- Page 1 and 2:
F. Stuart Chapin III Pamela A. Mats
- Page 3 and 4:
Preface Human activities are affect
- Page 5 and 6:
Contents Preface . . . . . . . . .
- Page 7 and 8:
Contents ix Changes in Storage . .
- Page 9 and 10:
Contents xi Root Uptake Properties
- Page 11 and 12:
Contents xiii Disturbance . . . . .
- Page 13 and 14:
1 The Ecosystem Concept Ecosystem e
- Page 15 and 16:
Figure 1.1. Examples of ecosystems
- Page 17 and 18:
Community ecology Population ecolog
- Page 19 and 20:
ing from biotically driven changes
- Page 21 and 22:
The pool sizes and rates of cycling
- Page 23 and 24:
and alters patterns of vegetation d
- Page 25 and 26:
Figure 1.5. Direct and indirect eff
- Page 27 and 28:
many aspects of ecology, hydrology,
- Page 29 and 30:
Energy (W m -2 ) 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 Ab
- Page 31 and 32:
The Atmospheric System Atmospheric
- Page 33 and 34:
ecular O2 to form O3. The absorptio
- Page 35 and 36:
Hadley cell Hadley cell Ferrell cel
- Page 37 and 38:
early sailors as the doldrums. Subs
- Page 39 and 40:
phere, extends to depths of 75 to 2
- Page 41 and 42:
tures in Great Britain and western
- Page 43 and 44:
when the water vapor condenses to f
- Page 45 and 46:
Solar flux 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4
- Page 47 and 48:
Figure 2.16. Time course of the ave
- Page 49 and 50:
Radiative forcing (W m -2 ) Warming
- Page 51 and 52:
January September Sun March pattern
- Page 53 and 54:
access to light compete effectively
- Page 55 and 56:
the top? How does each of these atm
- Page 57 and 58:
(Dokuchaev 1879, Jenny 1941, Amunds
- Page 59 and 60:
Organic carbon (%) Erosion likely g
- Page 61 and 62:
erosion dominating on steep hillslo
- Page 63 and 64:
conductivity of soils. Groundwater
- Page 65 and 66:
chemical weathering through their c
- Page 67 and 68:
Although most of the transfers in s
- Page 69 and 70:
leached material from above, it is
- Page 71 and 72:
opment, so these soils have weak de
- Page 73 and 74:
y roots and bacteria are important
- Page 75 and 76:
Table 3.4. Sequence of H + - consum
- Page 77 and 78:
new chemical conditions cause them
- Page 79 and 80:
72 4. Terrestrial Water and Energy
- Page 81 and 82:
74 4. Terrestrial Water and Energy
- Page 83 and 84:
76 4. Terrestrial Water and Energy
- Page 85 and 86:
78 4. Terrestrial Water and Energy
- Page 87 and 88:
80 4. Terrestrial Water and Energy
- Page 89 and 90:
82 4. Terrestrial Water and Energy
- Page 91 and 92:
84 4. Terrestrial Water and Energy
- Page 93 and 94:
86 4. Terrestrial Water and Energy
- Page 95 and 96:
88 4. Terrestrial Water and Energy
- Page 97 and 98:
90 4. Terrestrial Water and Energy
- Page 99 and 100:
92 4. Terrestrial Water and Energy
- Page 101 and 102:
94 4. Terrestrial Water and Energy
- Page 103 and 104:
96 4. Terrestrial Water and Energy
- Page 105 and 106:
98 5. Carbon Input to Terrestrial E
- Page 107 and 108:
100 5. Carbon Input to Terrestrial
- Page 109 and 110:
102 5. Carbon Input to Terrestrial
- Page 111 and 112:
104 5. Carbon Input to Terrestrial
- Page 113 and 114:
106 5. Carbon Input to Terrestrial
- Page 115 and 116:
108 5. Carbon Input to Terrestrial
- Page 117 and 118:
110 5. Carbon Input to Terrestrial
- Page 119 and 120:
112 5. Carbon Input to Terrestrial
- Page 121 and 122:
114 5. Carbon Input to Terrestrial
- Page 123 and 124:
116 5. Carbon Input to Terrestrial
- Page 125 and 126:
118 5. Carbon Input to Terrestrial
- Page 127 and 128:
120 5. Carbon Input to Terrestrial
- Page 129 and 130:
122 5. Carbon Input to Terrestrial
- Page 131 and 132:
124 6. Terrestrial Production Proce
- Page 133 and 134:
126 6. Terrestrial Production Proce
- Page 135 and 136:
128 6. Terrestrial Production Proce
- Page 137 and 138:
130 6. Terrestrial Production Proce
- Page 139 and 140:
132 6. Terrestrial Production Proce
- Page 141 and 142:
134 6. Terrestrial Production Proce
- Page 143 and 144:
136 6. Terrestrial Production Proce
- Page 145 and 146:
138 6. Terrestrial Production Proce
- Page 147 and 148:
140 6. Terrestrial Production Proce
- Page 149 and 150:
142 6. Terrestrial Production Proce
- Page 151 and 152:
144 6. Terrestrial Production Proce
- Page 153 and 154:
146 6. Terrestrial Production Proce
- Page 155 and 156:
148 6. Terrestrial Production Proce
- Page 157 and 158:
150 6. Terrestrial Production Proce
- Page 159 and 160:
152 7. Terrestrial Decomposition So
- Page 161 and 162:
154 7. Terrestrial Decomposition su
- Page 163 and 164:
156 7. Terrestrial Decomposition a
- Page 165 and 166:
158 7. Terrestrial Decomposition Ma
- Page 167 and 168:
160 7. Terrestrial Decomposition Re
- Page 169 and 170:
162 7. Terrestrial Decomposition cy
- Page 171 and 172:
164 7. Terrestrial Decomposition Ma
- Page 173 and 174:
166 7. Terrestrial Decomposition li
- Page 175 and 176:
168 7. Terrestrial Decomposition ar
- Page 177 and 178:
170 7. Terrestrial Decomposition R
- Page 179 and 180:
172 7. Terrestrial Decomposition LO
- Page 181 and 182: 174 7. Terrestrial Decomposition Me
- Page 183 and 184: 8 Terrestrial Plant Nutrient Use In
- Page 185 and 186: 178 8. Terrestrial Plant Nutrient U
- Page 187 and 188: 180 8. Terrestrial Plant Nutrient U
- Page 189 and 190: 182 8. Terrestrial Plant Nutrient U
- Page 191 and 192: 184 8. Terrestrial Plant Nutrient U
- Page 193 and 194: 186 8. Terrestrial Plant Nutrient U
- Page 195 and 196: 188 8. Terrestrial Plant Nutrient U
- Page 197 and 198: 190 8. Terrestrial Plant Nutrient U
- Page 199 and 200: 192 8. Terrestrial Plant Nutrient U
- Page 201 and 202: 194 8. Terrestrial Plant Nutrient U
- Page 203 and 204: 196 8. Terrestrial Plant Nutrient U
- Page 205 and 206: 198 9. Terrestrial Nutrient Cycling
- Page 207 and 208: 200 9. Terrestrial Nutrient Cycling
- Page 209 and 210: 202 9. Terrestrial Nutrient Cycling
- Page 211 and 212: 204 9. Terrestrial Nutrient Cycling
- Page 213 and 214: 206 9. Terrestrial Nutrient Cycling
- Page 215 and 216: 208 9. Terrestrial Nutrient Cycling
- Page 217 and 218: 210 9. Terrestrial Nutrient Cycling
- Page 219 and 220: 212 9. Terrestrial Nutrient Cycling
- Page 221 and 222: 214 9. Terrestrial Nutrient Cycling
- Page 223 and 224: 216 9. Terrestrial Nutrient Cycling
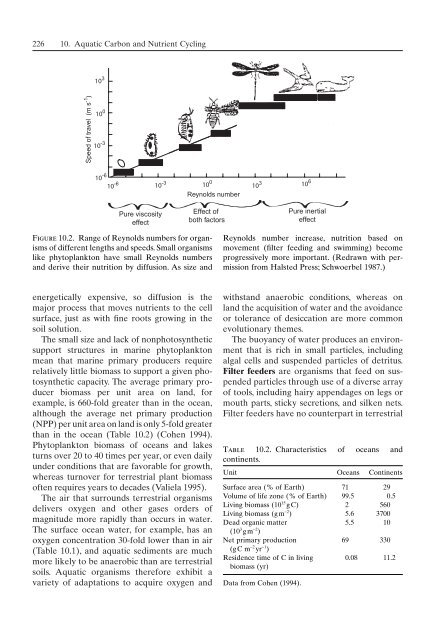
- Page 225 and 226: 218 9. Terrestrial Nutrient Cycling
- Page 227 and 228: 220 9. Terrestrial Nutrient Cycling
- Page 229 and 230: 222 9. Terrestrial Nutrient Cycling
- Page 231: 10 Aquatic Carbon and Nutrient Cycl
- Page 235 and 236: 228 10. Aquatic Carbon and Nutrient
- Page 237 and 238: 230 10. Aquatic Carbon and Nutrient
- Page 239 and 240: 232 10. Aquatic Carbon and Nutrient
- Page 241 and 242: 234 10. Aquatic Carbon and Nutrient
- Page 243 and 244: 236 10. Aquatic Carbon and Nutrient
- Page 245 and 246: 238 10. Aquatic Carbon and Nutrient
- Page 247 and 248: 240 10. Aquatic Carbon and Nutrient
- Page 249 and 250: 242 10. Aquatic Carbon and Nutrient
- Page 251 and 252: 11 Trophic Dynamics Introduction Al
- Page 253 and 254: 246 11. Trophic Dynamics People, fo
- Page 255 and 256: 248 11. Trophic Dynamics Consumptio
- Page 257 and 258: 250 11. Trophic Dynamics Plant defe
- Page 259 and 260: 252 11. Trophic Dynamics Biomass Te
- Page 261 and 262: 254 11. Trophic Dynamics promote ra
- Page 263 and 264: 256 11. Trophic Dynamics eating rat
- Page 265 and 266: 258 11. Trophic Dynamics 4 th 3 rd
- Page 267 and 268: 260 11. Trophic Dynamics terrestria
- Page 269 and 270: 262 11. Trophic Dynamics R R trophi
- Page 271 and 272: 264 11. Trophic Dynamics food chain
- Page 273 and 274: 266 12. Community Effects on Ecosys
- Page 275 and 276: 268 12. Community Effects on Ecosys
- Page 277 and 278: 270 12. Community Effects on Ecosys
- Page 279 and 280: 272 12. Community Effects on Ecosys
- Page 281 and 282: 274 12. Community Effects on Ecosys
- Page 283 and 284:
276 12. Community Effects on Ecosys
- Page 285 and 286:
278 12. Community Effects on Ecosys
- Page 287 and 288:
282 13. Temporal Dynamics An emergi
- Page 289 and 290:
284 13. Temporal Dynamics Small rod
- Page 291 and 292:
286 13. Temporal Dynamics regime (H
- Page 293 and 294:
288 13. Temporal Dynamics successio
- Page 295 and 296:
290 13. Temporal Dynamics Stage Lif
- Page 297 and 298:
292 13. Temporal Dynamics that redu
- Page 299 and 300:
294 13. Temporal Dynamics Soil carb
- Page 301 and 302:
296 13. Temporal Dynamics Nutrient
- Page 303 and 304:
298 13. Temporal Dynamics are aband
- Page 305 and 306:
300 13. Temporal Dynamics leaf area
- Page 307 and 308:
302 13. Temporal Dynamics account f
- Page 309 and 310:
304 13. Temporal Dynamics 6. How do
- Page 311 and 312:
306 14. Landscape Heterogeneity and
- Page 313 and 314:
308 14. Landscape Heterogeneity and
- Page 315 and 316:
310 14. Landscape Heterogeneity and
- Page 317 and 318:
312 14. Landscape Heterogeneity and
- Page 319 and 320:
314 14. Landscape Heterogeneity and
- Page 321 and 322:
316 14. Landscape Heterogeneity and
- Page 323 and 324:
318 14. Landscape Heterogeneity and
- Page 325 and 326:
320 14. Landscape Heterogeneity and
- Page 327 and 328:
322 14. Landscape Heterogeneity and
- Page 329 and 330:
324 14. Landscape Heterogeneity and
- Page 331 and 332:
326 14. Landscape Heterogeneity and
- Page 333 and 334:
328 14. Landscape Heterogeneity and
- Page 335 and 336:
330 14. Landscape Heterogeneity and
- Page 337 and 338:
15 Global Biogeochemical Cycles The
- Page 339 and 340:
tion of surface waters. On daily to
- Page 341 and 342:
Crowley 1995). An improved understa
- Page 343 and 344:
therefore limits the long-term rate
- Page 345 and 346:
important for understanding the rec
- Page 347 and 348:
Terrestrial N fixation (Tg yr -1 )
- Page 349 and 350:
The addition of limiting nutrients
- Page 351 and 352:
has a significant atmospheric compo
- Page 353 and 354:
cled. Evaporation and precipitation
- Page 355 and 356:
Figure 15.11. Trends in (A) world p
- Page 357 and 358:
which cycles are soil pools and flu
- Page 359 and 360:
Our use, mismanagement, and uninten
- Page 361 and 362:
mycorrhizal or nitrogen-fixing mutu
- Page 363 and 364:
Major human impacts on the natural
- Page 365 and 366:
promote long-term sustainability of
- Page 367 and 368:
Coral reef ecosystems have recently
- Page 369 and 370:
Table 16.3. Examples of services pr
- Page 371 and 372:
anthropogenic change and to sustain
- Page 373 and 374:
Abbreviations an nutrient productiv
- Page 375 and 376:
Abbreviations 373 NEE net ecosystem
- Page 377 and 378:
Glossary A horizon. Uppermost miner
- Page 379 and 380:
Biomass. Quantity of living materia
- Page 381 and 382:
Coriolis effect. Tendency, due to E
- Page 383 and 384:
Exoenzyme. Enzyme that is secreted
- Page 385 and 386:
Inceptisol. Soil order characterize
- Page 387 and 388:
Microbial loop. Microbial food web
- Page 389 and 390:
Phototroph. Nitrogen-fixing microor
- Page 391 and 392:
simply to the greater number of spe
- Page 393 and 394:
Sun leaf. Leaf that is acclimated t
- Page 395 and 396:
Color Plate I monthly averages of t
- Page 397 and 398:
Plate 3. The global pattern of net