Kinetic Analysis and Characterization of Epoxy Resins ... - FedOA
Kinetic Analysis and Characterization of Epoxy Resins ... - FedOA
Kinetic Analysis and Characterization of Epoxy Resins ... - FedOA
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Introduction 47<br />
Debye equations based on the microscopic interaction <strong>of</strong> the dipoles with applied<br />
electromagnetic fields [9, 10]. The classical Debye description <strong>of</strong> an ideal dielectric<br />
liquid is useful to underst<strong>and</strong> the physics behind the interaction <strong>of</strong> microwaves<br />
with materials at the molecular level. In the Debye description, a single molecule<br />
with a small electric dipole is assumed to be at the center <strong>of</strong> a spherical volume.<br />
When there is no electromagnetic field present, the dipoles are r<strong>and</strong>omly oriented<br />
throughout the material. When the electromagnetic field is applied, the dipoles<br />
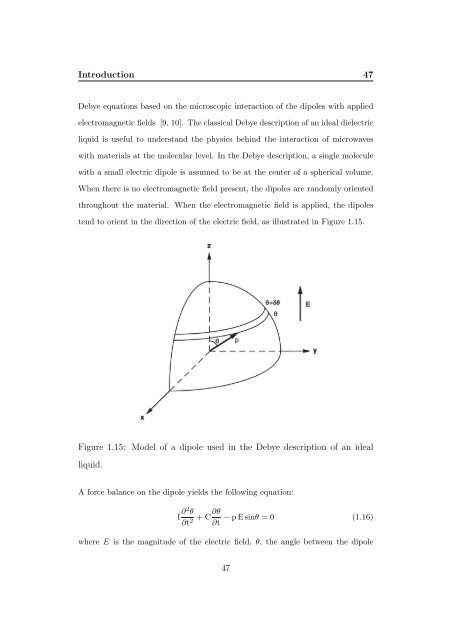
tend to orient in the direction <strong>of</strong> the electric field, as illustrated in Figure 1.15.<br />
Figure 1.15: Model <strong>of</strong> a dipole used in the Debye description <strong>of</strong> an ideal<br />
liquid.<br />
A force balance on the dipole yields the following equation:<br />
I ∂2 θ<br />
∂t 2 +C∂θ − pEsinθ = 0 (1.16)<br />
∂t<br />
where E is the magnitude <strong>of</strong> the electric field, θ, the angle between the dipole<br />
47