Clevertex - Grado Zero Espace Srl
Clevertex - Grado Zero Espace Srl
Clevertex - Grado Zero Espace Srl
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
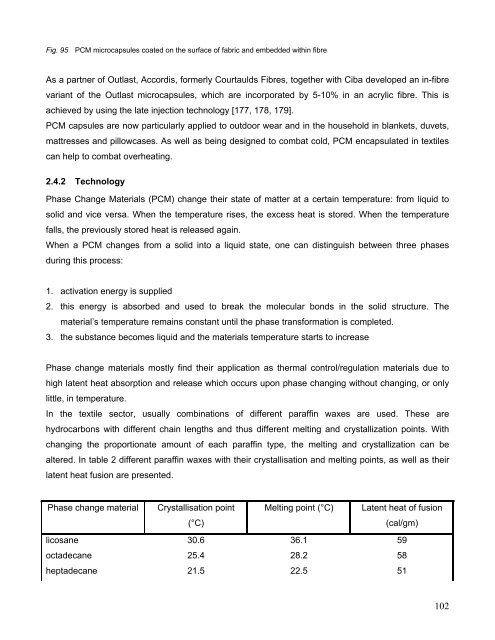
Fig. 95 PCM microcapsules coated on the surface of fabric and embedded within fibre<br />
As a partner of Outlast, Accordis, formerly Courtaulds Fibres, together with Ciba developed an in-fibre<br />
variant of the Outlast microcapsules, which are incorporated by 5-10% in an acrylic fibre. This is<br />
achieved by using the late injection technology [177, 178, 179].<br />
PCM capsules are now particularly applied to outdoor wear and in the household in blankets, duvets,<br />
mattresses and pillowcases. As well as being designed to combat cold, PCM encapsulated in textiles<br />
can help to combat overheating.<br />
2.4.2 Technology<br />
Phase Change Materials (PCM) change their state of matter at a certain temperature: from liquid to<br />
solid and vice versa. When the temperature rises, the excess heat is stored. When the temperature<br />
falls, the previously stored heat is released again.<br />
When a PCM changes from a solid into a liquid state, one can distinguish between three phases<br />
during this process:<br />
1. activation energy is supplied<br />
2. this energy is absorbed and used to break the molecular bonds in the solid structure. The<br />
material’s temperature remains constant until the phase transformation is completed.<br />
3. the substance becomes liquid and the materials temperature starts to increase<br />
Phase change materials mostly find their application as thermal control/regulation materials due to<br />
high latent heat absorption and release which occurs upon phase changing without changing, or only<br />
little, in temperature.<br />
In the textile sector, usually combinations of different paraffin waxes are used. These are<br />
hydrocarbons with different chain lengths and thus different melting and crystallization points. With<br />
changing the proportionate amount of each paraffin type, the melting and crystallization can be<br />
altered. In table 2 different paraffin waxes with their crystallisation and melting points, as well as their<br />
latent heat fusion are presented.<br />
Phase change material Crystallisation point<br />
(°C)<br />
Melting point (°C) Latent heat of fusion<br />
(cal/gm)<br />
licosane 30.6 36.1 59<br />
octadecane 25.4 28.2 58<br />
heptadecane 21.5 22.5 51<br />
102