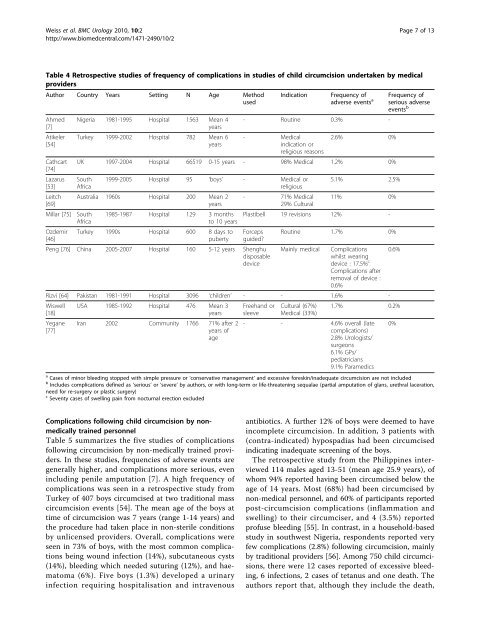
Weiss et al. BMC Urology 2010, 10:2http://www.bi<strong>om</strong>edcentral.c<strong>om</strong>/1471-2490/10/2Page 7 of 13Table 4 Retrospective studies of frequency of c<strong>om</strong>plications in studies of child circumcision undertaken by medicalprovidersAuthor Country Years Setting N Age MethodusedAhmed[7]Atikeler[54]Cathcart[74]Lazarus[53]Leitch[69]Millar [75]Ozdemir[46]Nigeria 1981-1995 Hospital 1563 Mean 4yearsTurkey 1999-2002 Hospital 782 Mean 6yearsIndicationFrequency ofadverse events a- Routine 0.3% -- Medicalindication orreligious reasons2.6% 0%UK 1997-2004 Hospital 66519 0-15 years - 98% Medical 1.2% 0%SouthAfrica1999-2005 Hospital 95 ‘boys’ - Medical orreligiousAustralia 1960s Hospital 200 Mean 2yearsSouthAfrica1985-1987 Hospital 129 3 monthsto 10 yearsTurkey 1990s Hospital 600 8 days topuberty- 71% Medical29% Cultural5.1% 2.5%11% 0%Plastibell 19 revisions 12% -Forcepsguided?Peng [76] China 2005-2007 Hospital 160 5-12 years ShenghudisposabledeviceRoutine 1.7% 0%Mainly medicalC<strong>om</strong>plicationswhilst wearingdevice : 17.5% cC<strong>om</strong>plications <strong>af</strong>terremoval of device :0.6%Rizvi [64] Pakistan 1981-1991 Hospital 3096 ‘children’ - - 1.6% -Wiswell[18]Yegane[77]USA 1985-1992 Hospital 476 Mean 3yearsIran 2002 C<strong>om</strong>munity 1766 71% <strong>af</strong>ter 2years ofageFreehand orsleeveCultural (67%)Medical (33%)Frequency ofserious adverseevents b0.6%1.7% 0.2%- - 4.6% overall (latec<strong>om</strong>plications)2.8% Urologists/surgeons6.1% GPs/pediatricians9.1% Paramedicsa Cases of minor bleeding stopped with simple pressure or ‘conservative management’ and excessive foreskin/inadequate circumcision are not includedb Includes c<strong>om</strong>plications defined as ‘serious’ or ‘severe’ by authors, or with long-term or life-threatening sequalae (partial amputation of glans, urethral laceration,need for re-surgery or plastic surgery)c Seventy cases of swelling pain fr<strong>om</strong> nocturnal erection excluded0%C<strong>om</strong>plications following child circumcision by nonmedicallytrained personnelTable 5 summarizes the five studies of c<strong>om</strong>plicationsfollowing circumcision by non-medically trained providers.In these studies, frequencies of adverse events aregenerally higher, and c<strong>om</strong>plications more serious, evenincluding penile amputation [7]. A high frequency ofc<strong>om</strong>plications was seen in a retrospective study fr<strong>om</strong>Turkey of 407 boys circumcised at two traditional masscircumcision events [54]. The mean age of the boys attime of circumcision was 7 years (range 1-14 years) andthe procedure had taken place in non-sterile conditionsby unlicensed providers. Overall, c<strong>om</strong>plications wereseen in 73% of boys, with the most c<strong>om</strong>mon c<strong>om</strong>plicationsbeing wound infection (14%), subcutaneous cysts(14%), bleeding which needed suturing (12%), and haemat<strong>om</strong>a(6%). Five boys (1.3%) developed a urinaryinfection requiring hospitalisation and intravenousantibiotics. A further 12% of boys were deemed to haveinc<strong>om</strong>plete circumcision. In addition, 3 patients with(contra-indicated) hypospadias had been circumcisedindicating inadequate screening of the boys.The retrospective study fr<strong>om</strong> the Philippines interviewed114 males aged 13-51 (mean age 25.9 years), ofwh<strong>om</strong> 94% reported having been circumcised below theage of 14 years. Most (68%) had been circumcised bynon-medical personnel, and 60% of participants reportedpost-circumcision c<strong>om</strong>plications (inflammation andswelling) to their circumciser, and 4 (3.5%) reportedprofuse bleeding [55]. In contrast, in a household-basedstudy in southwest Nigeria, respondents reported veryfew c<strong>om</strong>plications (2.8%) following circumcision, mainlyby traditional providers [56]. Among 750 child circumcisions,there were 12 cases reported of excessive bleeding,6 infections, 2 cases of tetanus and one death. Theauthors report that, although they include the death,
Weiss et al. BMC Urology 2010, 10:2http://www.bi<strong>om</strong>edcentral.c<strong>om</strong>/1471-2490/10/2Page 8 of 13Table 5 Retrospective studies of frequency of c<strong>om</strong>plications in studies of child circumcision undertaken by nonmedicalprovidersAuthor Country Years Setting Number ofmalesAhmed [7] Nigeria 1981-1995 C<strong>om</strong>munity 1360(approx)Age atcircumcisionProviderFrequency ofadverse events aMean 4 years Traditional 3.4% -Atikeler [54] Turkey 1999-2002 C<strong>om</strong>munity 407 Mean 7 years Traditional 73% cLee [55] Phillipines 2002 C<strong>om</strong>munity 114 42% 5-9 years52% 10-14years5% 15-18 years32% medical68%traditionalMyers [56] Nigeria - C<strong>om</strong>munity 750 Infant/child 68%traditional25% nurse/midwife4% doctorYegane [77] Iran 2002 C<strong>om</strong>munity 1359 71% <strong>af</strong>ter 2years of ageTraditionalcircumcisers63% d 3.5%2.8% -2.7%% (latec<strong>om</strong>plications)Frequency of seriousadverse events ba Cases of minor bleeding stopped with simple pressure or ‘conservative management’ and excessive foreskin/inadequate circumcision are not includedb Includes c<strong>om</strong>plications defined as ‘serious’ or ‘severe’ by authors, or with long-term or life-threatening sequalae (partial amputation of glans, urethral laceration,need for re-surgery or plastic surgery)c This very high rate of c<strong>om</strong>plications consisted of bleeding (24%), infection (14%), inc<strong>om</strong>plete circumcision (12%), subcutaneous cysts (15%), haemat<strong>om</strong>a (6%),ischaemia (3%), penile adhesion (3%), and other conditions. Of the 97 cases of bleeding, 48 could not be stopped by haemostatic bandage and were sutured.Infections were treated with parenteral or oral antibiotics.d Of these,94% were reported swollen or inflamed penises. Four respondents (3.5%) of those circumcised) reported profuse bleeding0%there was insufficient information to be certain it wascaused by circumcision. A study fr<strong>om</strong> Iran reported alate-phase c<strong>om</strong>plication frequency of 2.7% following traditionalcircumcision and a further 5% had excessiveresidual foreskin. This was similar to circumcisions performedby urologists or surgeons (2.8%), but lower thanfor GPs/paediatricians (6.1%) or paramedical personnel(9.1%). The authors argue that this is because traditionalcircumcisers in Iran are experienced and paramedicalpersonnel do not receive effective training.DiscussionMale circumcision is a c<strong>om</strong>mon surgical procedure, butfew epidemiological studies have reported frequency ofadverse events, most c<strong>om</strong>monly bleeding and infection.Our review shows that serious adverse events are rare,but there is wide variation in reported frequencies ofadverse events following circumcision. This is likely tobe due to several factors directly associated with c<strong>om</strong>plicationssuch as age at circumcision, training and expertiseof the provider, the sterility of the conditions underwhich the procedure is undertaken and the indication(medical/cultural) for circumcision. In addition, there isvariation due to methodological issues such as durationof follow-up, epidemiological study design, and definitionof c<strong>om</strong>plications.In general, c<strong>om</strong>plications (reported by parents) occurleast frequently among neonates and infants than amongolder boys, with the majority of prospective studies in neonatesand infants finding no serious c<strong>om</strong>plications, andrelatively few other adverse events, which were minor andtreatable. The prospective studies in older boys also foundvirtually no serious adverse events, but a higher frequencyof c<strong>om</strong>plications (up to 14%) even when conducted bytrained providers in sterile settings [47]. The lower frequencyof c<strong>om</strong>plications among neonates and infants islikely to be attributable to the simpler nature of the procedurein this age group, and the healing capability in thenewborn. Further, a major advantage of neonatal circumcisionis that suturing is not usually necessary, whereas itis c<strong>om</strong>monly needed for circumcisions in the post-neonatalperiod. This advantage is illustrated by the US study inwhich no c<strong>om</strong>plications were seen among 98 boys circumcisedin the first month of life, but 30% of boys aged 3-8.5months had significant postoperative bleeding [24]. Thereare alternatives to suturing, either with the disposableclamps, or with alternatives such as cynoacrylate glue [44]and further research in this area is needed.Several studies stress the importance of careful trainingand experience of the provider, and the sterility of the setting.This was most clearly noted in a Nigerian study [27]in which 24% of boys had reported c<strong>om</strong>plications (includingretention of excess residual foreskin), but only 1.6% ofthose circumcised at the public (University Teaching) hospitalby medical doctors. Similarly, two case-control studiesfr<strong>om</strong> Israel have found that UTI are 3-4 times morelikely to occur following circumcised by a traditional,rather than medical provider [57,58]. However, as noted inour review, neonatal circumcision following traditional circumcisionin Israel has low c<strong>om</strong>plication rates overall [9].A further example is the study fr<strong>om</strong> the C<strong>om</strong>oros Islandswhich reported results of an exercise in which specific
- Page 1 and 2:
OMSKÆRINGAF DRENGENotat2013
- Page 3 and 4:
Indhold1 Sundhedsstyrelsens sammenf
- Page 5 and 6:
1 Sundhedsstyrelsens sammenfatningO
- Page 7 and 8:
døgn under indlæggelse på sygehu
- Page 9 and 10:
arnet ligger på en pude på et bor
- Page 11 and 12:
se områder i Afrika. WHO understre
- Page 13 and 14:
3 Omskæring i DanmarkFor en del å
- Page 15 and 16:
Hvis en person, der hverken er læg
- Page 17 and 18:
4 Omskæring i andre landEfter Sund
- Page 19 and 20:
sundhedsmæssige fordele ikke er tu
- Page 21:
6 Bilagsfortegnelse:Bilag 1:Sundhed
- Page 24 and 25:
WHITEPAPER- OM RITUEL OMSKÆRELSE A
- Page 26 and 27:
OM RITUEL JØDISK OMSKÆRELSE AF DR
- Page 29 and 30:
White Paper om religiøs omskærels
- Page 31 and 32:
har været oppe med jævne mellemru
- Page 33 and 34:
To tredjedel færre infektioner på
- Page 35 and 36:
Der er en betydelig risiko for, at
- Page 37 and 38:
2.3 Beskrivelse af afrapporteringen
- Page 39 and 40:
3.5 Betydningen for den jødiske fa
- Page 41 and 42:
af medicinske årsager, hvoraf alvo
- Page 43 and 44:
lodtrækning fik foretaget omskære
- Page 45 and 46: Endvidere skal lægen i fornødent
- Page 47 and 48: Stritøreoperationer udføres både
- Page 49 and 50: Den foreliggende medicinske forskni
- Page 51 and 52: TECHNICAL REPORTMale Circumcisionab
- Page 53 and 54: principle on which each of thesedev
- Page 55 and 56: FIGURE 2Prevalence of male circumci
- Page 57 and 58: TABLE 2 Results from Medline, Cochr
- Page 59 and 60: Male Circumcision and Diseases,Morb
- Page 61 and 62: een diagnosed with genital herpes a
- Page 63 and 64: Results data indicate that the inci
- Page 65 and 66: participants’ ages and any coexis
- Page 67 and 68: without general anesthesia in boys
- Page 69 and 70: was reported in 2.2% of cases andin
- Page 71 and 72: nurse practitioners) should workcol
- Page 73 and 74: circumcision practices in theUnited
- Page 75 and 76: at: www.cdc.gov/hiv/resources/facts
- Page 77 and 78: childhood: a meta-analysis. Pediatr
- Page 79 and 80: multicenter survey. Isr Med Assoc J
- Page 81 and 82: Male CircumcisionTASK FORCE ON CIRC
- Page 83 and 84: The online version of this article,
- Page 85 and 86: COMMENTARYIn this commentary, a dif
- Page 87 and 88: COMMENTARYThe cardinal medical ques
- Page 89 and 90: Cultural Bias in the AAP's 2012 Tec
- Page 91 and 92: Weiss et al. BMC Urology 2010, 10:2
- Page 93 and 94: Weiss et al. BMC Urology 2010, 10:2
- Page 95: Weiss et al. BMC Urology 2010, 10:2
- Page 99 and 100: Weiss et al. BMC Urology 2010, 10:2
- Page 101 and 102: Weiss et al. BMC Urology 2010, 10:2
- Page 103 and 104: 2013-06-21 Dnr x.x-xxxxx/xxxx 1(4)T
- Page 105 and 106: SOCIALSTYRELSEN 2013-06-21 Dnr 3(4)