Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
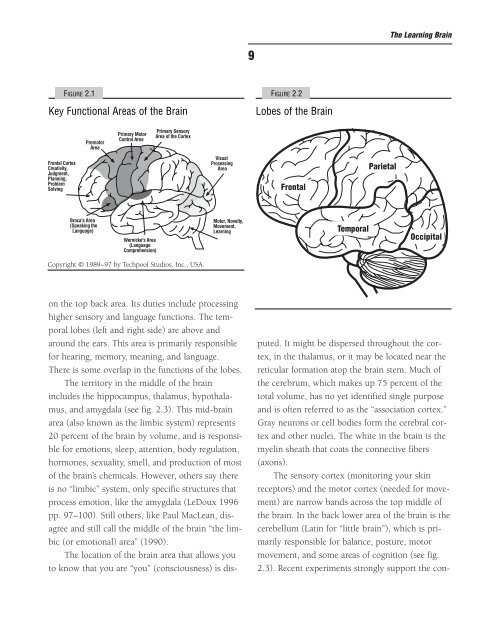
Frontal Cortex<br />
Creativity,<br />
Judgment,<br />
Plann<strong>in</strong>g,<br />
Problem<br />
Solv<strong>in</strong>g<br />
FIGURE 2.1<br />
Key Functional Areas of <strong>the</strong> <strong>Bra<strong>in</strong></strong><br />
Premotor<br />
Area<br />
Broca's Area<br />
(Speak<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong><br />
Language)<br />
Primary Motor<br />
Control Area<br />
Wernicke's Area<br />
(Language<br />
Comprehension)<br />
Primary Sensory<br />
Area of <strong>the</strong> Cortex<br />
Copyright © 1989–97 by Techpool Studios, Inc., USA.<br />
Visual<br />
Process<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Area<br />
Motor, Novelty,<br />
Movement,<br />
Learn<strong>in</strong>g<br />
on <strong>the</strong> top back area. Its duties <strong>in</strong>clude process<strong>in</strong>g<br />
higher sensory and language functions. The temporal<br />
lobes (left and right side) are above and<br />
around <strong>the</strong> ears. This area is primarily responsible<br />
for hear<strong>in</strong>g, memory, mean<strong>in</strong>g, and language.<br />
There is some overlap <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> functions of <strong>the</strong> lobes.<br />
The territory <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> middle of <strong>the</strong> bra<strong>in</strong><br />
<strong>in</strong>cludes <strong>the</strong> hippocampus, thalamus, hypothalamus,<br />
and amygdala (see fig. 2.3). This mid-bra<strong>in</strong><br />
area (also known as <strong>the</strong> limbic system) represents<br />
20 percent of <strong>the</strong> bra<strong>in</strong> by volume, and is responsible<br />
for emotions, sleep, attention, body regulation,<br />
hormones, sexuality, smell, and production of most<br />
of <strong>the</strong> bra<strong>in</strong>’s chemicals. However, o<strong>the</strong>rs say <strong>the</strong>re<br />
is no “limbic” system, only specific structures that<br />
process emotion, like <strong>the</strong> amygdala (LeDoux 1996<br />
pp. 97–100). Still o<strong>the</strong>rs, like Paul MacLean, disagree<br />
and still call <strong>the</strong> middle of <strong>the</strong> bra<strong>in</strong> “<strong>the</strong> limbic<br />
(or emotional) area” (1990).<br />
The location of <strong>the</strong> bra<strong>in</strong> area that allows you<br />
to know that you are “you” (consciousness) is dis-<br />
9<br />
FIGURE 2.2<br />
Lobes of <strong>the</strong> <strong>Bra<strong>in</strong></strong><br />
Frontal<br />
Temporal<br />
Parietal<br />
The Learn<strong>in</strong>g <strong>Bra<strong>in</strong></strong><br />
Occipital<br />
puted. It might be dispersed throughout <strong>the</strong> cortex,<br />
<strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> thalamus, or it may be located near <strong>the</strong><br />
reticular formation atop <strong>the</strong> bra<strong>in</strong> stem. Much of<br />
<strong>the</strong> cerebrum, which makes up 75 percent of <strong>the</strong><br />
total volume, has no yet identified s<strong>in</strong>gle purpose<br />
and is often referred to as <strong>the</strong> “association cortex.”<br />
Gray neurons or cell bodies form <strong>the</strong> cerebral cortex<br />
and o<strong>the</strong>r nuclei. The white <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> bra<strong>in</strong> is <strong>the</strong><br />
myel<strong>in</strong> sheath that coats <strong>the</strong> connective fibers<br />
(axons).<br />
The sensory cortex (monitor<strong>in</strong>g your sk<strong>in</strong><br />
receptors) and <strong>the</strong> motor cortex (needed for movement)<br />
are narrow bands across <strong>the</strong> top middle of<br />
<strong>the</strong> bra<strong>in</strong>. In <strong>the</strong> back lower area of <strong>the</strong> bra<strong>in</strong> is <strong>the</strong><br />
cerebellum (Lat<strong>in</strong> for “little bra<strong>in</strong>”), which is primarily<br />
responsible for balance, posture, motor<br />
movement, and some areas of cognition (see fig.<br />
2.3). Recent experiments strongly support <strong>the</strong> con-