dry anaerobic digestion of municipal solid waste and digestate ...
dry anaerobic digestion of municipal solid waste and digestate ...
dry anaerobic digestion of municipal solid waste and digestate ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Depending on its characteristics, it could be either applied directly on the agriculture l<strong>and</strong><br />
or treated by aerobic process <strong>of</strong> curing or composting. During its h<strong>and</strong>ling <strong>and</strong><br />
management, the <strong>digestate</strong> needs to be stored as well as dewatered. Thus, the main purpose<br />
<strong>of</strong> Phase III is to find environmentally suitable options for <strong>digestate</strong> management. The<br />
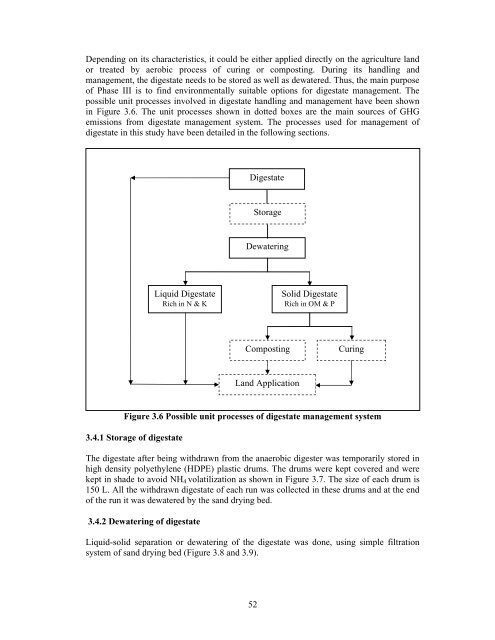
possible unit processes involved in <strong>digestate</strong> h<strong>and</strong>ling <strong>and</strong> management have been shown<br />
in Figure 3.6. The unit processes shown in dotted boxes are the main sources <strong>of</strong> GHG<br />
emissions from <strong>digestate</strong> management system. The processes used for management <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>digestate</strong> in this study have been detailed in the following sections.<br />
Figure 3.6 Possible unit processes <strong>of</strong> <strong>digestate</strong> management system<br />
3.4.1 Storage <strong>of</strong> <strong>digestate</strong><br />
Liquid Digestate<br />
Rich in N & K<br />
The <strong>digestate</strong> after being withdrawn from the <strong>anaerobic</strong> digester was temporarily stored in<br />
high density polyethylene (HDPE) plastic drums. The drums were kept covered <strong>and</strong> were<br />
kept in shade to avoid NH4 volatilization as shown in Figure 3.7. The size <strong>of</strong> each drum is<br />
150 L. All the withdrawn <strong>digestate</strong> <strong>of</strong> each run was collected in these drums <strong>and</strong> at the end<br />
<strong>of</strong> the run it was dewatered by the s<strong>and</strong> <strong>dry</strong>ing bed.<br />
3.4.2 Dewatering <strong>of</strong> <strong>digestate</strong><br />
Digestate<br />
Liquid-<strong>solid</strong> separation or dewatering <strong>of</strong> the <strong>digestate</strong> was done, using simple filtration<br />
system <strong>of</strong> s<strong>and</strong> <strong>dry</strong>ing bed (Figure 3.8 <strong>and</strong> 3.9).<br />
52<br />
Storage<br />
Dewatering<br />
Composting<br />
L<strong>and</strong> Application<br />
Solid Digestate<br />
Rich in OM & P<br />
Curing