You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Grundfos</strong> E-<strong>pumps</strong><br />
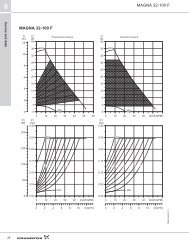
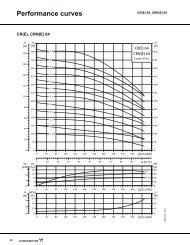
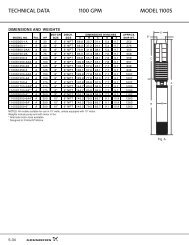
9<br />
Non-sinusoidal power input, variable<br />
frequency drives supplied by three-phase<br />
supply<br />
A variable frequency drive designed as the one<br />
described above will not receive sinusoidal current<br />
from the power supply. Among other things, this will<br />
influence the sizing of power supply cable, power<br />
switches, etc. Figure 74 shows how supply current and<br />
voltage appear for the following:<br />
a) three-phase, two-pole standard asynchronous<br />
motor<br />
b) three-phase, two-pole standard asynchronous<br />
motor with variable frequency drive.<br />
In both cases, the motor supplies 4 Hp to the shaft.<br />
a)<br />
TM00 8708 3396<br />
A comparison of the current in the two cases shows<br />
the following differences. See fig. 74.<br />
• The current for the system with variable frequency<br />
drive is not sinusoidal.<br />
• The peak current is much higher (approx. 52 %<br />
higher) for the variable frequency drive solution.<br />
Standard motor<br />
Motor with variable<br />
frequency drive<br />
Supply voltage 400 V 400 V<br />
Supply current, RMS 6.4 A 6.36 A<br />
Supply current, peak 9.1 A 13.8 A<br />
Power input, P1 4.93 Hp 4.94 Hp<br />
Cos φ, power factor (PF) Cos φ = 0.83 PF = 0.86<br />
This is due to the design of the variable frequency<br />
drive connecting the power supply to a rectifier<br />
followed by a capacitor. The charging of the capacitor<br />
happens during short time periods in which the<br />
rectified voltage is higher than the voltage in the<br />
capacitor at that moment. As mentioned above, the<br />
non-sinusoidal current results in other conditions at the<br />
power supply side of the motor. For a standard motor<br />
without a variable frequency drive, the relation<br />
between voltage (U), current (I) and power (P) is as<br />
follows:<br />
Frequency-controlled operation<br />
b)<br />
TM00 8709 3396<br />
P = 3 U I<br />
Cos <br />
U is the voltage between two phases and (I) is the<br />
phase current, both effective values (RMS values), and<br />
φ is phase displacement between current and voltage.<br />
In the example the following applies:<br />
U = 400 V, I = 6.2 A, Cos φ = 0.83.<br />
The result is a power input of P = 4.78 Hp.<br />
Fig. 74 Supply current and voltage for a) a standard<br />
asynchronous motor and b) a three-phase MLE<br />
motor<br />
63