- Page 4 and 5:
Fullerton, Californiawww.lightandma
- Page 7 and 8:
Contents0 Introduction and Review0.
- Page 9 and 10:
5.5 More About Heat Engines . . . .
- Page 11 and 12:
669.11.3 Magnetic Fields by Ampère
- Page 13 and 14:
The Mars Climate Orbiter is prepare
- Page 15:
temperatures and with many combinat
- Page 19 and 20:
idence that quarks have smaller par
- Page 21 and 22:
give clearer explanations.Finally,
- Page 23 and 24:
It can also be handy to have a rela
- Page 25 and 26:
The prefix centi-, meaning 10 −2
- Page 27 and 28:
goes like this:V = 1 3 Ah[1]A = πr
- Page 29 and 30:
the notation 10 0 to stand for one,
- Page 32 and 33:
calculation, 5.04 cm, was really no
- Page 34 and 35:
0.2 Scaling and Order-of-Magnitude
- Page 36 and 37:
to many times your own height. The
- Page 38 and 39:
g / 1. This plank is as long as it
- Page 40 and 41:
the front panels of the three violi
- Page 42 and 43:
Correct solution #4: The area of a
- Page 44 and 45:
here?” The scientific Mr. Spock w
- Page 46 and 47:
1. Don’t even attempt more than o
- Page 48 and 49:
Problem 10.mean, however, is define
- Page 50 and 51:
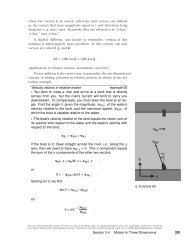
(d) Find the person’s acceleratio
- Page 52 and 53:
Albert Einstein, and his moustache,
- Page 54 and 55:
54 Chapter 0 Introduction and Revie
- Page 56 and 57:
a / Portrait of Monsieur Lavoisiera
- Page 58 and 59:
1.1.1 Problem-solving techniquesHow
- Page 60 and 61:
∆m = 0, where m is the total mass
- Page 62 and 63:
different substances will have diff
- Page 64 and 65:
c / Left: In a frame of referenceth
- Page 66 and 67:
f / Discussion question B.(discusse
- Page 68 and 69:
Self-check D.since the derivative o
- Page 70 and 71:
ProblemsThe symbols √ , , etc. ar
- Page 72 and 73:
difficult? ⊲ Solution, p. 932Key
- Page 74 and 75:
Heat energy can be convertedto ligh
- Page 76 and 77:
a new form of invisible “mystery
- Page 78 and 79:
f / A realistic drawing of Joule’
- Page 80 and 81:
numbers. With a purely numerical ap
- Page 82 and 83:
of gravity doesn’t change much if
- Page 84 and 85:
field. If the plane can start from
- Page 86 and 87:
m / Discussion question C.n / A hyd
- Page 88 and 89:
88 Chapter 2 Conservation of Energy
- Page 90 and 91:
A car drives over a cliff.new frame
- Page 92 and 93:
How long does it take to move 1 met
- Page 94 and 95:
a / Approximations to thebrachistoc
- Page 96 and 97:
a / An ellipse is circle that hasbe
- Page 98 and 99:
to deduce the general equation for
- Page 100 and 101:
to the mass of the object that inte
- Page 102 and 103:
The minimum velocity required for t
- Page 104 and 105:
and since sin θ dθ occurs in the
- Page 106 and 107:
that is deeper than r. Under the as
- Page 108 and 109:
2.3.6 ⋆ Evidence for repulsive gr
- Page 110 and 111:
a / A vivid demonstration thatheat
- Page 112 and 113:
ture. This is a very good question,
- Page 114 and 115:
Three functions with thesame curvat
- Page 116 and 117:
This looks like a cosine function,
- Page 118 and 119:
ProblemsThe symbols √ , , etc. ar
- Page 120 and 121:
Problem 16.13 Anya and Ivan lean ov
- Page 122 and 123:
Problem 27.then we’d have U/m =
- Page 124 and 125:
37 Two springs with spring constant
- Page 126 and 127:
ExercisesExercise 2A: Reasoning wit
- Page 128 and 129:
128 Chapter 2 Conservation of Energ
- Page 130 and 131:
3.1 Momentum In One Dimensiona / Sy
- Page 132 and 133:
eing to the right. The initial mome
- Page 134 and 135:
3.1.3 Momentum compared to kinetic
- Page 136 and 137:
3.1.4 Collisions in one dimensiong
- Page 138 and 139:
could never do that again in a mill
- Page 140 and 141:
i / The highjumper’s body passeso
- Page 142 and 143:
where x 1 is the mass of the first
- Page 144 and 145:
3.1.6 The center of mass frame of r
- Page 146 and 147:
The airbag increases ∆tso as to r
- Page 148 and 149:
d / Two magnets exert forceson each
- Page 150 and 151:
x (m) t (s)10 1.8420 2.8630 3.8040
- Page 152 and 153:
3.2.4 Forces between solidsConserva
- Page 154 and 155:
Maximum acceleration of a car examp
- Page 156 and 157:
Discussion QuestionA Criticize the
- Page 158 and 159:
C A pool ball is rebounding from th
- Page 160 and 161:
forces, as if the hand were a pair
- Page 162 and 163:
This may not sound like an impressi
- Page 164 and 165:
stroke are both executed in straigh
- Page 166 and 167:
Accelerating a cart example 35If yo
- Page 168 and 169:
w / A wedge.x / Archimedes’ screw
- Page 170 and 171:
As in the preceding example, we hav
- Page 172 and 173:
that have the same frequency is a s
- Page 174 and 175:
around until I got this result, sin
- Page 176 and 177:
quality factor, Q, is defined as Q
- Page 178 and 179:
ight direction to add energy to the
- Page 180 and 181:
i / Example 45: a viola withouta mu
- Page 182 and 183:
Collapse of the Nimitz Freeway exam
- Page 184 and 185:
end up canceling out, however:Q =
- Page 186 and 187:
186 Chapter 3 Conservation of Momen
- Page 188 and 189:
c / Bullets are dropped and shot at
- Page 190 and 191:
the asteroid’s energy and boostin
- Page 192 and 193:
coordinate axes. Even though ∆x,
- Page 194 and 195:
of the three components,∆p x = 0
- Page 196 and 197:
A useless vector operation example
- Page 198 and 199:
Solving for the unknowns gives∆x
- Page 200 and 201:
o / Example 64.p / Adding vectors g
- Page 202 and 203:
How to generalize one-dimensional e
- Page 204 and 205:
needed to support the object in fig
- Page 206 and 207:
The easiest method is the one demon
- Page 208 and 209:
Incorrect solution #4:(same notatio
- Page 210 and 211:
The magnitude of the acceleration i
- Page 212 and 213:
dropped out like a trap door, showi
- Page 214 and 215:
af / Breaking trail, by WalterE. Bo
- Page 216 and 217:
know how to integrate with respect
- Page 218 and 219:
ProblemsThe symbols √ , , etc. ar
- Page 220 and 221:
Problem 16.Problem 19.resistance.)1
- Page 222 and 223:
of gravity on Mars.(a) Find the tim
- Page 224 and 225:
partner force. (a) A swimmer speeds
- Page 226 and 227:
Problem 45the 0.4-gram masses would
- Page 228 and 229:
53 If you walk 35 km at an angle 25
- Page 230 and 231:
(b) Interpret this equation in the
- Page 232 and 233:
Problem 71.232 Chapter 3 Conservati
- Page 234 and 235:
77 A car accelerates from rest. At
- Page 236 and 237:
Problem 81.81 Complete example 71 o
- Page 238 and 239:
ExercisesExercise 3A: Force and Mot
- Page 240 and 241:
Exercise 3C: Worksheet on Resonance
- Page 242 and 243:
Exercise 3D: Vectors and MotionEach
- Page 244 and 245:
244 Chapter 3 Conservation of Momen
- Page 246 and 247:
An overhead view of apiece of putty
- Page 248 and 249:
inward toward the hinge will have n
- Page 250 and 251:
special case, we can choose to visu
- Page 252 and 253:
j / Two asteroids collide.k / Every
- Page 254 and 255:
Note that although the factors of 2
- Page 256 and 257:
Relationship between force and torq
- Page 258 and 259:
is straight down, which is perpendi
- Page 260 and 261:
⊲ All three objects in the figure
- Page 262 and 263:
aa / Example 10.to either side of e
- Page 264 and 265:
momentum tells us that L = mrv sin
- Page 266 and 267:
In the absence of any torque, a rig
- Page 268 and 269:
Radial acceleration at the surface
- Page 270 and 271:
The parallel axis theorem example 1
- Page 272 and 273:
differential. The result isarea ===
- Page 274 and 275:
of inertia as if the object was smo
- Page 276 and 277:
h / Moments of inertia of somegeome
- Page 278 and 279:
4.3 Angular Momentum In Three Dimen
- Page 280 and 281:
14 deg, and it points along an axis
- Page 282 and 283:
manner like this, then the definiti
- Page 284 and 285:
k / Example 27.torque to the left w
- Page 286 and 287:
We can also generalize the plane-ro
- Page 288 and 289:
Problem 1.Problem 6.Problem 8.Probl
- Page 290 and 291:
14 (a) The bar of mass m is attache
- Page 292 and 293:
Problem 22.22 The sun turns on its
- Page 294 and 295:
35 The nucleus 168 Er (erbium-168)
- Page 296 and 297:
ExercisesExercise 4A: TorqueEquipme
- Page 298 and 299:
pesky set of constraints on heat en
- Page 300 and 301:
mit more air into the cavity behind
- Page 302 and 303:
Pressure of lava underneath a volca
- Page 304 and 305:
h / A simplified version of anideal
- Page 306 and 307:
for us to construct a simple connec
- Page 308 and 309:
For the first time we have an inter
- Page 310 and 311:
a / 1. The temperature differencebe
- Page 312 and 313:
Carnot engines operating between a
- Page 314 and 315:
from A to B, he lets it by, but whe
- Page 316 and 317:
B When we run the Carnot engine in
- Page 318 and 319:
f / A phase space for a singleatom
- Page 320 and 321:
time, the energy sharing is very un
- Page 322 and 323:
will the the one that maximizes the
- Page 324 and 325:
If the gas is monoatomic, then we k
- Page 326 and 327:
5.4.4 The arrow of time, or “this
- Page 328 and 329:
5.4.6 Summary of the laws of thermo
- Page 330 and 331:
may be in the form of microscopic d
- Page 332 and 333:
significant amount of heat to flow
- Page 334 and 335:
while the smaller area under the bo
- Page 336 and 337:
7 (a) Determine the ratio between t
- Page 338 and 339:
338 Chapter 5 Thermodynamics
- Page 340 and 341:
end of this book, we’ll even see
- Page 342 and 343:
c / As the wave pattern passes the
- Page 344 and 345:
the wave move ahead faster and get
- Page 346 and 347:
k / Hitting a key on a pianocauses
- Page 348 and 349:
Our final result for the speed of t
- Page 350 and 351:
care, because the delay is the same
- Page 352 and 353:
An easy way to visualize this is in
- Page 354 and 355:
can be constructed as a superpositi
- Page 356 and 357:
⊲ Looking up the speed of light i
- Page 358 and 359:
scientists, to speak of the Big Ban
- Page 360 and 361:
6.2 Bounded WavesSpeech is what sep
- Page 362 and 363:
d / An uninverted reflection. There
- Page 364 and 365:
our intuitive expectation of strong
- Page 366 and 367:
valid solutions. In the following s
- Page 368 and 369:
j / In the mirror image, theareas o
- Page 370 and 371:
m / A pulse bounces backand forth.i
- Page 372 and 373:
q / Graphs of loudness versusfreque
- Page 374 and 375:
s / Standing waves on a rope. (PSSC
- Page 376 and 377:
“cavity” and “neck” parts o
- Page 378 and 379:
Problem 5.Problem 8.5 The figure sh
- Page 380 and 381:
Problem 16.16 A Fabry-Perot interfe
- Page 382 and 383:
c / Newton’s laws do not distingu
- Page 384 and 385:
f / The correspondence principlereq
- Page 386 and 387:
d / A Galilean version of therelati
- Page 388 and 389:
g / Three types of transformations
- Page 390 and 391:
system, velocities are always unitl
- Page 392 and 393:
p / Apparatus used for the testof r
- Page 394 and 395:
sumption, the assumption that it ma
- Page 396 and 397:
at rest relative to the water. But
- Page 398 and 399:
7.2.4 No action at a distanceThe Ne
- Page 400 and 401:
so that Alice can complete her moti
- Page 402 and 403:
time into different regions accordi
- Page 404 and 405:
position relative to the sun at exa
- Page 406 and 407:
7.2.7 ⋆ Four-vectors and the inne
- Page 408 and 409:
would depend on the relative veloci
- Page 410 and 411:
7.3 DynamicsSo far we have said not
- Page 412 and 413:
In this frame, as expected, the sma
- Page 414 and 415:
But this whole argument was based o
- Page 416 and 417:
meters per second, so converting to
- Page 418 and 419:
Expressing γ as ( 1 − v 2 /c 2)
- Page 420 and 421:
7.3.4 ⋆ ProofsThis optional secti
- Page 422 and 423:
these lines. For example, a car sit
- Page 424 and 425:
An Einstein’s ring. Thedistant ob
- Page 426 and 427:
two-dimensional universe as if it w
- Page 428 and 429:
h / 1. A ray of light is emittedupw
- Page 430 and 431:
object that that isn’t influenced
- Page 432 and 433:
it impossible for any observer to b
- Page 434 and 435:
a variant on the Penrose singularit
- Page 436 and 437:
in it. Instead, it is currently spe
- Page 438 and 439:
2 Astronauts in three different spa
- Page 440 and 441:
(d) Simplify your answer to part c
- Page 442 and 443:
Problem 25b. Redrawn fromVan Baak,
- Page 444 and 445:
ExercisesExercise 7A: The Michelson
- Page 446 and 447:
Exercise 7B: Sports in Slowlightlan
- Page 448 and 449:
448 Chapter 7 Relativity
- Page 450 and 451:
Exercise 7D: Misconceptions about R
- Page 452 and 453:
452 Chapter 7 Relativity
- Page 454 and 455:
sun, moon, stars, and planets were
- Page 456 and 457:
Two types of chargeWe can easily co
- Page 458 and 459:
the other acquires an equal amount
- Page 460 and 461:
to get the beam up to speed in the
- Page 462 and 463:
telling us that we know about matte
- Page 464 and 465:
the muddle. The row-and-column sche
- Page 466 and 467:
the force of air friction canceled
- Page 468 and 469:
ectly evaluate the implications of
- Page 470 and 471:
that they were indeed electrically
- Page 472 and 473:
C Thomson found that the m/q of an
- Page 474 and 475:
the object with a net positive char
- Page 476 and 477:
thickness of material the radioacti
- Page 478 and 479:
It was already known that although
- Page 480 and 481:
particle. It turned out that it was
- Page 482 and 483:
For example they could easily strip
- Page 484 and 485:
cording to Mosely, the atomic numbe
- Page 486 and 487:
that fly off to see what was inside
- Page 488 and 489:
solution was found by measuring the
- Page 490 and 491:
o / A nuclear power plant at Catten
- Page 492 and 493:
neutrons. In a nuclear fission bomb
- Page 494 and 495:
We can now list all four of the kno
- Page 496 and 497:
1. Our sun’s source of energy is
- Page 498 and 499:
a / The known nuclei, represented o
- Page 500 and 501:
killed, because the DNA becomes una
- Page 502 and 503:
e / Wild Przewalski’s horsesprosp
- Page 504 and 505:
Problem 1. Top: A realisticpicture
- Page 506 and 507:
12 The subatomic particles called m
- Page 508 and 509:
ExercisesExercise 8A: Nuclear decay
- Page 510 and 511:
saxophone, every technological tool
- Page 512 and 513:
Example 1Ions moving across a cell
- Page 514 and 515:
ut the original meaning was to trav
- Page 516 and 517:
Force depends only on position. Sin
- Page 518 and 519:
Here are a few questions and answer
- Page 520 and 521:
flow through it.For many substances
- Page 522 and 523:
superconductivity in metals that wo
- Page 524 and 525:
j / Example 9. In 1 and 2,charges t
- Page 526 and 527:
look like the usual resistor. The f
- Page 528 and 529:
9.1.5 Current-conducting properties
- Page 530 and 531:
attery acid becomes depleted of hyd
- Page 532 and 533:
9.2 Parallel and Series CircuitsIn
- Page 534 and 535:
to each resistance, resulting inI t
- Page 536 and 537:
where “...” means that the sum
- Page 538 and 539:
the two resistors in figure h/3.We
- Page 540 and 541:
Choice of high voltage for power li
- Page 542 and 543:
A complicated circuit example 20⊲
- Page 544 and 545:
Problem 2.ProblemsThe symbols √ ,
- Page 546 and 547:
Problem 16.only count that as one u
- Page 548 and 549:
knob turned all the way clockwise,
- Page 550 and 551:
A printed circuit board, likethe ki
- Page 552 and 553:
ExercisesExercise 9A: Voltage and C
- Page 554 and 555:
Exercise 9C: Reasoning About Circui
- Page 556 and 557:
556 Chapter 9 Circuits
- Page 558 and 559:
a / A bar magnet’s atoms are(part
- Page 560 and 561:
defined. The ship’s captain can m
- Page 562 and 563:
Reduction in gravity on Io due to J
- Page 564 and 565:
j / Example 3.self-check AFind an e
- Page 566 and 567:
a dipole moment — they are define
- Page 568 and 569:
10.2.1 One dimensionVoltage is elec
- Page 570 and 571:
The interpretation is that if you b
- Page 572 and 573:
Figure c shows some examples of way
- Page 574 and 575:
For large values of d, this express
- Page 576 and 577:
where Q is the total charge of the
- Page 578 and 579:
g / Example 12: variation of the fi
- Page 580 and 581:
corners to the disk and transform i
- Page 582 and 583:
10.4 Energy In Fieldsa / Two opposi
- Page 584 and 585:
self-check DWe can think of the qua
- Page 586 and 587:
of the inward field contributed by
- Page 588 and 589:
space, 2 while charge doesn’t, we
- Page 590 and 591:
a / The symbol for a capacitor.b /
- Page 592 and 593:
ounding each capacitor will be half
- Page 594 and 595:
in time:x ↔ qv ↔ Iself-check GH
- Page 596 and 597:
due to its own momentum. It perform
- Page 598 and 599:
or|V | =∣ LdIdt ∣ ,which in man
- Page 600 and 601:
the inductor resists such a sudden
- Page 602 and 603:
Example 26.Death by solenoid; spark
- Page 604 and 605:
ordering.( 1 √2+√ i ) 2 = √ 1
- Page 606 and 607:
x / The complex number e iφlies on
- Page 608 and 609:
Figure aa shows a useful way to vis
- Page 610 and 611:
Inductors tend to be big, heavy, ex
- Page 612 and 613:
The reason for using the trig ident
- Page 614 and 615:
a purely inductive or capacitive lo
- Page 616 and 617:
Resonance with damping example 33
- Page 618 and 619:
orE outward, on side 1 A + E outwar
- Page 620 and 621:
|E| = kq totalr 2 ,where r is the r
- Page 622 and 623:
y considering its point charges ind
- Page 624 and 625:
Discussion Questionsg / Discussion
- Page 626 and 627:
with charge, change the Coulomb con
- Page 628 and 629:
The symmetry between the two sides
- Page 630 and 631:
where dv is the volume of the cube.
- Page 632 and 633:
The three terms in the divergence a
- Page 634 and 635:
ProblemsThe symbols √ , , etc. ar
- Page 636 and 637:
Problem 19.Problem 20.proton, for e
- Page 638 and 639:
the lightning strike.(b) Based on y
- Page 640 and 641:
units.(b) Verify that RC has units
- Page 642 and 643:
lating freely (without any driving
- Page 644 and 645:
ExercisesExercise 10A: Field Vector
- Page 646 and 647:
5. Now hook up the two solenoids in
- Page 648 and 649:
A large current is createdby shorti
- Page 650 and 651:
time I used it implicitly was in fi
- Page 652 and 653:
f / A standard dipole madefrom a sq
- Page 654 and 655:
and substituting q = λh and v = m/
- Page 656 and 657:
o / Magnetic forces cause abeam of
- Page 658 and 659:
electric field, a magnetic one, can
- Page 660 and 661:
u / In this scene from SwanLake, th
- Page 662 and 663:
so the total field in the z directi
- Page 664 and 665:
For the y component, we havee / A s
- Page 666 and 667:
We can pin down the result even mor
- Page 668 and 669:
i / The field of a dipole.where r i
- Page 670 and 671:
circulates around the y axis, so at
- Page 672 and 673:
to be, not where it is now. Coulomb
- Page 674 and 675:
We have found one specific example
- Page 676 and 677:
to a flagpole, we can cancel out a
- Page 678 and 679:
11.4 Ampère’s Law In Differentia
- Page 680 and 681:
y evaluating the field at the midpo
- Page 682 and 683:
i.e.,F = axˆx + byˆx + cˆx + dx
- Page 684 and 685:
k / A summary of the derivative, gr
- Page 686 and 687:
c / Detail from Ascending andDescen
- Page 688 and 689:
the magnet. Are these atomic curren
- Page 690 and 691:
field in her region of space has be
- Page 692 and 693:
A changing magnetic flux makes a cu
- Page 694 and 695:
nearly zero. By Faraday’s law, th
- Page 696 and 697:
c / An Ampèrian surface superimpos
- Page 698 and 699:
and Maxwell’s equations becomeΦ
- Page 700 and 701:
k / Red and blue light travelat the
- Page 702 and 703:
second, the zero-point is located a
- Page 704 and 705:
is the magnitude of the momentum ve
- Page 706 and 707:
Discussion question A.Discussion qu
- Page 708 and 709:
only penetrates to a very small dep
- Page 710 and 711:
elationship D = ɛE would actually
- Page 712 and 713:
esulting in cancellation.The opposi
- Page 714 and 715:
a low permeability, while the other
- Page 716 and 717:
n / A fluxgate compass.is externall
- Page 718 and 719:
6 Two parallel wires of length L ca
- Page 720 and 721:
an instant at the upper right, but
- Page 722 and 723:
Problem 25.20 Four long wires are a
- Page 724 and 725:
Problem 35.Problem 37.32 Verify Amp
- Page 726 and 727:
Problem 42.beam of light usually co
- Page 728 and 729:
(c) Discuss the relationship betwee
- Page 730 and 731:
(f) Use conservation of energy to r
- Page 732 and 733:
5. Now position yourself with your
- Page 734 and 735:
12.1.1 The nature of lightThe cause
- Page 736 and 737:
An image of Jupiter andits moon Io
- Page 738 and 739:
d / Two self-portraits of theauthor
- Page 740 and 741:
ultimate truth about light, but the
- Page 742 and 743:
• There is a tendency to conceptu
- Page 744 and 745:
self-check AEach of these diagrams
- Page 746 and 747:
m / Discussion question B.Discussio
- Page 748 and 749:
12.2 Images by ReflectionInfants ar
- Page 750 and 751:
Discussion QuestionA The figure sho
- Page 752 and 753:
down magnification is AB/DE. A repe
- Page 754 and 755:
i / A Newtonian telescopebeing used
- Page 756 and 757:
B Locate the images formed by two p
- Page 758 and 759:
12.3 Images, QuantitativelyIt sound
- Page 760 and 761:
⊲ The object and image angles are
- Page 762 and 763:
12.3.2 Other cases with curved mirr
- Page 764 and 765:
signs also have to be memorized for
- Page 766 and 767: h / A diverging mirror in the shape
- Page 768 and 769: j / Spherical mirrors are thecheape
- Page 770 and 771: general type of eye that we share w
- Page 772 and 773: shown on this graph and then attemp
- Page 774 and 775: the mechanical model would predict
- Page 776 and 777: that your calculator will flash an
- Page 778 and 779: D Classify the examples shown in fi
- Page 780 and 781: 12.4.6 ⋆ Microscopic description
- Page 782 and 783: 12.5 Wave OpticsElectron microscope
- Page 784 and 785: of a crystal? Sound waves are used
- Page 786 and 787: j / Thomas Youngk / Double-slit dif
- Page 788 and 789: object that diffracts it, so the tr
- Page 790 and 791: Although the equation λ/d = sin θ
- Page 792 and 793: things we’ve learned about diffra
- Page 794 and 795: apidly changing distances; on reuni
- Page 796 and 797: 6 The figure on the next page shows
- Page 798 and 799: 14 Here’s a game my kids like to
- Page 800 and 801: 27 Suppose a converging lens is con
- Page 802 and 803: same depth, but not quite. [Check:
- Page 804 and 805: Problem 42.42 Panel 1 of the figure
- Page 806 and 807: 46 The figure below shows two diffr
- Page 808 and 809: 53 The beam of a laser passes throu
- Page 810 and 811: Problem 59.the ancient problem of i
- Page 812 and 813: 3. Now imagine the following new si
- Page 814 and 815: Exercise 12B: Object and Image Dist
- Page 818 and 819: Exercise 12E: Single-slit diffracti
- Page 820 and 821: Exercise 12F: Diffraction of LightE
- Page 822 and 823: energy, instead of being spread out
- Page 824 and 825: correlated. If they have been playi
- Page 826 and 827: small.The statement that the rule f
- Page 828 and 829: But the y axis can no longer be a u
- Page 830 and 831: for a long time once it gets there,
- Page 832 and 833: j / Calibration of the 14 C dating
- Page 834 and 835: given by(probability of a ≤ x ≤
- Page 836 and 837: k / In recent decades, a huge hole
- Page 838 and 839: A wave is partially absorbed.c / A
- Page 840 and 841: f / The hamster in her hamsterball
- Page 842 and 843: How would you extract h from the gr
- Page 844 and 845: F Does E = hf imply that a photon c
- Page 846 and 847: of approaching this issue.)j / Bull
- Page 848 and 849: We assume v is small enough so that
- Page 850 and 851: the probability distribution will b
- Page 852 and 853: trons that we have already used for
- Page 854 and 855: equations of general validity are t
- Page 856 and 857: wave carries high probability and w
- Page 858 and 859: An infinite sine wave can only tell
- Page 860 and 861: momentum implies a definite kinetic
- Page 862 and 863: of snapshots would amount to a desc
- Page 864 and 865: close are the electrons to the limi
- Page 866 and 867:
dimensional particle in a box, and
- Page 868 and 869:
Applying this to conservation of en
- Page 870 and 871:
the probability of making it throug
- Page 872 and 873:
Three dimensionsFor simplicity, we
- Page 874 and 875:
1. Oscillations can go backand fort
- Page 876 and 877:
C The figure shows a skateboarder t
- Page 878 and 879:
a / Eight wavelengths fit aroundthi
- Page 880 and 881:
As shown by these examples, the unc
- Page 882 and 883:
e / The three states of the hydroge
- Page 884 and 885:
f / The energy levels of a particle
- Page 886 and 887:
∂r/∂x = x/r comes in handy. Com
- Page 888 and 889:
50% of its time in each atom. It’
- Page 890 and 891:
tus to the z axis) and more memorab
- Page 892 and 893:
ut why does that have anything to d
- Page 894 and 895:
the data are only inaccurate due to
- Page 896 and 897:
14 The photoelectric effect can occ
- Page 898 and 899:
Problem 25.(b) Sketch a graph showi
- Page 900 and 901:
conservation of energy and momentum
- Page 902 and 903:
Problem 43.43 On pp. 884-885 of sub
- Page 904 and 905:
ExercisesExercise 13A: Quantum Vers
- Page 906 and 907:
⊲ First we convert the equation i
- Page 908 and 909:
Programming With PythonThe purpose
- Page 910 and 911:
Appendix 2: MiscellanyUnphysical
- Page 912 and 913:
18 bestt = t19 c1 = bestc120 c2 = b
- Page 914 and 915:
p i + ∑ iThe spin theoremTheorem:
- Page 916 and 917:
Appendix 3: Photo CreditsExcept as
- Page 918 and 919:
Appendix 4: Hints and SolutionsHint
- Page 920 and 921:
Hints for Chapter 6Page 377, proble
- Page 922 and 923:
Answers to Self-Checks for Chapter
- Page 924 and 925:
Page 301: (1) Not valid. The equati
- Page 926 and 927:
Page 584:N −1 m −2 C 2 V 2 m
- Page 928 and 929:
the dashed ray.Page 748: You should
- Page 930 and 931:
direction it was initially going (i
- Page 932 and 933:
Page 52, problem 38: The cone of mi
- Page 934 and 935:
Page 224, problem 37: (a) Spring co
- Page 936 and 937:
object, we have static friction, wh
- Page 938 and 939:
Page 549, problem 29:(a) Conservati
- Page 940 and 941:
Page 798, problem 19: (a) The objec
- Page 942 and 943:
.0.8 Notation and unitsquantity uni
- Page 944 and 945:
surfaces. For comparison, a typical
- Page 946 and 947:
elations:a = ∆v∆tx = 1 2 at2 +
- Page 948 and 949:
we are moving along with the projec
- Page 950 and 951:
the number of oscillations required
- Page 952 and 953:
In general, the cross product of ve
- Page 954 and 955:
Sound waves consist of increases an
- Page 956 and 957:
signs for charge is that with this
- Page 958 and 959:
know that there is a delay in time
- Page 960 and 961:
is related byΦ = 4πkq into the ch
- Page 962 and 963:
to use sophisticated models such as
- Page 964 and 965:
Chapter 13, Quantum Physics, page 8
- Page 966 and 967:
oth position and momentum, the Heis
- Page 968 and 969:
Schrödinger’s, 864cathode rays,
- Page 970 and 971:
unstable, 87equipartition theorem,
- Page 972 and 973:
Joule, James, 73paddlewheel experim
- Page 974 and 975:
Einstein’s early theory, 838energ
- Page 976 and 977:
Nikola, 178tesla (unit), 652thermal