https://goo.gl/sZ7V7x
293g79C
293g79C
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Number of programm<br />
100<br />
80<br />
60<br />
40<br />
1950<br />
20 80<br />
70<br />
70<br />
60<br />
0<br />
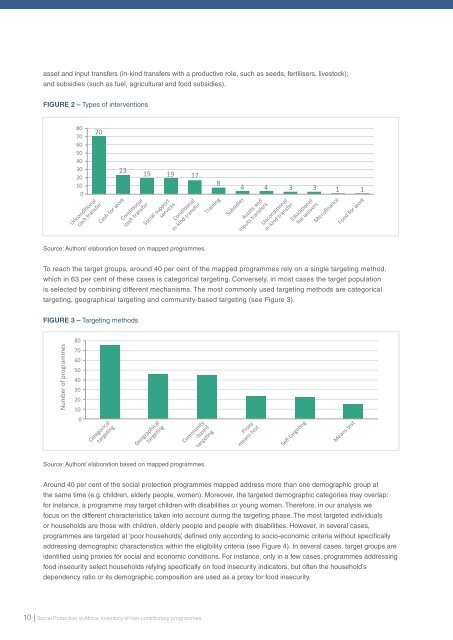
asset and input transfers (in-kind transfers with a productive role, such as seeds, fertilisers, livestock);<br />
50<br />
and subsidies 40 (such as fuel, agricultural and food subsidies).<br />
30<br />
23<br />
19 19 17<br />
FIGURE 220<br />
– Types of interventions<br />
10<br />
8<br />
4 4 3 3 1 1<br />
0<br />
1950<br />
80<br />
70<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
0<br />
70<br />
Unconditional<br />
cash transfer<br />
Unconditional<br />
cash transfer<br />
1955<br />
1955<br />
Cash for work<br />
23<br />
Cash for work<br />
1960<br />
1960<br />
Conditional<br />
cash transfer<br />
1965<br />
Conditional<br />
cash transfer<br />
1965<br />
1970<br />
1970<br />
Social support<br />
services<br />
1975<br />
19 19 17<br />
Social support<br />
services<br />
1975<br />
Conditional<br />
in-kind transfer<br />
1980<br />
1980<br />
Training<br />
8<br />
Conditional<br />
in-kind transfer<br />
Training<br />
1985<br />
1985<br />
Subsidies<br />
Subsidies<br />
1990<br />
1990<br />
Assets and<br />
inputs transfers<br />
4 4<br />
Assets and<br />
inputs transfers<br />
1995<br />
1995<br />
Unconditional<br />
in-kind transfer<br />
Unconditional<br />
in-kind transfer<br />
2000<br />
2000<br />
Educational<br />
fee waivers<br />
2005<br />
2010<br />
3 3 1 1<br />
Educational<br />
fee waivers<br />
2005<br />
Microfinance<br />
Microfinance<br />
2010<br />
Food for work<br />
Food for work<br />
2015<br />
2015<br />
Source: Authors’ elaboration based on mapped programmes.<br />
To reach the target groups, around 40 per cent of the mapped programmes rely on a sin<strong>gl</strong>e targeting method,<br />
which in 63 per cent of these cases is categorical targeting. Conversely, in most cases the target population<br />
is selected by combining different mechanisms. The most commonly used targeting methods are categorical<br />
targeting, geographical targeting and community-based targeting (see Figure 3).<br />
FIGURE 3 – Targeting methods<br />
Number of programmes<br />
Number of programmes<br />
10<br />
80<br />
0<br />
70<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
Source: Authors’ 30 elaboration based on mapped programmes.<br />
20<br />
Around 40 10 per cent of the social protection programmes mapped address more than one demographic group at<br />
the same time 0 (e.g. children, elderly people, women). Moreover, the targeted demographic categories may overlap:<br />
for instance, a programme may target children with disabilities or young women. Therefore, in our analysis we<br />
focus on the different characteristics taken into account during the targeting phase. The most targeted individuals<br />
or households are those with children, elderly people and people with disabilities. However, in several cases,<br />
programmes are targeted at ‘poor households’, defined only according to socio-economic criteria without specifically<br />
60<br />
addressing demographic characteristics within the eligibility criteria (see Figure 4). In several cases, target groups are<br />
50<br />
identified using proxies for social and economic conditions. For instance, only in a few cases, programmes addressing<br />
40<br />
food insecurity select households relying specifically on food insecurity indicators, but often the household’s<br />
30<br />
dependency ratio or its demographic composition are used as a proxy for food insecurity.<br />
20<br />
10<br />
Categorical<br />
targeting<br />
Geographical<br />
targeting<br />
0<br />
60<br />
10 | Social Protection in Africa: inventory of non-contributory programmes<br />
50<br />
40<br />
80<br />
70<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
20<br />
Children<br />
Categorical<br />
targeting<br />
Elderly people<br />
People with<br />
disabilities<br />
Geographical<br />
targeting<br />
oor households<br />
omen and girls<br />
Community<br />
-based<br />
targeting<br />
Community<br />
-based<br />
targeting<br />
our-constrained<br />
households<br />
Working-age<br />
individuals<br />
Proxy<br />
means test<br />
Proxy<br />
means test<br />
Food-insecure<br />
households<br />
Unemployed<br />
Self-targeting<br />
Self-targeting<br />
Smallholder<br />
farmers<br />
Young people<br />
War veterans<br />
Means test<br />
Means test<br />
Chronically ill<br />
individuals