- Page 1 and 2:
Handover Mechanisms in Next Generat
- Page 3 and 4:
ACKNOWLEDGMENT First of all, I woul
- Page 5 and 6:
TABLE OF CONTENTS 4.4.2 Power Save
- Page 7 and 8:
LIST OF FIGURES LIST OF FIGURES Fig
- Page 9 and 10:
LIST OF FIGURES Figure 7.2 A generi
- Page 11 and 12:
ABSTRACT New access technologies su
- Page 13 and 14:
Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION New access t
- Page 15 and 16:
INTRODUCTION becomes available. Han
- Page 17 and 18:
INTRODUCTION The above multipliciti
- Page 19 and 20:
INTRODUCTION network trust pattern
- Page 21 and 22:
INTRODUCTION 1.3 Related Publicatio
- Page 23 and 24:
INTRODUCTION TECHNICAL REPORTS XIII
- Page 25 and 26:
HANDOVER MANAGEMENT horizontally. H
- Page 27 and 28:
HANDOVER MANAGEMENT The objective o
- Page 29 and 30:
HANDOVER MANAGEMENT air interface,
- Page 31 and 32:
HANDOVER MANAGEMENT proposed archit
- Page 33 and 34:
HANDOVER MANAGEMENT Access point (A
- Page 35 and 36:
HANDOVER MANAGEMENT users. Moreover
- Page 37 and 38:
HANDOVER MANAGEMENT For IEEE 802.11
- Page 39 and 40:
HANDOVER MANAGEMENT The two schemes
- Page 41 and 42:
HANDOVER MANAGEMENT When a MH is mo
- Page 43 and 44:
3.1 Introduction Chapter 3 HANDOVER
- Page 45 and 46:
SECURITY FOR HANDOVER ACROSS HETERO
- Page 47 and 48:
SECURITY FOR HANDOVER ACROSS HETERO
- Page 49 and 50:
SECURITY FOR HANDOVER ACROSS HETERO
- Page 51 and 52:
SECURITY FOR HANDOVER ACROSS HETERO
- Page 53 and 54:
SECURITY FOR HANDOVER ACROSS HETERO
- Page 55 and 56:
SECURITY FOR HANDOVER ACROSS HETERO
- Page 57 and 58:
SECURITY FOR HANDOVER ACROSS HETERO
- Page 59 and 60:
SECURITY FOR HANDOVER ACROSS HETERO
- Page 61 and 62:
SECURITY FOR HANDOVER ACROSS HETERO
- Page 63 and 64:
SECURITY FOR HANDOVER ACROSS HETERO
- Page 65 and 66:
SECURITY FOR HANDOVER ACROSS HETERO
- Page 67 and 68:
SECURITY FOR HANDOVER ACROSS HETERO
- Page 69 and 70:
DYNAMIC NEIGHBOUR TRUST INFORMATION
- Page 71 and 72:
DYNAMIC NEIGHBOUR TRUST INFORMATION
- Page 73 and 74:
DYNAMIC NEIGHBOUR TRUST INFORMATION
- Page 75 and 76:
DYNAMIC NEIGHBOUR TRUST INFORMATION
- Page 77 and 78:
DYNAMIC NEIGHBOUR TRUST INFORMATION
- Page 79 and 80:
DYNAMIC NEIGHBOUR TRUST INFORMATION
- Page 81 and 82:
DYNAMIC NEIGHBOUR TRUST INFORMATION
- Page 83 and 84:
DYNAMIC NEIGHBOUR TRUST INFORMATION
- Page 85 and 86:
DYNAMIC NEIGHBOUR TRUST INFORMATION
- Page 87 and 88:
DYNAMIC NEIGHBOUR TRUST INFORMATION
- Page 89 and 90:
DYNAMIC NEIGHBOUR TRUST INFORMATION
- Page 91 and 92:
DYNAMIC NEIGHBOUR TRUST INFORMATION
- Page 93 and 94:
Chapter 5 TRUST ASSISTED HANDOVER A
- Page 95 and 96:
TRUST ASSISTED HANDOVER ALGORITHM F
- Page 97 and 98:
TRUST ASSISTED HANDOVER ALGORITHM F
- Page 99 and 100:
TRUST ASSISTED HANDOVER ALGORITHM F
- Page 101 and 102:
TRUST ASSISTED HANDOVER ALGORITHM F
- Page 103 and 104: TRUST ASSISTED HANDOVER ALGORITHM F
- Page 105 and 106: TRUST ASSISTED HANDOVER ALGORITHM F
- Page 107 and 108: TRUST ASSISTED HANDOVER ALGORITHM F
- Page 109 and 110: TRUST ASSISTED HANDOVER ALGORITHM F
- Page 111 and 112: TRUST ASSISTED HANDOVER ALGORITHM F
- Page 113 and 114: TRUST ASSISTED HANDOVER ALGORITHM F
- Page 115 and 116: TRUST ASSISTED HANDOVER ALGORITHM F
- Page 117 and 118: TRUST ASSISTED HANDOVER ALGORITHM F
- Page 119 and 120: TRUST ASSISTED HANDOVER ALGORITHM F
- Page 121 and 122: TRUST ASSISTED HANDOVER ALGORITHM F
- Page 123 and 124: Chapter 6 PROXY BASED AUTHENTICATIO
- Page 125 and 126: PROXY BASED AUTHENTICATION LOCALISA
- Page 127 and 128: PROXY BASED AUTHENTICATION LOCALISA
- Page 129 and 130: PROXY BASED AUTHENTICATION LOCALISA
- Page 131 and 132: PROXY BASED AUTHENTICATION LOCALISA
- Page 133 and 134: PROXY BASED AUTHENTICATION LOCALISA
- Page 135 and 136: PROXY BASED AUTHENTICATION LOCALISA
- Page 137 and 138: PROXY BASED AUTHENTICATION LOCALISA
- Page 139 and 140: PROXY BASED AUTHENTICATION LOCALISA
- Page 141 and 142: PROXY BASED AUTHENTICATION LOCALISA
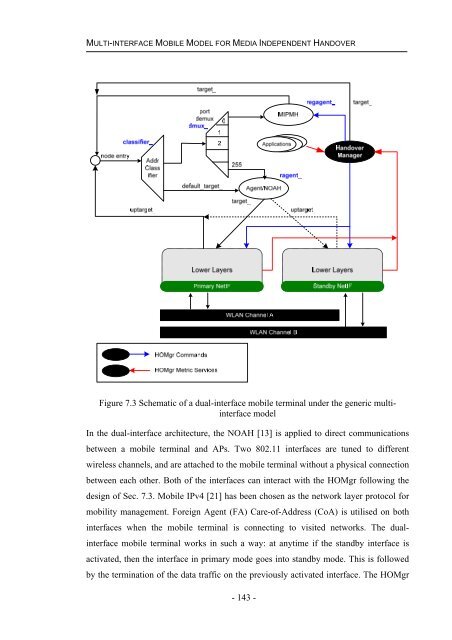
- Page 143 and 144: PROXY BASED AUTHENTICATION LOCALISA
- Page 145 and 146: PROXY BASED AUTHENTICATION LOCALISA
- Page 147 and 148: MULTI-INTERFACE MOBILE MODEL FOR ME
- Page 149 and 150: MULTI-INTERFACE MOBILE MODEL FOR ME
- Page 151 and 152: MULTI-INTERFACE MOBILE MODEL FOR ME
- Page 153: MULTI-INTERFACE MOBILE MODEL FOR ME
- Page 157 and 158: MULTI-INTERFACE MOBILE MODEL FOR ME
- Page 159 and 160: MULTI-INTERFACE MOBILE MODEL FOR ME
- Page 161 and 162: MULTI-INTERFACE MOBILE MODEL FOR ME
- Page 163 and 164: MULTI-INTERFACE MOBILE MODEL FOR ME
- Page 165 and 166: MULTI-INTERFACE MOBILE MODEL FOR ME
- Page 167 and 168: MULTI-INTERFACE MOBILE MODEL FOR ME
- Page 169 and 170: CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE RESEARCH WOR
- Page 171 and 172: CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE RESEARCH WOR
- Page 173 and 174: CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE RESEARCH WOR
- Page 175 and 176: ABBREVIATIONS 3G 3rd Generation Wir
- Page 177 and 178: ABBREVIATIONS LS Location Server MH
- Page 179 and 180: ABBREVIATIONS THOA Trust Assisted H
- Page 181 and 182: REFERENCES [12] C. Politis, T. Oda,
- Page 183 and 184: REFERENCES [37] Wi-Fi Alliance, "Wi
- Page 185 and 186: REFERENCES presented at IEEE Intern
- Page 187 and 188: REFERENCES [90] R. Verdone and A. Z
- Page 189: REFERENCES [116] K. E. Malki and H.