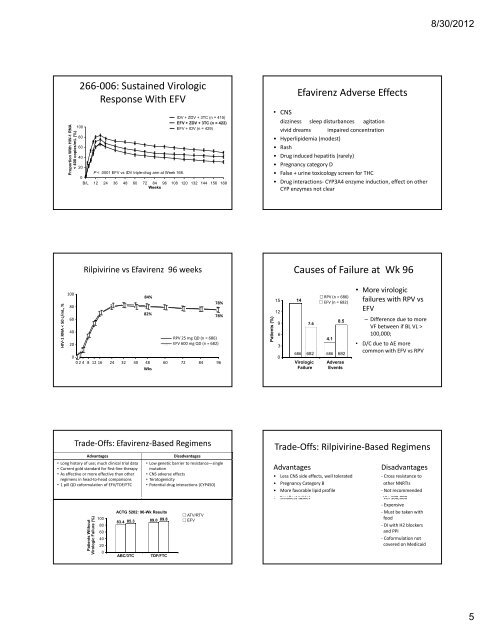
HIV‐1 RNA < 500<br />
c/mL, %<br />
Proportion With HIV-1 H RNA<br />
< 400 copies/mmL<br />
(%)<br />
100<br />
80<br />
60<br />
40<br />
20<br />
266‐006: Sustained Virologic<br />
Response With EFV<br />
100<br />
80<br />
60<br />
40<br />
IDV + ZDV + 3TC (n = 4<strong>15</strong>)<br />
EFV + ZDV + 3TC (n = 422)<br />
EFV + IDV (n = 429)<br />
20<br />
P < .0001 EFV vs IDV triple-drug arm at Week 168.<br />
0<br />
B/L 12 24 36 48 60 72 84<br />
Weeks<br />
96 108 120 <strong>13</strong>2 144 <strong>15</strong>6 168<br />
Rilpivirine vs Efavirenz 96 weeks<br />
84%<br />
82%<br />
78%<br />
78%<br />
RPV 25 mg QD (n = 686)<br />
EFV 600 mg QD (n = 682)<br />
0<br />
024 8 12 16 24 32 40 48<br />
Wks<br />
60 72 84 96<br />
Trade‐Offs: Efavirenz‐Based Regimens<br />
Advantages Disadvantages<br />
• Long history of use; much clinical trial data<br />
• Current gold standard for first‐line therapy<br />
• As effective or more effective than other<br />
regimens in head‐to‐head comparisons<br />
• 1 pill QD coformulation of EFV/TDF/FTC<br />
Patients Without<br />
Virologic Failure (%)<br />
100<br />
80<br />
60<br />
40<br />
20<br />
0<br />
ACTG 5202: 96-Wk Results<br />
83.4 85.3<br />
• Low genetic barrier to resistance—single<br />
mutation<br />
• CNS adverse effects<br />
• Teratogenicity<br />
• Potential drug interactions (CYP450)<br />
89.0 89.8<br />
ABC/3TC TDF/FTC<br />
ATV/RTV<br />
EFV<br />
Patients (% %)<br />
Efavirenz Adverse Effects<br />
• CNS<br />
dizziness sleep disturbances agitation<br />
vivid dreams impaired concentration<br />
• Hyperlipidemia (modest)<br />
• Rash<br />
• Drug induced hepatitis (rarely)<br />
• Pregnancy category D<br />
• False + urine toxicology screen for THC<br />
• Drug interactions‐ CYP3A4 enzyme induction, effect on other<br />
CYP enzymes not clear<br />
<strong>15</strong><br />
12<br />
6<br />
3<br />
0<br />
Causes of Failure at Wk 96<br />
14<br />
9 7.6<br />
346<br />
686 682<br />
Virologic<br />
Failure<br />
RPV (n = 686)<br />
EFV (n = 682)<br />
4.1<br />
686<br />
85 8.5<br />
682<br />
Adverse<br />
Events<br />
• More virologic<br />
failures with RPV vs<br />
EFV<br />
– Difference due to more<br />
VF between if BL VL ><br />
100,000;<br />
• D/C due to AE more<br />
common with EFV vs RPV<br />
Trade‐Offs: Rilpivirine‐Based Regimens<br />
Advantages Disadvantages<br />
• Less CNS side effects, well tolerated ‐ Cross resistance to<br />
• Pregnancy Category B other NNRTIs<br />
• More favorable lipid profile ‐ Not recommended<br />
• Smallest tablet VL>100 000<br />
• Smallest tablet VL>100,000<br />
‐ Expensive<br />
‐ Must be taken with<br />
food<br />
‐ DI with H2 blockers<br />
and PPI<br />
‐ Coformulation not<br />
covered on Medicaid<br />
8/30/2012<br />
5