Harmonized Perspectives - CDKN Global
Harmonized Perspectives - CDKN Global
Harmonized Perspectives - CDKN Global
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
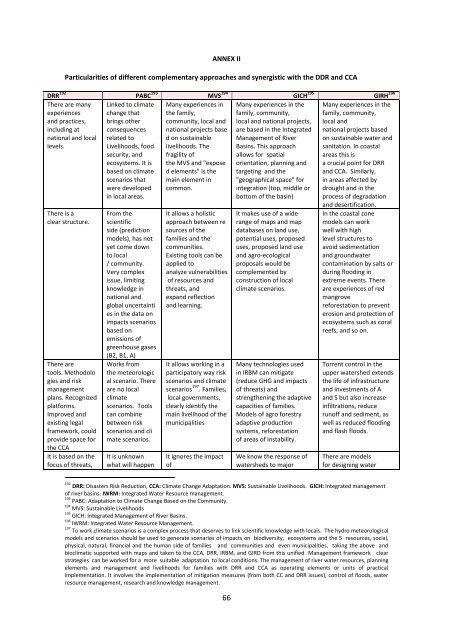
ANNEX IIParticularities of different complementary approaches and synergistic with the DDR and CCADRR 192 PABC 193 MVS 194 GICH 195 GIRH 196There are manyexperiencesand practices,including atnational and locallevels.There is aclear structure.There aretools. Methodologies and riskmanagementplans. Recognizedplatforms.Improved andexisting legalframework, couldprovide space forthe CCAIt is based on thefocus of threats,Linked to climatechange thatbrings otherconsequencesrelated toLivelihoods, foodsecurity, andecosystems. It isbased on climatescenarios thatwere developedin local areas.From thescientificside (predictionmodels), has notyet come downto local/ community.Very complexissue, limitingknowledge innational andglobal uncertainties in the data onimpacts scenariosbased onemissions ofgreenhouse gases(B2, B1, A)Works fromthe meteorological scenario. Thereare no localclimatescenarios. Toolscan combinebetween riskscenarios and climate scenarios.It is unknownwhat will happenMany experiences inthe family,community, local andnational projects based on sustainablelivelihoods. Thefragility ofthe MVS and "exposed elements" is themain element incommon.It allows a holisticapproach between resources of thefamilies and thecommunities.Existing tools can beapplied toanalyze vulnerabilitiesof resources andthreats, andexpand reflectionand learning.It allows working in aparticipatory way riskscenarios and climatescenarios 197 . Families,local governments,clearly identify themain livelihood of themunicipalitiesIt ignores the impactofMany experiences in thefamily, community,local and national projects,are based in the IntegratedManagement of RiverBasins. This approachallows for spatialorientation, planning andtargeting and the"geographical space" forintegration (top, middle orbottom of the basin)It makes use of a widerange of maps and mapdatabases on land use,potential uses, proposeduses, proposed land useand agro-ecologicalproposals would becomplemented byconstruction of localclimate scenarios.Many technologies usedin IRBM can mitigate(reduce GHG and impactsof threats) andstrengthening the adaptivecapacities of families.Models of agro forestryadaptive productionsystems, reforestationof areas of instability.We know the response ofwatersheds to majorMany experiences in thefamily, community,local andnational projects basedon sustainable water andsanitation. In coastalareas this isa crucial point for DRRand CCA. Similarly,in areas affected bydrought and in theprocess of degradationand desertification.In the coastal zonemodels can workwell with highlevel structures toavoid sedimentationand groundwatercontamination by salts orduring flooding inextreme events. Thereare experiences of redmangrovereforestation to preventerosion and protection ofecosystems such as coralreefs, and so on.Torrent control in theupper watershed extendsthe life of infrastructureand investments of Aand S but also increaseinfiltrations, reducerunoff and sediment, aswell as reduced floodingand flash floods.There are modelsfor designing water192DRR: Disasters Risk Reduction, CCA: Climate Change Adaptation. MVS: Sustainable Livelihoods. GICH: Integrated managementof river basins. IWRM: Integrated Water Resource management.193 PABC: Adaptation to Climate Change Based on the Community.194 MVS: Sustainable Livelihoods195 GICH: Integrated Management of River Basins.196 IWRM: Integrated Water Resource Management.197 To work climate scenarios is a complex process that deserves to link scientific knowledge with locals. The hydro meteorologicalmodels and scenarios should be used to generate scenarios of impacts on biodiversity, ecosystems and the 5 resources, social,physical, natural, financial and the human side of families and communities and even municipalities, taking the above andbioclimatic supported with maps and taken to the CCA, DRR, IRBM, and GIRD from this unified Management framework clearstrategies can be worked for a more suitable adaptation to local conditions. The management of river water resources, planningelements and management and livelihoods for families with DRR and CCA as operating elements or units of practicalimplementation. It involves the implementation of mitigation measures (from both CC and DRR issues), control of floods, waterresource management, research and knowledge management.66