Unit A Reproduction
Unit A Reproduction
Unit A Reproduction
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
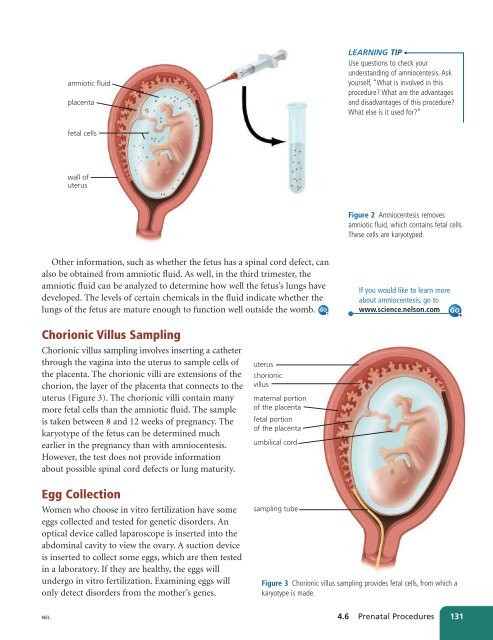
amniotic fluid<br />
placenta<br />
LEARNING TIP<br />
Use questions to check your<br />
understanding of amniocentesis. Ask<br />
yourself, “What is involved in this<br />
procedure? What are the advantages<br />
and disadvantages of this procedure?<br />
What else is it used for?”<br />
fetal cells<br />
wall of<br />
uterus<br />
Figure 2 Amniocentesis removes<br />
amniotic fluid, which contains fetal cells.<br />
These cells are karyotyped.<br />
Other information, such as whether the fetus has a spinal cord defect, can<br />
also be obtained from amniotic fluid. As well, in the third trimester, the<br />
amniotic fluid can be analyzed to determine how well the fetus’s lungs have<br />
developed. The levels of certain chemicals in the fluid indicate whether the<br />
lungs of the fetus are mature enough to function well outside the womb. GO<br />
If you would like to learn more<br />
about amniocentesis, go to<br />
www.science.nelson.com GO<br />
Chorionic Villus Sampling<br />
Chorionic villus sampling involves inserting a catheter<br />
through the vagina into the uterus to sample cells of<br />
the placenta. The chorionic villi are extensions of the<br />
chorion, the layer of the placenta that connects to the<br />
uterus (Figure 3). The chorionic villi contain many<br />
more fetal cells than the amniotic fluid. The sample<br />
is taken between 8 and 12 weeks of pregnancy. The<br />
karyotype of the fetus can be determined much<br />
earlier in the pregnancy than with amniocentesis.<br />
However, the test does not provide information<br />
about possible spinal cord defects or lung maturity.<br />
Egg Collection<br />
Women who choose in vitro fertilization have some<br />
eggs collected and tested for genetic disorders. An<br />
optical device called laparoscope is inserted into the<br />
abdominal cavity to view the ovary. A suction device<br />
is inserted to collect some eggs, which are then tested<br />
in a laboratory. If they are healthy, the eggs will<br />
undergo in vitro fertilization. Examining eggs will<br />
only detect disorders from the mother’s genes.<br />
NEL<br />
uterus<br />
chorionic<br />
villus<br />
maternal portion<br />
of the placenta<br />
fetal portion<br />
of the placenta<br />
umbilical cord<br />
sampling tube<br />
Figure 3 Chorionic villus sampling provides fetal cells, from which a<br />
karyotype is made.<br />
4.6 Prenatal Procedures 131