Download - FDCL
Download - FDCL
Download - FDCL
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
3.2 European foreign investment in MERCOSUR<br />
The European economic interest in the Common Market of the South (MER-<br />
COSUR) lies in the realized and expected profits obtained by the resident European<br />
corporations within the domestic markets and in the area of foreign trade. In terms<br />
of foreign trade the EU between 1990 and 1994 was able to “more than double”<br />
their exports to MERCOSUR countries, whereas imports rose only slightly: “a consequence<br />
of the unilateral liberalization on the part of the MERCOSUR countries.<br />
Especially Brazil, which lowered their tariffs from an average of 52 to 14 percent,<br />
became a desired market.” 176<br />
Between 1995 and 2002 the EU realized a current account surplus of 4.2 billion<br />
US-dollars with Brazil. According to the German employers’ umbrella organization<br />
BDI:<br />
“[...]since 1995, in its trade with Brazil, Germany has been benefiting from<br />
surpluses averaging approximately 1.5 billion dollars a year.” 177<br />
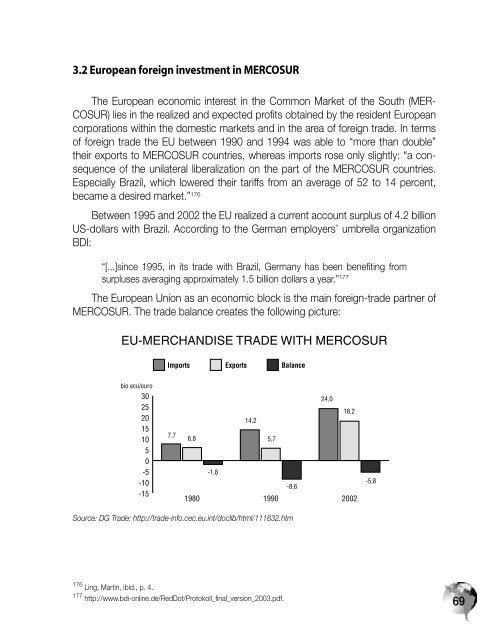
The European Union as an economic block is the main foreign-trade partner of<br />
MERCOSUR. The trade balance creates the following picture:<br />
EU-MERCHANDISE TRADE WITH MERCOSUR<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
Source: DG Trade: http://trade-info.cec.eu.int/doclib/html/111832.htm<br />
176 Ling, Martin, ibid., p. 4.<br />
177 http://www.bdi-online.de/RedDot/Protokoll_final_version_2003.pdf.<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
69