Avalon Interface Specifications (PDF) - Altera
Avalon Interface Specifications (PDF) - Altera
Avalon Interface Specifications (PDF) - Altera
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
3–2 Chapter 3: <strong>Avalon</strong> Memory-Mapped <strong>Interface</strong>s<br />
Signals<br />
3.2. Signals<br />
<strong>Avalon</strong>-MM components typically include only the signals required for the<br />
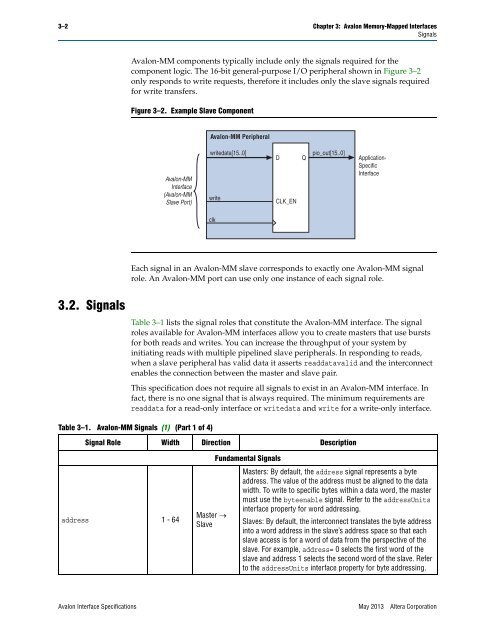
component logic. The 16-bit general-purpose I/O peripheral shown in Figure 3–2<br />
only responds to write requests, therefore it includes only the slave signals required<br />
for write transfers.<br />
Figure 3–2. Example Slave Component<br />
<strong>Avalon</strong>-MM<br />
<strong>Interface</strong><br />
(<strong>Avalon</strong>-MM<br />
Slave Port)<br />
<strong>Avalon</strong>-MM Peripheral<br />
writedata[15..0]<br />
write<br />
clk<br />
D Q<br />
CLK_EN<br />
pio_out[15..0]<br />
Application-<br />
Specific<br />
<strong>Interface</strong><br />
Each signal in an <strong>Avalon</strong>-MM slave corresponds to exactly one <strong>Avalon</strong>-MM signal<br />
role. An <strong>Avalon</strong>-MM port can use only one instance of each signal role.<br />
Table 3–1 lists the signal roles that constitute the <strong>Avalon</strong>-MM interface. The signal<br />
roles available for <strong>Avalon</strong>-MM interfaces allow you to create masters that use bursts<br />
for both reads and writes. You can increase the throughput of your system by<br />
initiating reads with multiple pipelined slave peripherals. In responding to reads,<br />
when a slave peripheral has valid data it asserts readdatavalid and the interconnect<br />
enables the connection between the master and slave pair.<br />
This specification does not require all signals to exist in an <strong>Avalon</strong>-MM interface. In<br />
fact, there is no one signal that is always required. The minimum requirements are<br />
readdata for a read-only interface or writedata and write for a write-only interface.<br />
Table 3–1. <strong>Avalon</strong>-MM Signals (1) (Part 1 of 4)<br />
Signal Role Width Direction Description<br />
address 1 - 64<br />
Master →<br />
Slave<br />
Fundamental Signals<br />
Masters: By default, the address signal represents a byte<br />
address. The value of the address must be aligned to the data<br />
width. To write to specific bytes within a data word, the master<br />
must use the byteenable signal. Refer to the addressUnits<br />
interface property for word addressing.<br />
Slaves: By default, the interconnect translates the byte address<br />
into a word address in the slave’s address space so that each<br />
slave access is for a word of data from the perspective of the<br />
slave. For example, address= 0 selects the first word of the<br />
slave and address 1 selects the second word of the slave. Refer<br />
to the addressUnits interface property for byte addressing.<br />
<strong>Avalon</strong> <strong>Interface</strong> <strong>Specifications</strong> May 2013 <strong>Altera</strong> Corporation