You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
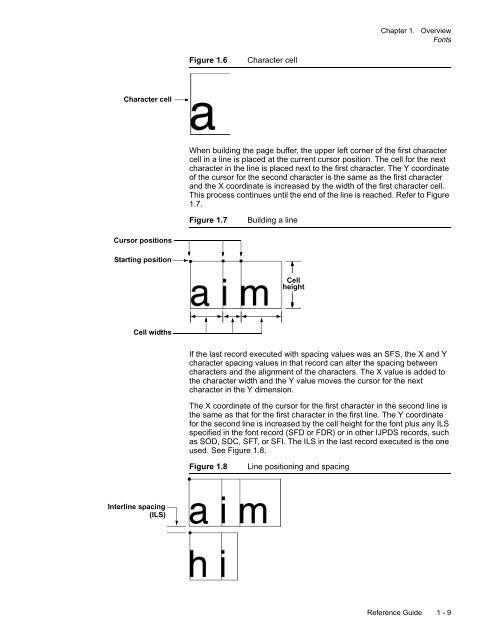
Character cell<br />
Cursor positions<br />
Starting position<br />
Cell widths<br />
Interline spacing<br />
(ILS)<br />
Figure 1.6 Character cell<br />
Chapter 1. Overview<br />
Fonts<br />
When building the page buffer, the upper left corner of the first character<br />
cell in a line is placed at the current cursor position. The cell for the next<br />
character in the line is placed next to the first character. The Y coordinate<br />
of the cursor for the second character is the same as the first character<br />
and the X coordinate is increased by the width of the first character cell.<br />
This process continues until the end of the line is reached. Refer to Figure<br />
1.7.<br />
Figure 1.7 Building a line<br />
Cell<br />
height<br />
If the last record executed with spacing values was an SFS, the X and Y<br />
character spacing values in that record can alter the spacing between<br />
characters and the alignment of the characters. The X value is added to<br />
the character width and the Y value moves the cursor for the next<br />
character in the Y dimension.<br />
The X coordinate of the cursor for the first character in the second line is<br />
the same as that for the first character in the first line. The Y coordinate<br />
for the second line is increased by the cell height for the font plus any ILS<br />
specified in the font record (SFD or FDR) or in other IJPDS records, such<br />
as SOD, SDC, SFT, or SFI. The ILS in the last record executed is the one<br />
used. See Figure 1.8.<br />
Figure 1.8 Line positioning and spacing<br />
Reference Guide 1 - 9