The Development of Novel Antibiotics Using ... - Jacobs University
The Development of Novel Antibiotics Using ... - Jacobs University
The Development of Novel Antibiotics Using ... - Jacobs University
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
2<br />
Similar to the case <strong>of</strong> trianglimine chemistry, macrocycles A<br />
and B form under conformational bias <strong>of</strong> dicarbohydrazides. 32-40<br />
2. Results and discussion<br />
2.1. Synthesis and molecular modeling<br />
In continuation to our work with cyclophane macrocycles A and<br />
B, we decided to synthesize a class <strong>of</strong> two-armed receptors which<br />
simulates the structural framework <strong>of</strong> macrocycle B. Receptors<br />
with such structural features are expected to be more flexible and<br />
to show improved molecular recognition abilities. Two-armed<br />
receptors 7-13 were synthesized from chiral dicarbohydrazides 1-<br />
3 by reacting with substituted aromatic isocyanate 4-6 in<br />
anhydrous THF (Fig. 1). <strong>The</strong> sidewalls <strong>of</strong> the receptors are made<br />
<strong>of</strong> amide moieties, which function as the receptor binding motifs,<br />
while dioxolane rings constitute the spacer units. <strong>The</strong> recognition<br />
affinity <strong>of</strong> the novel receptors in the gas phase to a selection <strong>of</strong><br />
chiral carboxylic acids and oligopeptides is demonstrated by<br />
using electrospray ionization time <strong>of</strong> flight mass spectrometry<br />
(ESI-TOF/MS) and tandem MS. Structures <strong>of</strong> the novel receptors<br />
were fully assigned by various spectroscopic techniques such as<br />
FT IR, 1 H NMR, 13 C NMR, 2D ROESY, Circular Dichroism<br />
spectroscopy (CD), ESI-TOF/MS and MS/MS.<br />
for subsequent structure modeling calculations. Structure <strong>of</strong><br />
receptor 7 was energy-minimized using HyperChem s<strong>of</strong>tware<br />
(Release 8.0) at the Austin Model 1 level (AM1). 41,42 Molecular<br />
modeling calculations are in good agreement with data from 2D<br />
ROESY NMR and suggests a spiral-like structure for receptor 7<br />
in which the NH moieties are syn/syn oriented. Structures <strong>of</strong><br />
receptors 7-13 are stabilized by intramolecular hydrogen bonds as<br />
shown in Figure 3.<br />
Table 1. High resolution ESI-TOF/MS data for receptors 7-13<br />
Entry<br />
Molecular<br />
formula<br />
Calcd. m/z<br />
a Meas. m/z<br />
Error<br />
[ppm]<br />
Yield<br />
%<br />
7 C 21H 24N 6O 8 487.1583 487.1588 –1.0 78<br />
8 C 26H 32N 6O 8 555.2209 555.2224 –2.8 74<br />
9 C 23H 28N 6O 10 547.1794 547.1782 2.2 93<br />
10 C 23H 30N 8O 6 513.2216 513.2240 –4.8 89<br />
11 C 21H 24N 6O 8 487.1583 487.1570 2.7 96<br />
12 C 23H 28N 6O 10 547.1794 547.1799 –1.0 99<br />
13 C 23H 30N 8O 6 513.2216 513.2233 –3.5 93<br />
a Product ions appeared as [M – H] –<br />
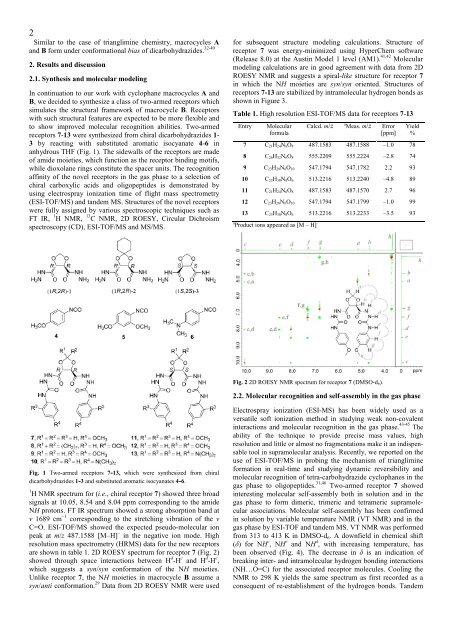
Fig. 2 2D ROESY NMR spectrum for receptor 7 (DMSO-d 6).<br />
2.2. Molecular recognition and self-assembly in the gas phase<br />
Fig. 1 Two-armed receptors 7-13, which were synthesized from chiral<br />
dicarbohydrazides 1-3 and substituted aromatic isocyanates 4-6.<br />
1 H NMR spectrum for (i.e., chiral receptor 7) showed three broad<br />
signals at 10.05, 8.54 and 8.04 ppm corresponding to the amide<br />
NH protons. FT IR spectrum showed a strong absorption band at<br />
ν 1689 cm −1 corresponding to the stretching vibration <strong>of</strong> the ν<br />
C=O. ESI-TOF/MS showed the expected pseudo-molecular ion<br />
peak at m/z 487.1588 [M–H] – in the negative ion mode. High<br />
resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) data for the new receptors<br />
are shown in table 1. 2D ROESY spectrum for receptor 7 (Fig. 2)<br />
showed through space interactions between H d -H c and H d -H e ,<br />
which suggests a syn/syn conformation <strong>of</strong> the NH moieties.<br />
Unlike receptor 7, the NH moieties in macrocycle B assume a<br />
syn/anti conformation. 29 Data from 2D ROESY NMR were used<br />
Electrospray ionization (ESI-MS) has been widely used as a<br />
versatile s<strong>of</strong>t ionization method in studying weak non-covalent<br />
interactions and molecular recognition in the gas phase. 43-45 <strong>The</strong><br />
ability <strong>of</strong> the technique to provide precise mass values, high<br />
resolution and little or almost no fragmentations make it an indispensable<br />
tool in supramolecular analysis. Recently, we reported on the<br />
use <strong>of</strong> ESI-TOF/MS in probing the mechanism <strong>of</strong> trianglimine<br />
formation in real-time and studying dynamic reversibility and<br />
molecular recognition <strong>of</strong> tetra-carbohydrazide cyclophanes in the<br />
gas phase to oligopeptides. 31,46 Two-armed receptor 7 showed<br />
interesting molecular self-assembly both in solution and in the<br />
gas phase to form dimeric, trimeric and tetrameric supramolecular<br />
associations. Molecular self-assembly has been confirmed<br />
in solution by variable temperature NMR (VT NMR) and in the<br />
gas phase by ESI-TOF and tandem MS. VT NMR was performed<br />
from 313 to 413 K in DMSO-d 6 . A downfield in chemical shift<br />
(δ) for NH c , NH e and NH d , with increasing temperature, has<br />
been observed (Fig. 4). <strong>The</strong> decrease in δ is an indication <strong>of</strong><br />
breaking inter- and intramolecular hydrogen bonding interactions<br />
(NH…O=C) for the associated receptor molecules. Cooling the<br />
NMR to 298 K yields the same spectrum as first recorded as a<br />
consequent <strong>of</strong> re-establishment <strong>of</strong> the hydrogen bonds. Tandem