Drosophila - Severo Ochoa - Universidad Autónoma de Madrid
Drosophila - Severo Ochoa - Universidad Autónoma de Madrid
Drosophila - Severo Ochoa - Universidad Autónoma de Madrid
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Jefe <strong>de</strong> Línea /<br />
Group Lea<strong>de</strong>r:<br />
Miguel A. Rodríguez Marcos<br />
Desarrollo hematopoyético en el<br />
embrión <strong>de</strong> ratón post-gastrulación<br />
Hematopoietic <strong>de</strong>velopment in the<br />
post-gastrulation mouse embryo<br />
C11<br />
Publicaciones<br />
Publications<br />
Resumen <strong>de</strong> investigación<br />
Research summary<br />
Marcos, M.A.R. and Gaspar, M.L. (2005). Apuntes para un encuentro<br />
entre la biología emergente y la clínica médica <strong>de</strong>l tercer milenio.<br />
En: Biotecnología y Sociedad. Fundación Pablo VI, pp. 7-28.<br />
CBM 2005/2006<br />
76<br />
Personal Científico /<br />
Scientific Staff:<br />
Isabel Cortegano<br />
Beatriz Palacio<br />
Inmunología y Virología Immunology and Virology<br />
Nuestro grupo estudia el <strong>de</strong>sarrollo linfohematopoyético y<br />
hepático en el embrión post-gastrulación <strong>de</strong>l ratón. Queremos<br />
elucidar las diferencias entre los procesos embrionarios y los<br />
adultos, <strong>de</strong> relevancia en medicina regenerativa.<br />
Durante los dos últimos años, hemos <strong>de</strong>finido:<br />
(1) La presencia <strong>de</strong> linfocitos NKT funcionales con TCRs no<br />
canónicos (Vβ8.2/Vα3.2) en órganos hematopoyéticos<br />
tempranos: Antes <strong>de</strong> que el epitelio tímico sea receptivo a<br />
progenitores extrínsecos, hemos objetivado una onda<br />
transitoria <strong>de</strong> diferenciación hacia estos linfocitos pseudoinnatos,<br />
implicados en respuestas rápidas a glicolípidos.<br />
Intentamos dilucidar su posible papel en la ontogenia precoz.<br />
(2) Una población <strong>de</strong> linfocitos B/pre-plasmáticas, secretora<br />
<strong>de</strong> IgGs naturales, que sólo es generada por progenitores<br />
embrionarios: Los primeros precursores B <strong>de</strong>tectables en el<br />
embrión son células CD19 + CD45R - que <strong>de</strong>scribimos<br />
recientemente. En el adulto dan lugar a una pequeña<br />
fracción <strong>de</strong> linfocitos B naturalmente activados que<br />
producen espontáneamente altos niveles <strong>de</strong> IgG e IgA.<br />
(3) La variabilidad genética <strong>de</strong> las primeras uniones D-J <strong>de</strong><br />
IgH <strong>de</strong> la ontogenia y el papel <strong>de</strong> la polimerasa µ (en<br />
colaboración con Luis Blanco): Hemos analizado el repertorio<br />
genético <strong>de</strong> las primeras recombinaciones D-JH <strong>de</strong> las Igs en<br />
la gestación media <strong>de</strong>l ratón. Estos reor<strong>de</strong>namientos difieren<br />
<strong>de</strong> los presentes en neonatos, por la inclusión <strong>de</strong> nucleótidos<br />
no-templados N en ausencia <strong>de</strong> TdT. A diferencia <strong>de</strong>l adulto,<br />
la polimerasa µ protege los extremos codificantes <strong>de</strong>l<br />
procesamiento nucleolítico en ellos.<br />
(4) Una nueva vía <strong>de</strong> diferenciación a megacariocitos en el<br />
hígado fetal, que promueven el <strong>de</strong>sarrollo <strong>de</strong> linajes<br />
epiteliales hepáticos: El hígado emergente reúne la mayor<br />
concentración <strong>de</strong> megacariocitos <strong>de</strong>l individuo, aunque las<br />
plaquetas no son necesarias para la supervivencia <strong>de</strong>l<br />
embrión. En co-cultivos in vitro, este linaje celular estimula la<br />
diferenciación <strong>de</strong> precursores hepáticos. Intentamos<br />
explorar las bases moleculares <strong>de</strong> este fenómeno.<br />
Nuestra investigación se <strong>de</strong>sarrolla en colaboración con ML<br />
Gaspar <strong>de</strong>l ISCIII.<br />
Our team is studying the lymphohematopoietic and hepatic<br />
<strong>de</strong>velopment in the post-gastrulation mouse embryo. We<br />
attempt to elucidate the differences between equivalent<br />
embryonic and adult events, which may be of relevance to<br />
regenerative medicine.<br />
During the last couple of years, we have studied:<br />
(1) The presence of functional, non-canonical NKT<br />
lymphocytes (Vβ8.2/Vα3.2) in embryo hematopoietic<br />
organs: A transient wave of lymphoid differentiation giving<br />
rise to innate-like NKT cells emerges in the post-gastrulation<br />
mouse embryo, which are involved in rapid responses to<br />
glycolipids, before the thymic epithelium becomes receptive<br />
to extrinsic progenitors. We attempt to elucidate their<br />
putative role in the early ontogeny.<br />
(2) A population of B lymphocytes/pre-plasma cells that<br />
secretes natural IgGs, selectively emerging from embryonic<br />
progenitors: We recently <strong>de</strong>scribed the earliest embryo B-<br />
lineage precursors, <strong>de</strong>fined as CD19 + CD45R - cells. They<br />
generate a small subset of naturally activated B cells in the<br />
adult that spontaneously produce high levels of IgG and IgA.<br />
(3) The genetic variability of the earliest IgH VDJ coding<br />
junctions and the role of the polymerase µ (in collaboration<br />
with Luis Blanco): We have analyzed the genetic repertoire<br />
of the first Ig D-JH gene rearrangements of midgestation<br />
mouse embryos. They differed from those present in<br />
newborns by the inclusion of non-templated N-nucleoti<strong>de</strong>s<br />
in the absence of TdT. Polymerase µ protects their coding<br />
ends from nucleolytic processing, in contrast to what<br />
happens in adult VDJH joints.<br />
(4) A new pathway of differentiation to megakaryocytes in the<br />
embryonic liver, which support the <strong>de</strong>velopment of fetal<br />
hepatoblasts: The emerging liver contains the major<br />
concentration of megakaryocytes of the economy, although<br />
platelets are dispensable for embryo survival. In vitro co-cultures<br />
have revealed that these cells promote hepatic differentiation.<br />
We are studying the molecular bases of this phenomenon.<br />
This research has been ma<strong>de</strong> in collaboration with ML<br />
Gaspar from the ISCIII.<br />
Marcos, M.A.R., Toribio, M.L. and Gaspar, M.L. (2006). Immune<br />
system: Early ontogeny. In: Encyclopedia of Life Sciences.<br />
John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. Chichester (online publication).<br />
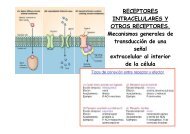
Figura 1. Nichos hematopoyéticos <strong>de</strong>l embrión <strong>de</strong> ratón en la<br />
gestación media. En embriones E7-8, el único proceso es la<br />
mieloeritropoyesis primitiva. La hematopoyesis <strong>de</strong> tipo adulto<br />
aparece simultáneamente en la SP/AGM y el YS <strong>de</strong> embriones<br />
>E8. La vista transversal <strong>de</strong>scribe la AGM con los agregados<br />
celulares intraaórticos y subaórticos. El hígado es colonizado<br />
por progenitores <strong>de</strong>l YS y <strong>de</strong> la SP/AGM (1, 2). El timo es injertado<br />
por precursores <strong>de</strong> la SP/AGM y <strong>de</strong>l hígado (3, 4). No está claro si<br />
progenitores hematopoyéticos migran entre el YS y la SP/AGM (5,<br />
6). Órganos hematopoyéticos embrionarios, rojo; tubo neural, azul;<br />
aorta dorsal, ver<strong>de</strong>; mesonephros, marrón; gónadas, naranja.<br />
Reproducido <strong>de</strong> la Encyclopedia of Life Sciences, con permiso<br />
<strong>de</strong> John Wiley & Sons.<br />
Figure 1. Haematopoietic sites in mid-gestation mouse embryos.<br />
Primitive myeloerythropoiesis is the only process occuring in E7-8<br />
embryos. Adult-type haematopoiesis simultaneously appears in<br />
Sp/AGM and YS of >E8 embryos. The transversal view <strong>de</strong>picting<br />
AGM region inclu<strong>de</strong>s subaortic and intraaortic cell clusters. FL is<br />
colonized by both YS- and Sp/AGM-<strong>de</strong>rived progenitors (1, 2).<br />
The embryo thymus is engrafted with Sp/AGM- and FL-<strong>de</strong>rived<br />
precursors (3, 4). Whether haematopoietic progenitors migrate<br />
between both YS and Sp/AGM is unclear (5, 6). Embryo<br />
haematopoietic sites, red; neural tube, blue; dorsal aorta, green;<br />
mesonephros, brown; gonads, orange. Reproduced from the<br />
Encyclopedia of Life Sciences by permission of John Wiley & Sons.<br />
77