Harmonized Perspectives - CDKN Global
Harmonized Perspectives - CDKN Global
Harmonized Perspectives - CDKN Global
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
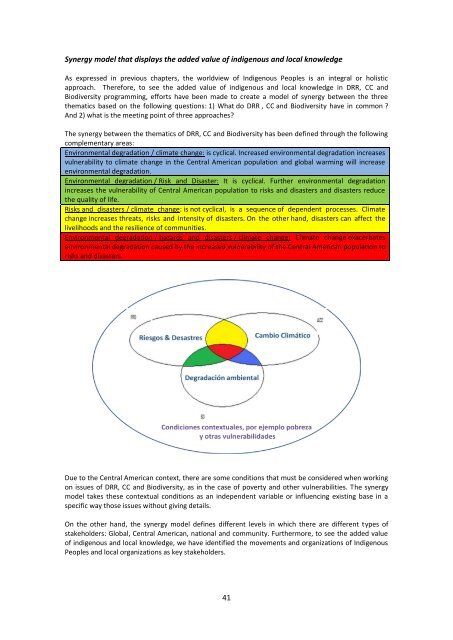
Synergy model that displays the added value of indigenous and local knowledgeAs expressed in previous chapters, the worldview of Indigenous Peoples is an integral or holisticapproach. Therefore, to see the added value of indigenous and local knowledge in DRR, CC andBiodiversity programming, efforts have been made to create a model of synergy between the threethematics based on the following questions: 1) What do DRR , CC and Biodiversity have in common ?And 2) what is the meeting point of three approaches?The synergy between the thematics of DRR, CC and Biodiversity has been defined through the followingcomplementary areas:Environmental degradation / climate change: is cyclical. Increased environmental degradation increasesvulnerability to climate change in the Central American population and global warming will increaseenvironmental degradation.Environmental degradation / Risk and Disaster: It is cyclical. Further environmental degradationincreases the vulnerability of Central American population to risks and disasters and disasters reducethe quality of life.Risks and disasters / climate change: is not cyclical, is a sequence of dependent processes. Climatechange increases threats, risks and intensity of disasters. On the other hand, disasters can affect thelivelihoods and the resilience of communities.Environmental degradation / hazards and disasters / climate change: Climate change exacerbatesenvironmental degradation caused by the increased vulnerability of the Central American population torisks and disasters.Due to the Central American context, there are some conditions that must be considered when workingon issues of DRR, CC and Biodiversity, as in the case of poverty and other vulnerabilities. The synergymodel takes these contextual conditions as an independent variable or influencing existing base in aspecific way those issues without giving details.On the other hand, the synergy model defines different levels in which there are different types ofstakeholders: <strong>Global</strong>, Central American, national and community. Furthermore, to see the added valueof indigenous and local knowledge, we have identified the movements and organizations of IndigenousPeoples and local organizations as key stakeholders.41