- Page 1 and 2:
USGS Prepared in collaboration with
- Page 3 and 4:
U.S. Department of the Interior Gal
- Page 5 and 6:
iv Hart River SEDEX Zn-Cu-Ag Deposi
- Page 7 and 8:
vi Specific Events for Middle Throu
- Page 9 and 10:
viii Metallogenic Belts Formed Duri
- Page 11 and 12:
x Origin of and Tectonic Controls f
- Page 13 and 14:
xii Toodoggone Metallogenic Belt of
- Page 15 and 16:
xiv Slate Creek Serpentinite-Hosted
- Page 17 and 18:
xvi Left Omolon Belt of Porphyry Mo
- Page 19 and 20:
xviii Origin of and Tectonic Contro
- Page 21 and 22:
xx Chukotka Metallogenic Belt of Au
- Page 23 and 24:
xxii Plutonic Rocks Hosting East-Ce
- Page 25 and 26:
xxiv Skeena Metallogenic Belt of Po
- Page 27 and 28:
xxvi Bee Creek Porphyry Cu Deposit
- Page 29 and 30:
xxviii 36. Wellgreen gabbroic Ni-Cu
- Page 31 and 32:
xxx 87. Partizanskoe Pb-Zn skarn de
- Page 33 and 34:
Metallogenesis and Tectonics of the
- Page 35 and 36:
format (Nokleberg and others, 1996)
- Page 37 and 38:
logenesis of the region (1) subduct
- Page 39 and 40:
Subterrane—A fault-bounded unit w
- Page 41 and 42:
dilemma consists of two conflicting
- Page 43 and 44:
2 to 20 m thick. A related dolomite
- Page 45 and 46:
Lantarsky-Dzhugdzhur Metallogenic B
- Page 47 and 48:
Origin of and Tectonic Controls for
- Page 49 and 50:
Metallogenic Belts Formed During Pr
- Page 51 and 52:
as at Oz, Monster, and Tart, may al
- Page 53 and 54:
Monashee Metallogenic Belt of Sedim
- Page 55 and 56:
Clark Range Metallogenic Belt of Se
- Page 57 and 58:
in addition to the Fe deposits. Min
- Page 59 and 60:
study) consists of lenses, from 100
- Page 61 and 62:
Omulev Austrian Alps W Deposit The
- Page 63 and 64:
ock, including coarse clastic rock,
- Page 65 and 66:
lative metalliferous brines in a re
- Page 67 and 68:
Prince of Wales Island Metallogenic
- Page 69 and 70:
suite of deposits and host rocks ar
- Page 71 and 72:
margin of the North American Craton
- Page 73 and 74:
newly created terranes migrated int
- Page 75 and 76:
(Ryazantzeva and Shurko, 1992). The
- Page 77 and 78:
tonnes Au and an average grade of a
- Page 79 and 80:
mafic and felsic metavolcanic rocks
- Page 81 and 82:
intrusion from about 402 to 366 Ma
- Page 83 and 84:
Origin of and Tectonic Controls for
- Page 85 and 86:
mentary rocks of the Cambrian to De
- Page 87 and 88:
(Preto and Schiarizza, 1985; Schiar
- Page 89 and 90:
Origin of and Tectonic Controls for
- Page 91 and 92:
ate and clastic rocks and volcanicl
- Page 93 and 94:
(Nokleberg and others, 1994c, 1997c
- Page 95 and 96:
Berezovka River Metallogenic Belt o
- Page 97 and 98:
Origin of and Tectonic Controls for
- Page 99 and 100:
Finlayson Lake Metallogenic Belt of
- Page 101 and 102:
and barite in siliceous black turbi
- Page 103 and 104:
Windermere Creek (Western Gypsum) C
- Page 105 and 106:
(NX, DL, MY), Viliga (VL), and Zolo
- Page 107 and 108:
South of the main east-west-trendin
- Page 109 and 110:
ated subduction zone in the Wrangel
- Page 111 and 112:
icite-biotite-quartz bodies in frac
- Page 113 and 114:
Canada Cordillera. The granitoid ro
- Page 115 and 116:
Viliga (VL) passive continental-mar
- Page 117 and 118:
32; tables 3, 4) occurs along the n
- Page 119 and 120:
superterrane, consists mainly of ma
- Page 121 and 122:
ers, 1994c, 1997c). In southern Bri
- Page 123 and 124:
mental volcanic rocks of intermedia
- Page 125 and 126:
a resource of 34.3 million tonnes o
- Page 127 and 128:
potassic zone. Combined estimated p
- Page 129 and 130:
and quartz monzodiorite stock and s
- Page 131 and 132:
and Omolon (OM) cratonal terranes,
- Page 133 and 134:
in volcanic and volcaniclastic rock
- Page 135 and 136:
minor calcite, and sporadic pyrite
- Page 137 and 138:
supergene blanket are interpreted a
- Page 139 and 140:
deposits and occurrences consist of
- Page 141 and 142:
onto the Omulevka terrane to form t
- Page 143 and 144:
superterrane. This belt is interpre
- Page 145 and 146:
to form along the leading edge of t
- Page 147 and 148:
quartz, and is virtually not associ
- Page 149 and 150:
deposits are at Terrassnoe and Kuna
- Page 151 and 152:
Peschanka Porphyry Cu-Mo Deposit Th
- Page 153 and 154:
The belt is hosted in the Late Jura
- Page 155 and 156:
in a island arc that was tectonical
- Page 157 and 158:
and Early Cretaceous Koyukuk island
- Page 159 and 160:
The deposit consists of disseminate
- Page 161 and 162:
The Orange Hill deposit contains an
- Page 163 and 164:
49; tables 3, 4) (Foley and others,
- Page 165 and 166:
locally Late Triassic marine volcan
- Page 167 and 168:
gold in a gangue of quartz, calcite
- Page 169 and 170:
Verkhoyansk granite belt, which int
- Page 171 and 172:
metallogenic belts are interpreted
- Page 173 and 174:
assemblages, which may have been mo
- Page 175 and 176:
during hypogene and supergene alter
- Page 177 and 178:
collision and regional thrusting, t
- Page 179 and 180:
Yur Au Quartz Vein Deposit The smal
- Page 181 and 182:
phase has a Rb-Sr isotopic age of 1
- Page 183 and 184:
sian Northeast. The belt is hosted
- Page 185 and 186:
Host Granitoid Rocks and Associated
- Page 187 and 188:
that are up to 600-1,500 m long, av
- Page 189 and 190:
Metallogenic Belts Formed During La
- Page 191 and 192:
y partly coeval plutons that range
- Page 193 and 194:
tion is interpreted as occuring by
- Page 195 and 196:
the Badzhal-Ezop and Khingan parts
- Page 197 and 198:
and comagmatic with volcanic rocks;
- Page 199 and 200:
as interpreted for the Rock Creek d
- Page 201 and 202:
source (Yeo, 1992). The Blow River
- Page 203 and 204:
2000). The spatial location of the
- Page 205 and 206:
to the east in the central Yukon Te
- Page 207 and 208:
occur in a 30-km-long belt along ir
- Page 209 and 210:
The Emerald deposit has produced ap
- Page 211 and 212:
Metallogenic-Tectonic Model for Ear
- Page 213 and 214:
cham oceans were closed, and the Ch
- Page 215 and 216:
greisenized Mesozoic granite that i
- Page 217 and 218:
composition magmatic bodies (with a
- Page 219 and 220:
Origin of and Tectonic Controls for
- Page 221 and 222:
to Albian pelecypods (Nokleberg and
- Page 223 and 224:
quartz-arsenopyrite-pyrrhotite, pol
- Page 225 and 226:
thermally altered to siliceous and
- Page 227 and 228:
These ore bodies are as much as 1 m
- Page 229 and 230:
Eastern Asia-Arctic Metallogenic Be
- Page 231 and 232:
Demin, and Krasilnikov, 1974; Nekra
- Page 233 and 234:
10 percent Cu, as much as 0.92 perc
- Page 235 and 236:
pyrite, pyrite, galena, sphalerite,
- Page 237 and 238:
content decreases with depth, as do
- Page 239 and 240:
azdelnoye, (2) porphyry Sn deposits
- Page 241 and 242:
Karalveem Au Quartz Vein Deposit Th
- Page 243 and 244:
Democrat (Mitchell Lode) Granitoid-
- Page 245 and 246:
with high-temperature and high-pres
- Page 247 and 248:
chalcocite and covellite and also h
- Page 249 and 250:
cum-North Pacific, (2) completion o
- Page 251 and 252:
(6) In the Paleocene (about 56 to 6
- Page 253 and 254:
sists of cinnabar and metacinnabari
- Page 255 and 256:
Eastern Asia-Arctic Metallogenic Be
- Page 257 and 258:
groups of deposits are interpreted
- Page 259 and 260:
Indian Mountain and Purcell Mountai
- Page 261 and 262:
and southeastern Alaska (Moll and P
- Page 263 and 264:
Nokleberg and others, 1995a; Bundtz
- Page 265 and 266:
g/t Au or 368.2 Au gold. The deposi
- Page 267 and 268:
wim Group and altered mafic dikes.
- Page 269 and 270:
Mount Nansen porphyry Cu-Mo deposit
- Page 271 and 272:
A Map 450 500 550 Cross section Dik
- Page 273 and 274:
Cretaceous and early Tertiary conti
- Page 275 and 276:
deposits, at Chichagoff and Hirst-C
- Page 277 and 278:
others, 1994c, 1997c). The signific
- Page 279 and 280:
tonnes grading 0.53 percent Ni, 0.3
- Page 281 and 282:
with a 0.25 percent cut-off. The de
- Page 283 and 284:
Bulkley Metallogenic Belt of Porphy
- Page 285 and 286:
Red Rose W-Au-Cu-Ag Polymetallic Ve
- Page 287 and 288:
ish Columbia and consists of severa
- Page 289 and 290:
during back-arc extension or transt
- Page 291 and 292:
stocks and dikes, is associated wit
- Page 293 and 294:
etrograde minnesotaite (Fe talc), F
- Page 295 and 296:
Specific Events for Early to Middle
- Page 297 and 298:
of fractured and faulted Permian-Tr
- Page 299 and 300:
sists of a mineralized fracture zon
- Page 301 and 302:
dolomite. Wall rock alteration incl
- Page 303 and 304:
elt of late Tertiary plutons that a
- Page 305 and 306:
plates that exhibit magnetic anomal
- Page 307 and 308:
stages (Petrenko, 1999): (1) In the
- Page 309 and 310:
mon. The deposit is of medium size
- Page 311 and 312:
Metallogenic-Tectonic Model for Lat
- Page 313 and 314:
The origin of the Hg deposits of th
- Page 315 and 316:
margin or island-arc tectonic envir
- Page 317 and 318:
Columbia: Implicatons for the Middl
- Page 319 and 320:
Bazard, D.R., Butler, R.F., Gehrels
- Page 321 and 322:
Bradley, D.C., Haeussler, P.J., and
- Page 323 and 324:
Bundtzen, T.K., Laird, G.M., Caluti
- Page 325 and 326:
Cecile, M.P., 1982, The lower Paleo
- Page 327 and 328:
Debari, S.M., and Coleman, R.G., 19
- Page 329 and 330:
U.S. Bureau of Land Management Open
- Page 331 and 332:
Cordilleran Orogen in Canada: Geolo
- Page 333 and 334:
Goldfarb, R., Hart, C., Miller, M.,
- Page 335 and 336:
Grove, E.W., 1986, Geology and mine
- Page 337 and 338:
Høy, T., 1982a, Stratigraphic and
- Page 339 and 340:
Jones, D.L., Silberling, N.J., Cone
- Page 341 and 342:
Kutyev, F. Sh., Baikov, A.I., Sidor
- Page 343 and 344:
Shield—Ultramafic magma and its m
- Page 345 and 346: Manns, F.T., 1981, Stratigraphic as
- Page 347 and 348: Miller, M.L., and Bundtzen, T.K., 1
- Page 349 and 350: Mortimer, N., 1987, The Nicola Grou
- Page 351 and 352: Noble, S.R., Spooner, E.T.C., and H
- Page 353 and 354: Canada Annual Meeting, Saskatoon, S
- Page 355 and 356: Perello, J.A., Fleming, J.A., O’K
- Page 357 and 358: Far East—Mineralogical criteria f
- Page 359 and 360: Roeske, S.M., Mattinson, J.M., and
- Page 361 and 362: Schmidt, J.M., and Zierenberg, R.A.
- Page 363 and 364: formation occurrences: Materialy po
- Page 365 and 366: Struik, L.C., 1986, Imbricated terr
- Page 367 and 368: Valuy, G., and Rostovsky, F., 1988,
- Page 369 and 370: Wolfe, W.J., 1995, Exploration and
- Page 371 and 372: Appendix Table 1. Mineral deposit m
- Page 373 and 374: Table 2 Summary of correlations and
- Page 375 and 376: Table 2—Continued Unit(s) and Cor
- Page 377 and 378: Table 2—Continued Unit(s) and Cor
- Page 379 and 380: Table 3—Continued Metallogenic Be
- Page 381 and 382: Table 3—Continued Metallogenic Be
- Page 383 and 384: Table 3—Continued Metallogenic Be
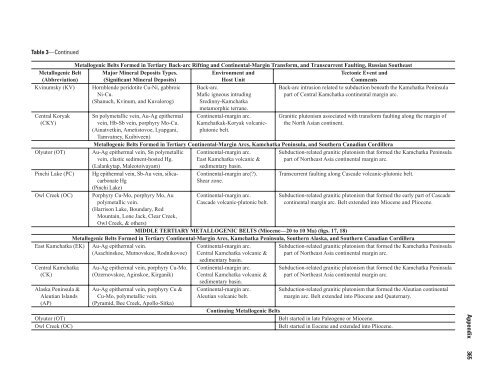
- Page 385 and 386: Table 3—Continued Metallogenic Be
- Page 387 and 388: Table 3—Continued Metallogenic Be
- Page 389 and 390: Table 3—Continued Metallogenic Be
- Page 391 and 392: Table 3—Continued Metallogenic Be
- Page 393 and 394: Table 3—Continued Metallogenic Be
- Page 395: Table 3—Continued Metallogenic Be
- Page 399 and 400: Table 4. Significant lode deposits,
- Page 401 and 402: Table 4—Continued Appendix 369 De
- Page 403 and 404: Table 4—Continued Tracy Metalloge
- Page 405 and 406: Table 4—Continued Appendix 373 In
- Page 407 and 408: Table 4—Continued Deposit Name Mi
- Page 409 and 410: Table 4—Continued Mainits Metallo
- Page 411 and 412: Table 4—Continued Deposit Name Mi
- Page 413 and 414: Table 4—Continued Appendix 381 De
- Page 415 and 416: Table 4—Continued Whitehorse Meta
- Page 417 and 418: Table 4—Continued Deposit Name Mi
- Page 419 and 420: Table 4—Continued Appendix 387 De
- Page 421 and 422: Table 4—Continued Appendix 389 LA
- Page 423 and 424: Table 4—Continued Deposit Name Mi
- Page 425 and 426: Table 4—Continued Surprise Lake M
- Page 427 and 428: Table 4—Continued Sredinny Metall
- Page 429: Table 4—Continued Deposit Name Mi