- Page 1 and 2: Joint Publication 3-33 Joint Task F
- Page 3 and 4: Preface and procedures ratified by
- Page 5 and 6: Summary of Changes Intentionally Bl
- Page 7 and 8: Table of Contents Organization ...
- Page 9 and 10: Table of Contents V-1 Notional Join
- Page 11 and 12: Executive Summary maneuver, protect
- Page 13 and 14: Executive Summary Joint Task Force
- Page 15 and 16: Executive Summary Joint Task Force
- Page 17 and 18: Executive Summary matters. The JOC
- Page 19 and 20: Executive Summary J-5 Responsibilit
- Page 21 and 22: Executive Summary Intentionally Bla
- Page 23 and 24: Chapter I Joint Task Force Establis
- Page 25 and 26: Chapter I the JTF. JTF commanders a
- Page 27 and 28: Chapter I (3) Operations Directorat
- Page 29 and 30: Chapter I b. The CJTF, joint force
- Page 31 and 32: Chapter I Additional multinational
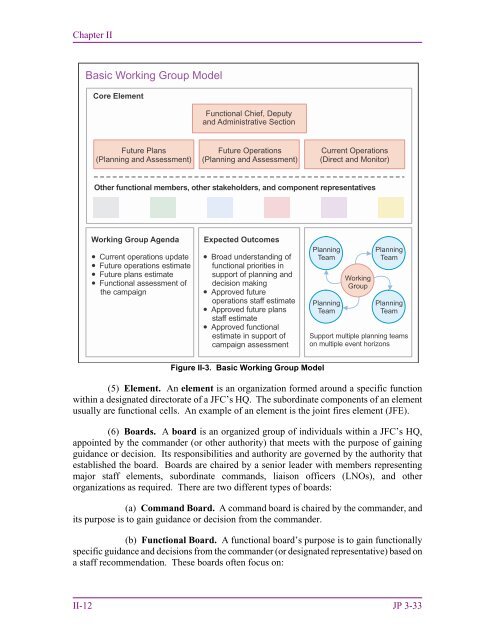
- Page 33 and 34: Chapter II c. Tasking an Existing J
- Page 35 and 36: Chapter II enabling capability pack
- Page 37 and 38: Chapter II actions in the operation
- Page 39 and 40: Chapter II (18) Establishing person
- Page 41: Chapter II Force Personal and Speci
- Page 45 and 46: Chapter II c. Employment of Cross-F
- Page 47 and 48: Chapter II Staff Interaction Suppor
- Page 49 and 50: Chapter II (4) Assist. LNOs provide
- Page 51 and 52: Chapter III Possible Joint Task For
- Page 53 and 54: Chapter III with JP 1, Doctrine for
- Page 55 and 56: Chapter III b. However, it is more
- Page 57 and 58: Chapter IV (3) Commander’s Guidan
- Page 59 and 60: Chapter IV (d) Coordination and lia
- Page 61 and 62: Chapter IV (1) Organization of the
- Page 63 and 64: Chapter IV coordination with their
- Page 65 and 66: Chapter IV measures that may be pro
- Page 67 and 68: Chapter IV (b) The military, on the
- Page 69 and 70: Chapter IV an electronic version of
- Page 71 and 72: Chapter IV Commander’s Decision C
- Page 73 and 74: Chapter IV 1. Providing a routine f
- Page 75 and 76: Chapter IV collaborative tools, suc
- Page 77 and 78: Chapter V Notional Joint Task Force
- Page 79 and 80: Chapter V requirements, joint missi
- Page 81 and 82: Chapter V situation, a pre-position
- Page 83 and 84: Chapter V (c) Hostile fire pay and
- Page 85 and 86: Chapter V For additional informatio
- Page 87 and 88: Chapter V (7) Ensures that personne
- Page 89 and 90: Chapter V Intentionally Blank V-14
- Page 91 and 92: Chapter VI Notional Joint Task Forc
- Page 93 and 94:
Chapter VI k. The JTF intelligence
- Page 95 and 96:
Chapter VI o. Validating intelligen
- Page 97 and 98:
Chapter VI 6. National Intelligence
- Page 99 and 100:
Chapter VI e. In addition, the JISE
- Page 101 and 102:
Chapter VI NOTE The JCMEC and JDEC
- Page 103 and 104:
Chapter VII Notional Joint Task For
- Page 105 and 106:
Chapter VII addition, functional LN
- Page 107 and 108:
Chapter VII staff planning, coordin
- Page 109 and 110:
Chapter VII Protection Working Grou
- Page 111 and 112:
Chapter VII (2) The organization of
- Page 113 and 114:
Chapter VII (12) Coordinate with mu
- Page 115 and 116:
Chapter VII x. Establish a JPRC wit
- Page 117 and 118:
Chapter VIII contract support, and
- Page 119 and 120:
Chapter VIII a. Determine personnel
- Page 121 and 122:
Chapter VIII 4. Authority a. Title
- Page 123 and 124:
Chapter VIII mission, enemy, terrai
- Page 125 and 126:
Chapter VIII b. The JTF J-4 staff s
- Page 127 and 128:
Chapter VIII government contains st
- Page 129 and 130:
Chapter VIII (d) Component commande
- Page 131 and 132:
Chapter VIII (7) Joint Mortuary Aff
- Page 133 and 134:
Chapter VIII Intentionally Blank VI
- Page 135 and 136:
Chapter IX Notional Joint Task Forc
- Page 137 and 138:
Chapter IX p. Provide the CJTF with
- Page 139 and 140:
Chapter IX achieve their end state.
- Page 141 and 142:
Chapter IX b. The primary purposes
- Page 143 and 144:
Chapter IX (7) Often IGOs and NGOs
- Page 145 and 146:
Chapter IX Forming and Informing th
- Page 147 and 148:
Chapter X d. Component tactical com
- Page 149 and 150:
Chapter X (2) Coordinate communicat
- Page 151 and 152:
Chapter X (h) In consultation with
- Page 153 and 154:
Chapter X (5) CJCSM 6231.01, Manual
- Page 155 and 156:
Chapter X Intentionally Blank X-10
- Page 157 and 158:
Appendix A Intentionally Blank A-2
- Page 159 and 160:
Annex A to Appendix A g. If the mis
- Page 161 and 162:
Annex A to Appendix A Intentionally
- Page 163 and 164:
Annex B to Appendix A b. Visit each
- Page 165 and 166:
Annex B to Appendix A Intentionally
- Page 167 and 168:
Annex C to Appendix A 8. Considerat
- Page 169 and 170:
Annex C to Appendix A Intentionally
- Page 171 and 172:
Annex D to Appendix A j. Has NIST s
- Page 173 and 174:
Annex D to Appendix A pp. Has tailo
- Page 175 and 176:
Annex E to Appendix A 15. Have comp
- Page 177 and 178:
Annex E to Appendix A b. Have US an
- Page 179 and 180:
Annex E to Appendix A c. Have speci
- Page 181 and 182:
Annex E to Appendix A Intentionally
- Page 183 and 184:
Annex F to Appendix A r. Are suppor
- Page 185 and 186:
Annex F to Appendix A b. Have mortu
- Page 187 and 188:
Annex F to Appendix A e. Has engine
- Page 189 and 190:
Annex G to Appendix A 20. Do curren
- Page 191 and 192:
Annex H to Appendix A r. Has an inf
- Page 193 and 194:
Annex H to Appendix A nn. Are plans
- Page 195 and 196:
Annex H to Appendix A (8) Civilian
- Page 197 and 198:
Annex J to Appendix A 15. Have the
- Page 199 and 200:
Annex J to Appendix A Intentionally
- Page 201 and 202:
Annex K to Appendix A n. War trophi
- Page 203 and 204:
Annex L to Appendix A c. Informatio
- Page 205 and 206:
Annex L to Appendix A h. Virtual co
- Page 207 and 208:
Annex L to Appendix A NON-DEPARTMEN
- Page 209 and 210:
Annex L to Appendix A (17) Power. (
- Page 211 and 212:
Annex M to Appendix A 17. Identify
- Page 213 and 214:
Appendix B Core Tasks for Joint Tas
- Page 215 and 216:
Appendix B d. Manning. In conjuncti
- Page 217 and 218:
Appendix B Management; CJCSI 3265.0
- Page 219 and 220:
Appendix C Intentionally Blank C-2
- Page 221 and 222:
Annex A to Appendix C cross-functio
- Page 223 and 224:
Annex A to Appendix C b. The MOC di
- Page 225 and 226:
Annex B to Appendix C (7) Ensure al
- Page 227 and 228:
Annex B to Appendix C (10) Identify
- Page 229 and 230:
Annex C to Appendix C articles. The
- Page 231 and 232:
Annex C to Appendix C Intentionally
- Page 233 and 234:
Annex D to Appendix C Intentionally
- Page 235 and 236:
Annex E to Appendix C (2) Resources
- Page 237 and 238:
Annex E to Appendix C reconstitutio
- Page 239 and 240:
Annex F to Appendix C Intentionally
- Page 241 and 242:
Annex G to Appendix C Intentionally
- Page 243 and 244:
Annex H to Appendix C c. Headquarte
- Page 245 and 246:
Annex J to Appendix C d. All other
- Page 247 and 248:
Annex K to Appendix C d. Notify CCM
- Page 249 and 250:
Appendix D 2. Information Managemen
- Page 251 and 252:
Appendix D location. (g) Limiting a
- Page 253 and 254:
Appendix D (2) The JIMB: (a) Identi
- Page 255 and 256:
Appendix D (2) Takes guidance publi
- Page 257 and 258:
Appendix D IMO must focus on the in
- Page 259 and 260:
Appendix D establishes a security C
- Page 261 and 262:
Appendix D (2) Support the JTF plan
- Page 263 and 264:
Appendix D Intentionally Blank D-16
- Page 265 and 266:
Appendix E the affected state under
- Page 267 and 268:
Appendix E (2) A dual-status comman
- Page 269 and 270:
Appendix E JTF-State operates in cl
- Page 271 and 272:
Appendix F d. CJCSI 3110.10D, Comma
- Page 273 and 274:
Appendix F bb. JP 3-63, Detainee Op
- Page 275 and 276:
Appendix G 6. Distribution of Elect
- Page 277 and 278:
Glossary DCMA DCO DFE DIA DII DIRMO
- Page 279 and 280:
Glossary JIMB JIOC JIOWC JIPOE JISE
- Page 281 and 282:
Glossary RUF S&TI SATCOM SCA SecDef
- Page 283 and 284:
Glossary nonrepudiation, which incl
- Page 285 and 286:
Glossary Intentionally Blank GL-10