GAMMON INDIA LIMITED
GAMMON INDIA LIMITED
GAMMON INDIA LIMITED
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
INDUSTRY OVERVIEW<br />
The information in this section is derived from various government publications, publicly available<br />
information and industry sources. Neither we nor any other person connected with the Placement have<br />
verified this information. Industry sources and publications generally state that the information contained<br />
therein has been obtained from sources generally believed to be reliable, but that their accuracy,<br />
completeness and underlying assumptions are not guaranteed and their reliability cannot be assured and,<br />
accordingly, investment decisions should not be based on such information.<br />
Overview of the Indian Economy<br />
India is the world’s largest democracy by population size, and one of the fastest growing economies in the<br />
world and has grown at an average rate of 8.20% per annum during the last three years. According to CIA<br />
World Factbook, India’s estimated population was 1.16 billion people as of July 2009. India had a GDP on<br />
a purchasing power parity basis estimated at approximately US$3,267.00 billion in 2008, which makes it<br />
the fourth largest economy in the world after the United States of America, China and Japan in purchasing<br />
power parity terms. Per capita GDP in current prices in India has grown from Rs.7,170.00 for the 1991<br />
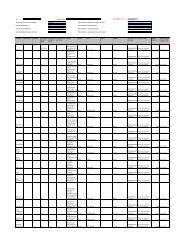
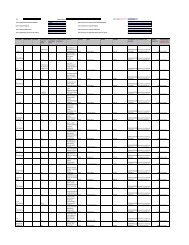
calendar year at the time of liberalization to Rs.44,231.00 for the 2008 calendar year. The following table<br />
presents a comparison of India's real GDP growth rate with the real GDP growth rate of certain other<br />
countries.<br />
Countries* 2006 2007 2008<br />
Australia ........................... 2.90% 4.00% 2.20%<br />
Brazil ................................ 4.00% 5.40% 5.20%<br />
China ................................ 11.60% 13.00% 9.80%<br />
India................................. 9.60% 9.00% 6.60%<br />
Japan................................. 2.40% 1.50% -0.40%<br />
South Korea...................... 5.10% 5.00% 2.50%<br />
Malaysia ........................... 5.80% 6.30% 5.10%<br />
Russia ............................... 7.70% 8.10% 6.00%<br />
Thailand............................ 5.20% 4.90% 3.60%<br />
United Kingdom ............... 2.80% 3.00% 0.70%<br />
United States..................... 2.80% 2.00% 1.30%<br />
* Represents calendar year growth rates<br />
Source: CIA World Factbook<br />
Indian Infrastructure : Government Initiatives<br />
The Central and State Governments of lndia are focusing on establishing an appropriate policy framework<br />
for the infrastructure sector which provides the private sector with incentives to make large-scale<br />
investments, at the same time preserving adequate checks and balances through transparency, competition<br />
and regulation. There has been a shift towards financing of infrastructure development to the private sector,<br />
primarily through Public Private Partnerships (“PPPs”), which are based on a partnership between the<br />
public and the private sectors for the purpose of delivering a project or service traditionally provided by the<br />
public sector. PPPs are designed to mobilise financial resources and realise benefits from private sector<br />
efficiencies to meet the growing demand for infrastructure services. The formation of a stable government<br />
in the centre is expected to result in a boost to the infrastructure sector in India. The initiatives undertaken in<br />
the Union Budget for fiscal 2010 as regards infrastructure sector is a positive step in that direction. Recently<br />
in order to give a push to economic activity, the government constituted the Cabinet Committee on<br />
Infrastructure (CCI) to fast-track the implementation of the infrastructure sector projects and monitor their<br />
performance. The 12-member committee will be headed by the Prime Minister. The functions of the<br />
Cabinet Committee on Infrastructure will be to consider and take decisions in respect of all infrastructure<br />
related proposals costing over Rs 150 crore specifically those concerning Energy, Railways, Roads and<br />
National Highways, Ports, Airports, Telecommunications, Information Technology, Irrigation, Housing and<br />
Urban Development with particular emphasis on rural housing and urban slum clearance.<br />
The government agencies with responsibilities for different infrastructure sectors include the National<br />
Highways Authority of lndia (“NHAI”), National Thermal Power Corporation, the National Hydro Power<br />
Corporation and the Power Grid Corporation of India Limited (“PGCIL”), ONGC, GAIL, Port Authorities,<br />
Central Water Commission, Indian Railways, IOL/ HPCL/ BPCL, NPCIL/ BARC, State Level Urban<br />
53