Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
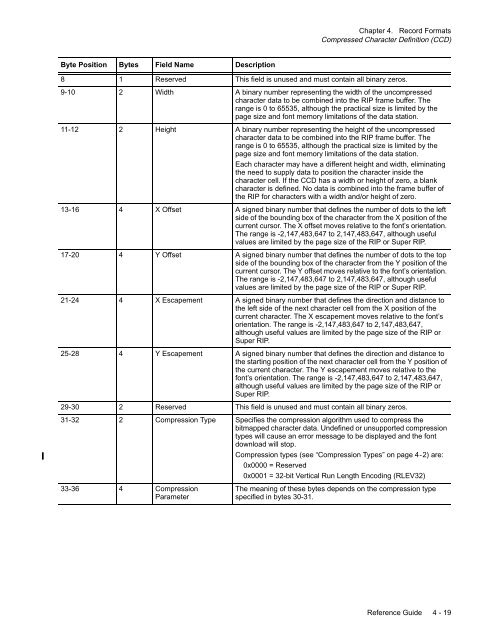
Byte Position Bytes Field Name Description<br />
Chapter 4. Record Formats<br />
Compressed Character Definition (CCD)<br />
8 1 Reserved This field is unused and must contain all binary zeros.<br />
9-10 2 Width A binary number representing the width of the uncompressed<br />
character data to be combined into the RIP frame buffer. The<br />
range is 0 to 65535, although the practical size is limited by the<br />
page size and font memory limitations of the data station.<br />
11-12 2 Height A binary number representing the height of the uncompressed<br />
character data to be combined into the RIP frame buffer. The<br />
range is 0 to 65535, although the practical size is limited by the<br />
page size and font memory limitations of the data station.<br />
Each character may have a different height and width, eliminating<br />
the need to supply data to position the character inside the<br />
character cell. If the CCD has a width or height of zero, a blank<br />
character is defined. No data is combined into the frame buffer of<br />
the RIP for characters with a width and/or height of zero.<br />
13-16 4 X Offset A signed binary number that defines the number of dots to the left<br />
side of the bounding box of the character from the X position of the<br />
current cursor. The X offset moves relative to the font’s orientation.<br />
The range is -2,147,483,647 to 2,147,483,647, although useful<br />
values are limited by the page size of the RIP or Super RIP.<br />
17-20 4 Y Offset A signed binary number that defines the number of dots to the top<br />
side of the bounding box of the character from the Y position of the<br />
current cursor. The Y offset moves relative to the font’s orientation.<br />
The range is -2,147,483,647 to 2,147,483,647, although useful<br />
values are limited by the page size of the RIP or Super RIP.<br />
21-24 4 X Escapement A signed binary number that defines the direction and distance to<br />
the left side of the next character cell from the X position of the<br />
current character. The X escapement moves relative to the font’s<br />
orientation. The range is -2,147,483,647 to 2,147,483,647,<br />
although useful values are limited by the page size of the RIP or<br />
Super RIP.<br />
25-28 4 Y Escapement A signed binary number that defines the direction and distance to<br />
the starting position of the next character cell from the Y position of<br />
the current character. The Y escapement moves relative to the<br />
font’s orientation. The range is -2,147,483,647 to 2,147,483,647,<br />
although useful values are limited by the page size of the RIP or<br />
Super RIP.<br />
29-30 2 Reserved This field is unused and must contain all binary zeros.<br />
31-32 2 Compression Type Specifies the compression algorithm used to compress the<br />
bitmapped character data. Undefined or unsupported compression<br />
types will cause an error message to be displayed and the font<br />
download will stop.<br />
Compression types (see “Compression Types” on page 4-2) are:<br />
0x0000 = Reserved<br />
0x0001 = 32-bit Vertical Run Length Encoding (RLEV32)<br />
33-36 4 Compression<br />
The meaning of these bytes depends on the compression type<br />
Parameter<br />
specified in bytes 30-31.<br />
Reference Guide 4 - 19