TESTING INTERNATIONAL PRICE TRANSMISSION UNDER ...
TESTING INTERNATIONAL PRICE TRANSMISSION UNDER ...
TESTING INTERNATIONAL PRICE TRANSMISSION UNDER ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Annexes<br />
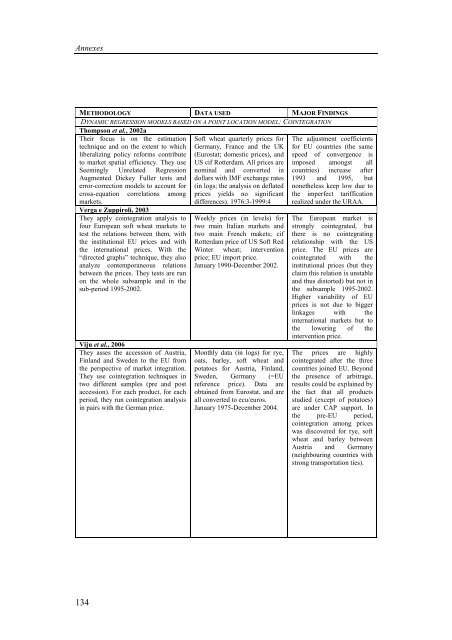
METHODOLOGY DATA USED MAJOR FINDINGS<br />
DYNAMIC REGRESSION MODELS BASED ON A POINT LOCATION MODEL: COINTEGRATION<br />
Thompson et al., 2002a<br />
Their focus is on the estimation<br />
technique and on the extent to which<br />
liberalizing policy reforms contribute<br />
to market spatial efficiency. They use<br />
Seemingly Unrelated Regression<br />
Augmented Dickey Fuller tests and<br />
error-correction models to account for<br />
cross-equation correlations among<br />
markets.<br />
Verga e Zuppiroli, 2003<br />
They apply cointegration analysis to<br />
four European soft wheat markets to<br />
test the relations between them, with<br />
the institutional EU prices and with<br />
the international prices. With the<br />
“directed graphs” technique, they also<br />
analyze contemporaneous relations<br />
between the prices. They tests are run<br />
on the whole subsample and in the<br />
sub-period 1995-2002.<br />
Viju et al., 2006<br />
They asses the accession of Austria,<br />
Finland and Sweden to the EU from<br />
the perspective of market integration.<br />
They use cointegration techniques in<br />
two different samples (pre and post<br />
accession). For each product, for each<br />
period, they run cointegration analysis<br />
in pairs with the German price.<br />
134<br />
Soft wheat quarterly prices for<br />
Germany, France and the UK<br />
(Eurostat; domestic prices), and<br />
US cif Rotterdam. All prices are<br />
nominal and converted in<br />
dollars with IMF exchange rates<br />
(in logs; the analysis on deflated<br />
prices yields no significant<br />
differences). 1976:3-1999:4<br />
Weekly prices (in levels) for<br />
two main Italian markets and<br />
two main French makets; cif<br />
Rotterdam price of US Soft Red<br />
Winter wheat; intervention<br />
price; EU import price.<br />
January 1990-December 2002.<br />
Monthly data (in logs) for rye,<br />
oats, barley, soft wheat and<br />
potatoes for Austria, Finland,<br />
Sweden, Germany (=EU<br />
reference price). Data are<br />
obtained from Eurostat, and are<br />
all converted to ecu/euros.<br />
January 1975-December 2004.<br />
The adjustment coefficients<br />
for EU countries (the same<br />
speed of convergence is<br />
imposed amongst all<br />
countries) increase after<br />
1993 and 1995, but<br />
nonetheless keep low due to<br />
the imperfect tariffication<br />
realized under the URAA.<br />
The European market is<br />
strongly cointegrated, but<br />
there is no cointegrating<br />
relationship with the US<br />
price. The EU prices are<br />
cointegrated with the<br />
institutional prices (but they<br />
claim this relation is unstable<br />
and thus distorted) but not in<br />
the subsample 1995-2002.<br />
Higher variability of EU<br />
prices is not due to bigger<br />
linkages with the<br />
international markets but to<br />
the lowering of the<br />
intervention price.<br />
The prices are highly<br />
cointegrated after the three<br />
countries joined EU. Beyond<br />
the presence of arbitrage,<br />
results could be explained by<br />
the fact that all products<br />
studied (except of potatoes)<br />
are under CAP support. In<br />
the pre-EU period,<br />
cointegration among prices<br />
was discovered for rye, soft<br />
wheat and barley between<br />
Austria and Germany<br />
(neighbouring countries with<br />
strong transportation ties).