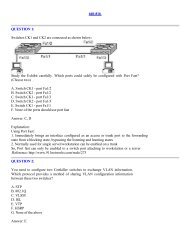
CCNA Complete Guide 2nd Edition.pdf - Cisco Learning Home
CCNA Complete Guide 2nd Edition.pdf - Cisco Learning Home
CCNA Complete Guide 2nd Edition.pdf - Cisco Learning Home
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Determining <strong>Cisco</strong> Router Memory Size<br />
- The show version EXEC command is able to tell how much Dynamic RAM (DRAM) and<br />
packet memory (separate SRAM or shared memory) are installed in a <strong>Cisco</strong> router.<br />
- The <strong>Cisco</strong> 4000, 4500, 4700, and 7500 series routers have separate DRAM and packet memory.<br />
The example below shows a router with 64M of DRAM and 2M of SRAM (packet memory):<br />
cisco RSP4 (R5000) processor with 65536K/2072K bytes of memory.<br />
The example below shows a router with 256M of DRAM and 8M of SRAM (packet memory):<br />
cisco RSP8 (R7000) processor with 262144K/8216K bytes of memory.<br />
- The <strong>Cisco</strong> 1600, 2500, 2600, 3600, and 7200 series routers use a fraction of their DRAM as<br />
packet memory. Hence both numbers need to be added to find out the real amount of DRAM.<br />
The example below shows a router with 29696K + 3072K = 32768K = 32M of DRAM.<br />
cisco 2611 (MPC860) processor (revision x) with 29696K/3072K bytes of memory.<br />
The example below shows a router with 93184K + 5120K = 98304K = 98M of DRAM.<br />
cisco 2621XM (MPC860P) processor (revision) with 93184K/5120K bytes of memory.<br />
- DRAM is mainly used for system processing, eg: storing routing tables, routing protocols data,<br />
network accounting information, and running the <strong>Cisco</strong> IOS software; while packet memory is<br />
used for packet buffering of the router network interfaces and CPU cache memory functions.<br />
The packet memory on <strong>Cisco</strong> 4000, 4500, 4700, and 7500 series routers is the total physical I/O<br />
memory (also known as SRAM or Fast Memory); while the packet memory on <strong>Cisco</strong> 1600,<br />
2500, 2600, 3600, and 7200 series routers is the amount of shared memory, which is a portion<br />
of the DRAM.<br />
- The terms I/O memory (iomem), shared memory, Fast Memory, and PCI memory are all refer to<br />
Packet Memory, which is either a separate physical RAM stick or module, or shared DRAM.<br />
- Static RAM (SRAM) is a type of semiconductor memory that does not need to be periodically<br />
refreshed as Dynamic RAM (DRAM). Memory refresh is the process of periodically reading<br />
information from an area of computer memory, and rewriting the read information back to the<br />
same area immediately without any modification. SRAM is still volatile, as the data stored in it is<br />
eventually lost when the memory is not powered.<br />
- SRAM is more expensive, but faster and far less power hungry when idle (no periodical refresh)<br />
compared to DRAM. Additionally, due to a more complex internal structure, SRAM is less dense<br />
that DRAM and hence not used for high-capacity, low-cost applications, eg: PC main memory.<br />
The Myth of the Running Configuration file<br />
- The reload privileged command is the only way to restore the configuration of a device into its<br />
last reboot state. Replacing the running-config with the startup-config or a configuration file<br />
from a TFTP server will be unsuccessful – configuration is merged instead of being overwritten.<br />
- The Configuration Replace and Configuration Rollback feature which introduced in <strong>Cisco</strong> IOS<br />
Release 12.3(7)T and 12.2(25)S provides the capability to replace the current running<br />
configuration with any configuration file. The configure replace privileged command can be<br />
used to overwrite the running configuration.<br />
253<br />
Copyright © 2008 Yap Chin Hoong<br />
yapchinhoong@hotmail.com