World Investment Report 2009: Transnational Corporations - Unctad
World Investment Report 2009: Transnational Corporations - Unctad
World Investment Report 2009: Transnational Corporations - Unctad
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
CHAPTER I 33<br />
������<br />
���<br />
���<br />
���<br />
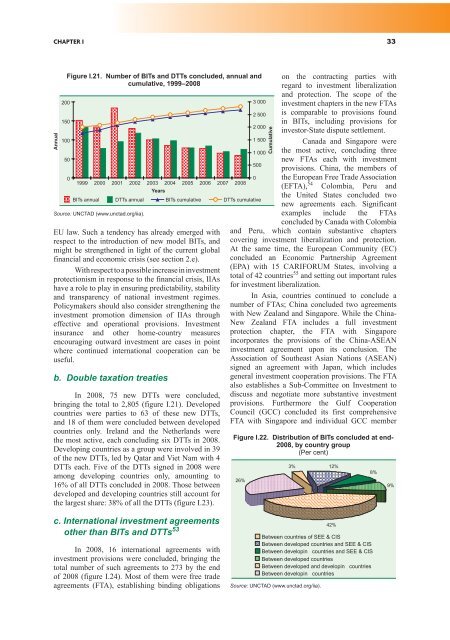
Figure I.21. Number of BITs and DTTs concluded, annual and<br />
cumulative, 1999–2008<br />
��<br />
�<br />
���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ����<br />
���� ������ ���� ������ ���� ���������� ���� ����������<br />
Source: UNCTAD (www.unctad.org/iia).<br />
�����<br />
EU law. Such a tendency has already emerged with<br />
respect to the introduction of new model BITs, and<br />
might be strengthened in light of the current global<br />
financial and economic crisis (see section 2.e).<br />
With respect to a possible increase in investment<br />
protectionism in response to the financial crisis, IIAs<br />
have a role to play in ensuring predictability, stability<br />
and transparency of national investment regimes.<br />
Policymakers should also consider strengthening the<br />
investment promotion dimension of IIAs through<br />
effective and operational provisions. <strong>Investment</strong><br />
insurance and other home-country measures<br />
encouraging outward investment are cases in point<br />
where continued international cooperation can be<br />
useful.<br />
b. Double taxation treaties<br />
In 2008, 75 new DTTs were concluded,<br />
bringing the total to 2,805 (figure I.21). Developed<br />
countries were parties to 63 of these new DTTs,<br />
and 18 of them were concluded between developed<br />
countries only. Ireland and the Netherlands were<br />
the most active, each concluding six DTTs in 2008.<br />
Developing countries as a group were involved in 39<br />
of the new DTTs, led by Qatar and Viet Nam with 4<br />
DTTs each. Five of the DTTs signed in 2008 were<br />
among developing countries only, amounting to<br />
16% of all DTTs concluded in 2008. Those between<br />
developed and developing countries still account for<br />
the largest share: 38% of all the DTTs (figure I.23).<br />
c. International investment agreements<br />
other than BITs and DTTs 53<br />
In 2008, 16 international agreements with<br />
investment provisions were concluded, bringing the<br />
total number of such agreements to 273 by the end<br />
of 2008 (figure I.24). Most of them were free trade<br />
agreements (FTA), establishing binding obligations<br />
� ���<br />
� ���<br />
� ���<br />
� ���<br />
� ���<br />
���<br />
�<br />
����������<br />
Figure I.22. Distribution of BITs concluded at end-<br />
2008, by country group<br />
(Per cent)<br />
���<br />
�� ���<br />
Source: UNCTAD (www.unctad.org/iia).<br />
on the contracting parties with<br />
������� ��� ����������� ���������������<br />
and protection. The scope of the<br />
investment chapters in the new FTAs<br />
is comparable to provisions found<br />
in BITs, including provisions for<br />
investor-State dispute settlement.<br />
Canada and Singapore were<br />
the most active, concluding three<br />
new FTAs each with investment<br />
provisions. China, the members of<br />
the European Free Trade Association<br />
(EFTA), 54 Colombia, Peru and<br />
the United States concluded two<br />
new agreements each. Significant<br />
examples include the FTAs<br />
concluded by Canada with Colombia<br />
and Peru, which contain substantive chapters<br />
��������� ����������� ��������������� ���� ������������<br />
At the same time, the European Community (EC)<br />
concluded an Economic Partnership Agreement<br />
(EPA) with 15 CARIFORUM States, involving a<br />
total of 42 countries 55 and setting out important rules<br />
�������������������������������<br />
In Asia, countries continued to conclude a<br />
number of FTAs; China concluded two agreements<br />
with New Zealand and Singapore. While the China-<br />
New Zealand FTA includes a full investment<br />
protection chapter, the FTA with Singapore<br />
incorporates the provisions of the China-ASEAN<br />
investment agreement upon its conclusion. The<br />
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)<br />
signed an agreement with Japan, which includes<br />
general investment cooperation provisions. The FTA<br />
also establishes a Sub-Committee on <strong>Investment</strong> to<br />
discuss and negotiate more substantive investment<br />
provisions. Furthermore the Gulf Cooperation<br />
Council (GCC) concluded its first comprehensive<br />
FTA with Singapore and individual GCC member<br />
���<br />
������� ��������� �� ��� � ���<br />
������� ��������� ��������� ��� ��� � ���<br />
������� ���������� ��������� ��� ��� � ���<br />
������� ��������� ���������<br />
������� ��������� ��� ���������� ���������<br />
������� ���������� ���������<br />
��<br />
��