Crossroads: The Psychology of Immigration in the New Century
Crossroads: The Psychology of Immigration in the New Century
Crossroads: The Psychology of Immigration in the New Century
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
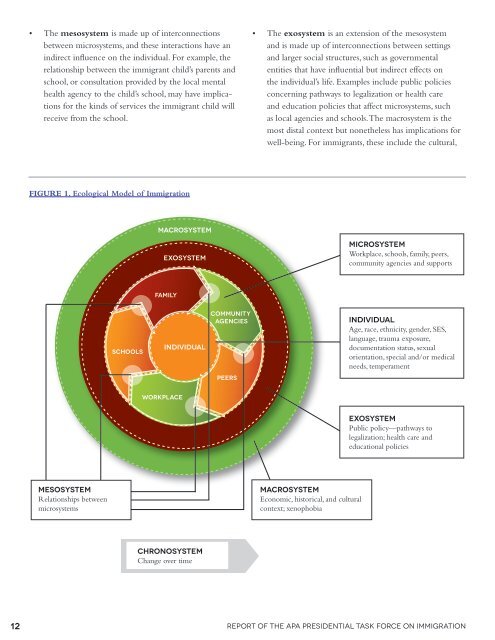
• <strong>The</strong> mesosystem is made up <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>terconnections<br />
between microsystems, and <strong>the</strong>se <strong>in</strong>teractions have an<br />
<strong>in</strong>direct <strong>in</strong>fluence on <strong>the</strong> <strong>in</strong>dividual. For example, <strong>the</strong><br />
relationship between <strong>the</strong> immigrant child’s parents and<br />
school, or consultation provided by <strong>the</strong> local mental<br />
health agency to <strong>the</strong> child’s school, may have implications<br />
for <strong>the</strong> k<strong>in</strong>ds <strong>of</strong> services <strong>the</strong> immigrant child will<br />
receive from <strong>the</strong> school.<br />
FIGURE 1. ecological model <strong>of</strong> <strong>Immigration</strong><br />
MESOSYSTEM<br />
Relationships between<br />
microsystems<br />
SCHOOLS<br />
MACROSYSTEM<br />
EXOSYSTEM<br />
Family<br />
Workplace<br />
INDIVIDUAL<br />
CHRONOSYSTEM<br />
Change over time<br />
Community<br />
agencies<br />
PEERS<br />
• <strong>The</strong> exosystem is an extension <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> mesosystem<br />
and is made up <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>terconnections between sett<strong>in</strong>gs<br />
and larger social structures, such as governmental<br />
entities that have <strong>in</strong>fluential but <strong>in</strong>direct effects on<br />
<strong>the</strong> <strong>in</strong>dividual’s life. Examples <strong>in</strong>clude public policies<br />
concern<strong>in</strong>g pathways to legalization or health care<br />
and education policies that affect microsystems, such<br />
as local agencies and schools. <strong>The</strong> macrosystem is <strong>the</strong><br />
most distal context but none<strong>the</strong>less has implications for<br />
well-be<strong>in</strong>g. For immigrants, <strong>the</strong>se <strong>in</strong>clude <strong>the</strong> cultural,<br />
MACROSYSTEM<br />
Economic, historical, and cultural<br />
context; xenophobia<br />
MICROSYSTEM<br />
Workplace, schools, family, peers,<br />
community agencies and supports<br />
INDIVIDUAL<br />
Age, race, ethnicity, gender, SES,<br />
language, trauma exposure,<br />
documentation status, sexual<br />
orientation, special and/or medical<br />
needs, temperament<br />
EXOSYSTEM<br />
Public policy—pathways to<br />
legalization; health care and<br />
educational policies<br />
12 Report <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> APA Presidential Task Force on <strong>Immigration</strong>