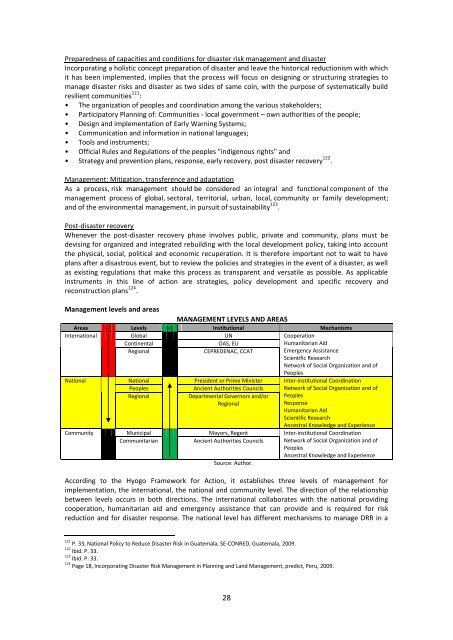
Preparedness of capacities and conditions for disaster risk management and disasterIncorporating a holistic concept preparation of disaster and leave the historical reductionism with whichit has been implemented, implies that the process will focus on designing or structuring strategies tomanage disaster risks and disaster as two sides of same coin, with the purpose of systematically buildresilient communities 121 :• The organization of peoples and coordination among the various stakeholders;• Participatory Planning of: Communities - local government – own authorities of the people;• Design and implementation of Early Warning Systems;• Communication and information in national languages;• Tools and instruments;• Official Rules and Regulations of the peoples "indigenous rights" and• Strategy and prevention plans, response, early recovery, post disaster recovery 122 .Management: Mitigation, transference and adaptationAs a process, risk management should be considered an integral and functional component of themanagement process of global, sectoral, territorial, urban, local, community or family development;and of the environmental management, in pursuit of sustainability 123 .Post-disaster recoveryWhenever the post-disaster recovery phase involves public, private and community, plans must bedevising for organized and integrated rebuilding with the local development policy, taking into accountthe physical, social, political and economic recuperation. It is therefore important not to wait to haveplans after a disastrous event, but to review the policies and strategies in the event of a disaster, as wellas existing regulations that make this process as transparent and versatile as possible. As applicableinstruments in this line of action are strategies, policy development and specific recovery andreconstruction plans 124 .Management levels and areasMANAGEMENT LEVELS AND AREASAreas (-) Levels (+) Institutional MechanismsInternational <strong>Global</strong> UN CooperationContinentalOAS, EUHumanitarian AidRegionalCEPREDENAC, CCATEmergency AssistanceScientific ResearchNetwork of Social Organization and ofPeoplesNational National President or Prime Minister Inter-institutional CoordinationPeoplesAncient Authorities Councils Network of Social Organization and ofRegionalDepartmental Governors and/orRegionalPeoplesResponseHumanitarian AidScientific ResearchAncestral Knowledge and ExperienceCommunity ab Municipal Mayors, Regent Inter-institutional CoordinationCommunitarianAncient Authorities Councils Network of Social Organization and ofPeoplesAncestral Knowledge and ExperienceSource: Author.According to the Hyogo Framework for Action, it establishes three levels of management forimplementation, the international, the national and community level. The direction of the relationshipbetween levels occurs in both directions. The international collaborates with the national providingcooperation, humanitarian aid and emergency assistance that can provide and is required for riskreduction and for disaster response. The national level has different mechanisms to manage DRR in a121 P. 33, National Policy to Reduce Disaster Risk in Guatemala, SE-CONRED, Guatemala, 2009.122 Ibid. P. 33.123 Ibid. P. 33.124 Page 18, Incorporating Disaster Risk Management in Planning and Land Management, predict, Peru, 2009.28
participatory manner, to address disasters and distribute aid received. The community level is the onethat is taken into account in these cases, however, it has many important qualities such as organizationand knowledge that begin to interact with the other areas mentioned, in that sense, and the sense ofdirection of the relationship builds up, establishing a dialogue and coordination, indispensable for DRR.The state's role is to facilitate and support the process of empowerment at community-level and tocoordinate the institutions and of the distribution of the assistance received for the benefit of affectedcommunities and peoples 125 .Causes, relationships and major dynamicsDisaster risk is a result that emerges from the development, that is, it is not a condition that arisessuddenly or by external agents or factors to the development process, it is the cumulative result ofpolitical, economic and social taking place in the territory. The development process expressed asterritorial processes, as the use, occupation and transformation of the territory, and sectoral processes,such as flows of goods and services, resource use and waste disposal, have a deep connection with thegeneration and accumulation of risk and therefore with disasters 126 .The Latin America and the Caribbean countries, where disasters are a growing problem and its impactis growing are due to failures in development models and ways of occupying territory prevailing in theregion. Population growth, rapid urbanization, the location of human settlements in risk areas, housingconstruction and infrastructure without the use of appropriate techniques and pressure on naturalresources, have steadily increased the vulnerability of the population from a wide variety of naturalhazards 127 .Although from the technical point of view has been significant progress, still problem of disasters is notunderstood as an unresolved deficit in the development agenda, in the sense that disasters are notevents of nature per se, but rather situations that result from imbalances in the relationship betweenthe dynamics of the natural and human dynamics. Tangible evidence of these imbalances can be seenglobally every day 128 .Repeatedly, the poor are victims of the national development process, seeing that the school buildings,hospitals, homes and all their livelihoods are destroyed by floods, earthquakes or other natural hazards.However, this regression and destruction of the reported benefits of development can be largelyavoided. The successful investments in risk reduction can significantly protect against such losses toboth the population and the national treasury 129 .85% of people exposed to earthquakes, cyclones, floods and droughts live in developing countries. Theenormous cost of disasters threatens the achievement of the Millennium Development Goals,especially the first goal: Reduce poverty by half by 2015 130 .The combination of developmental factors such as growth and concentration of population,technological development in industry, information and communications, the expansion of urbanizedareas, the complexity of networks and infrastructure service provision and the mixture of uses andactivities in the territory, generate causal relationships between socio natural and anthropogenicthreats, so that the occurrence of one can lead to others, thereby in this way constituting multi-risk ormulti-hazard scenarios in which it is increasingly difficult to identify and individually intervene 131 .125 Systematization by consultant.126 Op. Cit. Pag. 15.127 Ibid. Pag. 5.128 Ibid. Pag. 5.129 Page 3, Disaster Risk Reduction: a tool for achieving the Millennium Development Goals. UIP, ISDR, Switzerland, 2010.130 Ibid. Pag. 8.131 Op. Cit. Pag. 15.29
- Page 3 and 4: Executive SummaryCentral America is
- Page 5 and 6: Central is located in the "Ring of
- Page 7 and 8: Study ContentAs an innovative theme
- Page 9 and 10: that coexist in the universe. This
- Page 11 and 12: Central America level, is the only
- Page 13 and 14: of Mesoamerica has been explained a
- Page 15 and 16: possesses effective cultural commun
- Page 17 and 18: Additionally, to succeed and achiev
- Page 19 and 20: eforestation, hydrological planning
- Page 21 and 22: General thematic introduction on Cl
- Page 23 and 24: Central American Governments should
- Page 25 and 26: projected 109 conditions, changes o
- Page 27: General introduction on the themati
- Page 31 and 32: Causes and complementary consequenc
- Page 33 and 34: Organizational and legal contextWhi
- Page 35 and 36: The three bodies within the SICA ar
- Page 37 and 38: Based on research of available info
- Page 39 and 40: SE-CONREDCivilProtectionSNETCCNISCO
- Page 41 and 42: Synergy model that displays the add
- Page 43 and 44: Added value of indigenous and local
- Page 45 and 46: They do not work in a separate mann
- Page 47 and 48: demand for agricultural raw materia
- Page 49 and 50: Amazon DIPECHO Project “Strengthe
- Page 51 and 52: Indigenous Knowledge on DisasterMit
- Page 53 and 54: The combination of indigenous andsc
- Page 55 and 56: Indigenous Skills and the mysticism
- Page 57 and 58: Weather forecast through indigenous
- Page 59 and 60: In various international convention
- Page 61 and 62: Recommended ReadingBennett, A., 200
- Page 63 and 64: ILO, 1993, Convenio sobre pueblos i
- Page 65 and 66: Local knowledgeIncludes people and
- Page 67 and 68: which are threatswith a certainprob
- Page 69 and 70: Appreciates and respects their orga
- Page 71 and 72: framework, without taking into acco
- Page 73 and 74: Currently Cacaopera ethnicity, alth
- Page 75 and 76: IDH 228 For 2007 is of 0.6999Politi
- Page 77 and 78: The Mayangnas are people who are de
- Page 79 and 80:
Rights of detainees to receive info
- Page 81 and 82:
Heritage Protection Article 128The
- Page 83 and 84:
19/09/1996 Law no. 230 Amendments a
- Page 85 and 86:
Indigenous Population:IDH 241 In 20
- Page 87 and 88:
Honduras, each has a different orig
- Page 89 and 90:
MISQUITOS 248 :In 1996 there were 3
- Page 91:
Internationalconventions signed wit