Mathur Ritika Passi
zVAWsQ
zVAWsQ
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
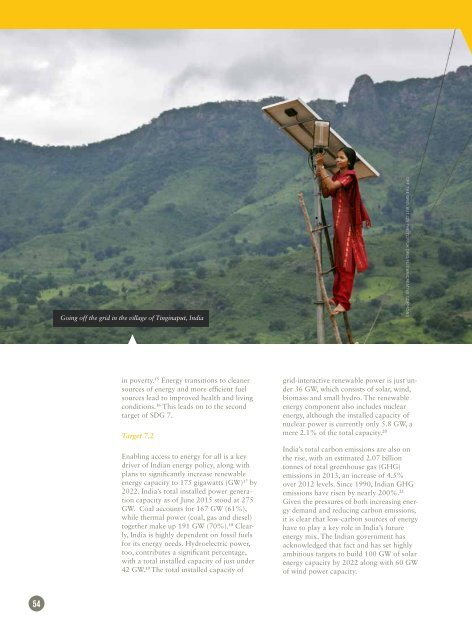
Going off the grid in the village of Tinginaput, India<br />
Off the grid, but on the top/UK DFID/Flickr/Creative Commons<br />
in poverty. 15 Energy transitions to cleaner<br />
sources of energy and more efficient fuel<br />
sources lead to improved health and living<br />
conditions. 16 This leads on to the second<br />
target of SDG 7.<br />
Target 7.2<br />
Enabling access to energy for all is a key<br />
driver of Indian energy policy, along with<br />
plans to significantly increase renewable<br />
energy capacity to 175 gigawatts (GW) 17 by<br />
2022. India’s total installed power generation<br />
capacity as of June 2015 stood at 275<br />
GW. Coal accounts for 167 GW (61%),<br />
while thermal power (coal, gas and diesel)<br />
together make up 191 GW (70%). 18 Clearly,<br />
India is highly dependent on fossil fuels<br />
for its energy needs. Hydroelectric power,<br />
too, contributes a significant percentage,<br />
with a total installed capacity of just under<br />
42 GW. 19 The total installed capacity of<br />
grid-interactive renewable power is just under<br />
36 GW, which consists of solar, wind,<br />
biomass and small hydro. The renewable<br />
energy component also includes nuclear<br />
energy, although the installed capacity of<br />
nuclear power is currently only 5.8 GW, a<br />
mere 2.1% of the total capacity. 20<br />
India’s total carbon emissions are also on<br />
the rise, with an estimated 2.07 billion<br />
tonnes of total greenhouse gas (GHG)<br />
emissions in 2013, an increase of 4.5%<br />
over 2012 levels. Since 1990, Indian GHG<br />
emissions have risen by nearly 200%. 21<br />
Given the pressures of both increasing energy<br />
demand and reducing carbon emissions,<br />
it is clear that low-carbon sources of energy<br />
have to play a key role in India’s future<br />
energy mix. The Indian government has<br />
acknowledged that fact and has set highly<br />
ambitious targets to build 100 GW of solar<br />
energy capacity by 2022 along with 60 GW<br />
of wind power capacity.<br />
54