Asbestos Fibers and Other Elongate Mineral Particles: State of the ...
Asbestos Fibers and Other Elongate Mineral Particles: State of the ...
Asbestos Fibers and Other Elongate Mineral Particles: State of the ...
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
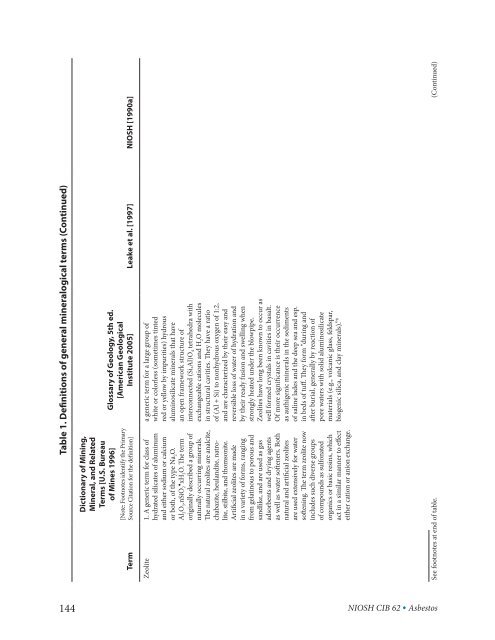
Table 1. Definitions <strong>of</strong> general mineralogical terms (Continued)<br />
144<br />
Glossary <strong>of</strong> Geology, 5th ed.<br />
[American Geological<br />
Institute 2005] Leake et al. [1997] NIOSH [1990a]<br />
Dictionary <strong>of</strong> Mining,<br />
<strong>Mineral</strong>, <strong>and</strong> Related<br />
Terms [U.S. Bureau<br />
<strong>of</strong> Mines 1996]<br />
[Note: Footnotes identify <strong>the</strong> Primary<br />
Source Citation for <strong>the</strong> definition]<br />
Term<br />
a generic term for a large group <strong>of</strong><br />
white or colorless (sometimes tinted<br />
red or yellow by impurities) hydrous<br />
aluminosilicate minerals that have<br />
an open framework structure <strong>of</strong><br />
interconnected (Si,Al)O4 tetrahedra with<br />
exchangeable cations <strong>and</strong> H2O molecules<br />
in structural cavities. They have a ratio<br />
<strong>of</strong> (Al + Si) to nonhydrous oxygen <strong>of</strong> 1:2,<br />
<strong>and</strong> are characterized by <strong>the</strong>ir easy <strong>and</strong><br />
reversible loss <strong>of</strong> water <strong>of</strong> hydration <strong>and</strong><br />
by <strong>the</strong>ir ready fusion <strong>and</strong> swelling when<br />
strongly heated under <strong>the</strong> blowpipe.<br />
Zeolites have long been known to occur as<br />
well formed crystals in cavities in basalt.<br />
Of more significance is <strong>the</strong>ir occurrence<br />
as authigenic minerals in <strong>the</strong> sediments<br />
<strong>of</strong> saline lades <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> deep sea <strong>and</strong> esp.<br />
in beds <strong>of</strong> tuff. They form “during <strong>and</strong><br />
after burial, generally by reaction <strong>of</strong><br />
pore waters with solid aluminosilicate<br />
materials (e.g., volcanic glass, feldspar,<br />
biogenic silica, <strong>and</strong> clay minerals).” 8<br />
Zeolite 1. A generic term for class <strong>of</strong><br />
hydrated silicates <strong>of</strong> aluminum<br />
<strong>and</strong> ei<strong>the</strong>r sodium or calcium<br />
or both, <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> type Na2O. Al •<br />
2O3.nSiO2 xH2O. The term<br />
originally described a group <strong>of</strong><br />
naturally occurring minerals.<br />
The natural zeolites are analcite,<br />
chabazite, heul<strong>and</strong>ite, natrolite,<br />
stilbite, <strong>and</strong> thomsonite.<br />
Artificial zeolites are made<br />
in a variety <strong>of</strong> forms, ranging<br />
from gelatinous to porous <strong>and</strong><br />
s<strong>and</strong>like, <strong>and</strong> are used as gas<br />
adsorbents <strong>and</strong> drying agents<br />
as well as water s<strong>of</strong>teners. Both<br />
natural <strong>and</strong> artificial zeolites<br />
are used extensively for water<br />
s<strong>of</strong>tening. The term zeolite now<br />
includes such diverse groups<br />
<strong>of</strong> compounds as sulfonated<br />
organics or basic resins, which<br />
act in a similar manner to effect<br />
ei<strong>the</strong>r cation or anion exchange.<br />
See footnotes at end <strong>of</strong> table. (Continued)<br />
NIOSH CIB 62 • <strong>Asbestos</strong>