- Page 1:
Making Forestry Work for the Poor A
- Page 4 and 5:
© FAO ISBN The designations employ
- Page 7 and 8:
Contents Foreword .................
- Page 9 and 10:
Figures Table VII.6. Characteristic
- Page 11 and 12:
Acronyms and Abbreviations AAC Annu
- Page 13 and 14:
MDG Millennium Development Goal MGN
- Page 15 and 16:
Acknowledgements This publication o
- Page 17 and 18: Introduction Overview Peter Walpole
- Page 19 and 20: Table 1: Status of Poverty Reductio
- Page 21 and 22: Although poverty alleviation is inc
- Page 23 and 24: Past efforts to address poverty thr
- Page 25 and 26: Lack of Support for NWFP Developmen
- Page 27 and 28: to absorb the large number of peopl
- Page 29 and 30: Smallholder tree farming Engaging i
- Page 31 and 32: cultures is a major challenge. Cult
- Page 33 and 34: 2. Capacity building for individual
- Page 35: Poffenberger, M. and Smith-Hanssen,
- Page 38 and 39: Life in an unforgiving environment
- Page 40 and 41: Forest Policy and Its Objectives Ab
- Page 42 and 43: to meet the expenses during communi
- Page 44 and 45: Chirata is an important medicinal p
- Page 46 and 47: From 2003-04 until 2004-05, revenue
- Page 48 and 49: Payment for Environmental Services
- Page 50 and 51: The auction yard for pipla at Gelep
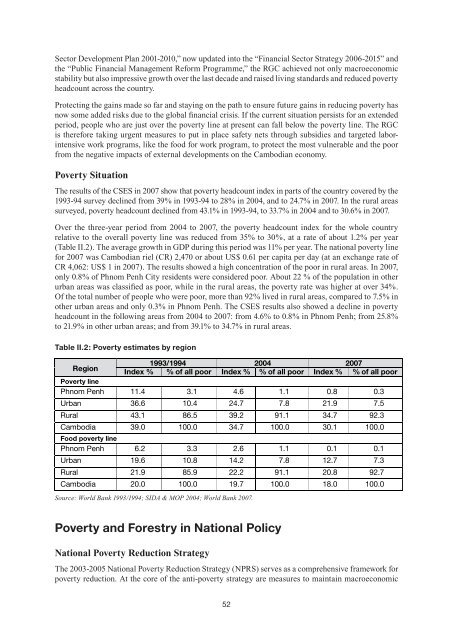
- Page 52 and 53: Recommendations Pipla collection is
- Page 54 and 55: whose incomes are at the lower end.
- Page 56 and 57: Figure I.3. Net income per distilla
- Page 58 and 59: domestic demand of traditional medi
- Page 60 and 61: auction chirata. However, due to In
- Page 62 and 63: Product improvement • Improvement
- Page 64 and 65: Policy and Planning Division (PPD).
- Page 66 and 67: • reforestation and protection of
- Page 70 and 71: Forest Policy The RGC endeavors to
- Page 72 and 73: eserved forests and ensure their ap
- Page 74 and 75: It is generally accepted that the e
- Page 76 and 77: contributions to rural livelihoods,
- Page 78 and 79: Case Study 1: Community forest in P
- Page 80 and 81: she can buy a total of two to three
- Page 82 and 83: Members of the Trapang Kbal Khmoach
- Page 84 and 85: Capacity building for CF members Ed
- Page 86 and 87: After the integration of the Khmer
- Page 88 and 89: Livelihood situation after concessi
- Page 90 and 91: for institutional reforms. Based on
- Page 92 and 93: Meta, B. C. (2010). Community-based
- Page 94 and 95: Table III.1. Summary of past NFI re
- Page 96 and 97: During the Twelfth Five-Year Plan p
- Page 98 and 99: nationwide to contract the collecti
- Page 100 and 101: alleviating rural poverty. Collecti
- Page 102 and 103: areas. All these create pressure on
- Page 104 and 105: Table III.5. List of economic fores
- Page 106 and 107: stations, and others. In addition,
- Page 108 and 109: farmers to increase to over US$ 310
- Page 110 and 111: year and his national special care
- Page 112 and 113: enough capital to invest, leading t
- Page 115 and 116: Introduction IV Assessment of the C
- Page 117 and 118: value of forests reflected in the S
- Page 119 and 120:
Poverty Alleviation and Forestry in
- Page 121 and 122:
Reduction Strategy papers. Furtherm
- Page 123 and 124:
Figure IV.1. Coincidence of forests
- Page 125 and 126:
Fodder from the forest provided abo
- Page 127 and 128:
landless and marginal landholding h
- Page 129 and 130:
70% was exported. It is estimated t
- Page 131 and 132:
Table IV.5. Registered projects und
- Page 133 and 134:
Case Studies Case Study 1: A Tradit
- Page 135 and 136:
our land.” All agree that forests
- Page 137 and 138:
The forest around the village was d
- Page 139 and 140:
Figure IV.2. Value chain analysis W
- Page 141 and 142:
A popular tourist attraction in Ker
- Page 143 and 144:
Innovative mechanism for resource g
- Page 145 and 146:
Outlook for Forestry and Poverty Al
- Page 147 and 148:
Wood demand. Trees from non-forest
- Page 149 and 150:
their livelihoods. Resolution of po
- Page 151 and 152:
Forest Survey of India. (1999). Sta
- Page 153 and 154:
Saxena. (1999). NTFP policy and the
- Page 155:
a resolution to control seasonal fi
- Page 158 and 159:
(MoF 2009). A study by the TREES Pr
- Page 160 and 161:
is caused by (i) lack of recognitio
- Page 162 and 163:
that the development of the Kaliman
- Page 164 and 165:
plantations on community lands. How
- Page 166 and 167:
as the subsistence, livelihood and
- Page 168 and 169:
As of 2010, MoF was able to issue 2
- Page 170 and 171:
for HTI projects. The finding under
- Page 172 and 173:
do not follow these agreements or a
- Page 174 and 175:
Satyawati’s (1991) field research
- Page 176 and 177:
Morgan’s investigation (2011) of
- Page 178 and 179:
intercropping in at least 0.25-0.5
- Page 180 and 181:
Challenges and ways forward In the
- Page 182 and 183:
Challenges The target buyers of the
- Page 184 and 185:
end or scale down their operations.
- Page 186 and 187:
Increasing the Benefits from Large-
- Page 188 and 189:
Kayoi, M. et. al. (2006). Poverty a
- Page 190 and 191:
World Bank. (2006a). Sustaining eco
- Page 192 and 193:
in neighboring countries that incre
- Page 194 and 195:
Poverty Situation Despite the signi
- Page 196 and 197:
Subsistence Use of Forests and Allo
- Page 198 and 199:
allocated for communities to manage
- Page 200 and 201:
growth, increased per capita income
- Page 202 and 203:
of 311 villages (38%) preparing the
- Page 204 and 205:
Figure VI.1. Important household in
- Page 206 and 207:
Recently, Lao PDR was selected as o
- Page 208 and 209:
in this case study are based on the
- Page 210 and 211:
The contribution of NWFPs to the wh
- Page 212 and 213:
4% A brief about Ban Xom Figure VI.
- Page 214 and 215:
Table VI.6. Villagers’ opinion on
- Page 216 and 217:
The purpose of the SEMFOP 1 was to
- Page 218 and 219:
In addition, rice production was re
- Page 220 and 221:
mostly to reducing rural poverty. I
- Page 222 and 223:
• Enhancingexistingmechanismsands
- Page 224 and 225:
18, 2009. National Agriculture and
- Page 226 and 227:
(Table VII.2). Government-managed f
- Page 228 and 229:
to 2006. On the other hand, the hum
- Page 230 and 231:
The community based forest manageme
- Page 232 and 233:
for Agricultural Development (IFAD)
- Page 234 and 235:
grass and fodder production in both
- Page 236 and 237:
Timber market values vary according
- Page 238 and 239:
LF area forest Area coverage (ha) N
- Page 240 and 241:
as tree cover, biodiversity, NWFP,
- Page 242 and 243:
Operational management The operatio
- Page 244 and 245:
With regard to timber use, Jaspur C
- Page 246 and 247:
the primary forest products that co
- Page 248 and 249:
It is not surprising to note that t
- Page 250 and 251:
there is a greater chance of progra
- Page 252 and 253:
from poor and marginalized families
- Page 254 and 255:
Chand, P. B. and Ghimire, K. (2007)
- Page 256 and 257:
RECOFTC & FAO. (2009). Is there fut
- Page 258 and 259:
Shearman et al. (2008) estimated th
- Page 260 and 261:
markets and basic services like hea
- Page 262 and 263:
Figure VIII.2. Land and poverty ind
- Page 264 and 265:
those in the rural areas, to mobili
- Page 266 and 267:
Past and Current Contribution of Fo
- Page 268 and 269:
Village industries Village industri
- Page 270 and 271:
Government continues to be the prim
- Page 272 and 273:
Carbon payments PNG does not have a
- Page 274 and 275:
annually and harvest and process an
- Page 276 and 277:
The project generally improved the
- Page 278 and 279:
and no follow-up was done to sustai
- Page 280 and 281:
Forestry being a renewable resource
- Page 282 and 283:
Melnick, D., McNeely,J., Navaro, Y.
- Page 284 and 285:
Table IX.1. Philippine forest cover
- Page 286 and 287:
Livelihood and poverty context in t
- Page 288 and 289:
and basic services like health and
- Page 290 and 291:
services and quality of human devel
- Page 292 and 293:
CBFM is still recognized as a major
- Page 294 and 295:
In many parts of the country, colle
- Page 296 and 297:
Small-scale Commercial Forestry Non
- Page 298 and 299:
Tree plantations from IFMA and smal
- Page 300 and 301:
CARAGA region in the Philippines is
- Page 302 and 303:
eduction in the log supply contract
- Page 304 and 305:
viable spheres of production for sm
- Page 306 and 307:
3. Ensure sustainability of raw mat
- Page 308 and 309:
Garcia, B. Jr. (2005, December 1).
- Page 310 and 311:
Table X.1. Forest area by region, 1
- Page 312 and 313:
With the country’s remarkable gai
- Page 314 and 315:
Table X.3. Government agencies invo
- Page 316 and 317:
Table X.5. Registration of the poor
- Page 318 and 319:
poor. What reshaping meant in pract
- Page 320 and 321:
Community title The solutions to pr
- Page 322 and 323:
for commercial uses up to 2009 were
- Page 324 and 325:
demarcated the boundary. At present
- Page 326 and 327:
was not degraded forest but that it
- Page 328 and 329:
to the livelihoods of rural people.
- Page 330 and 331:
• No tree cutting is allowed in t
- Page 332 and 333:
“I have never regretted all the f
- Page 334 and 335:
costs. The service providers were i
- Page 336 and 337:
1. safeguarding and restoring the n
- Page 338 and 339:
is, and their right to participate.
- Page 340 and 341:
Linking Reforestation, Poverty Alle
- Page 342 and 343:
Office of National Economic and Soc
- Page 344 and 345:
mountain people (Ha 2009). Presentl
- Page 346 and 347:
However, while overall poverty leve
- Page 348 and 349:
one of the best forms of management
- Page 350 and 351:
26.2% of the total area of forest l
- Page 352 and 353:
Box XI.2. Factors constraining FLA
- Page 354 and 355:
average to reach US$ 700-800 millio
- Page 356 and 357:
River delta and Mekong River delta
- Page 358 and 359:
However, Tran (2009) pointed out th
- Page 360 and 361:
The Contribution of Traditional Com
- Page 362 and 363:
Fuel wood collected from forests is
- Page 364 and 365:
The Contribution of Viet Nam Forest
- Page 366 and 367:
are provided both input and output
- Page 368 and 369:
the PES fund per year, compared to
- Page 370 and 371:
Viet Nam’s forestry development s
- Page 372 and 373:
Decree 99/2010/ND-CP on the policy
- Page 374 and 375:
Sustainable poverty reduction perio