Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Chapter 4. Record Formats<br />
Stop (STP)<br />
Stop (STP)<br />
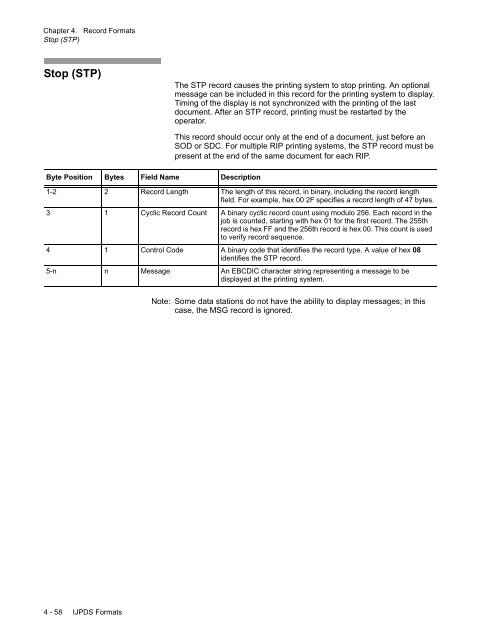
Byte Position Bytes Field Name Description<br />
4 - 58 IJPDS Formats<br />
The STP record causes the printing system to stop printing. An optional<br />
message can be included in this record for the printing system to display.<br />
Timing of the display is not synchronized with the printing of the last<br />
document. After an STP record, printing must be restarted by the<br />
operator.<br />
This record should occur only at the end of a document, just before an<br />
SOD or SDC. For multiple RIP printing systems, the STP record must be<br />
present at the end of the same document for each RIP.<br />
1-2 2 Record Length The length of this record, in binary, including the record length<br />
field. For example, hex 00 2F specifies a record length of 47 bytes.<br />
3 1 Cyclic Record Count A binary cyclic record count using modulo 256. Each record in the<br />
job is counted, starting with hex 01 for the first record. The 255th<br />
record is hex FF and the 256th record is hex 00. This count is used<br />
to verify record sequence.<br />
4 1 Control Code A binary code that identifies the record type. A value of hex 08<br />
identifies the STP record.<br />
5-n n Message An EBCDIC character string representing a message to be<br />
displayed at the printing system.<br />
Note: Some data stations do not have the ability to display messages; in this<br />
case, the MSG record is ignored.