Unit A Reproduction
Unit A Reproduction
Unit A Reproduction
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Errors in meiosis can result in changes to both the gametes and<br />
the offspring.<br />
• When homologous chromosomes do not separate in meiosis, gametes<br />
have either too many or too few chromosomes. Having an extra copy<br />
of chromosome 21 causes Down syndrome.<br />
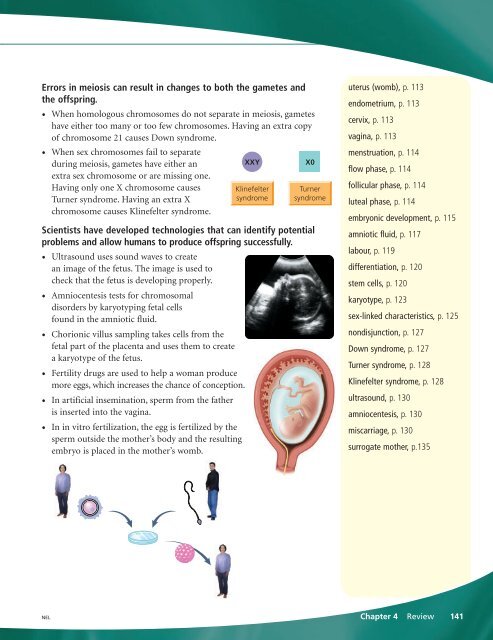
• When sex chromosomes fail to separate<br />
during meiosis, gametes have either an<br />
extra sex chromosome or are missing one.<br />
Having only one X chromosome causes<br />
Turner syndrome. Having an extra X<br />
chromosome causes Klinefelter syndrome.<br />
XXY<br />
Klinefelter<br />
syndrome<br />
Scientists have developed technologies that can identify potential<br />
problems and allow humans to produce offspring successfully.<br />
• Ultrasound uses sound waves to create<br />
an image of the fetus. The image is used to<br />
check that the fetus is developing properly.<br />
• Amniocentesis tests for chromosomal<br />
disorders by karyotyping fetal cells<br />
found in the amniotic fluid.<br />
• Chorionic villus sampling takes cells from the<br />
fetal part of the placenta and uses them to create<br />
a karyotype of the fetus.<br />
• Fertility drugs are used to help a woman produce<br />
more eggs, which increases the chance of conception.<br />
• In artificial insemination, sperm from the father<br />
is inserted into the vagina.<br />
• In in vitro fertilization, the egg is fertilized by the<br />
sperm outside the mother’s body and the resulting<br />
embryo is placed in the mother’s womb.<br />
X0<br />
Turner<br />
syndrome<br />
uterus (womb), p. 113<br />
endometrium, p. 113<br />
cervix, p. 113<br />
vagina, p. 113<br />
menstruation, p. 114<br />
flow phase, p. 114<br />
follicular phase, p. 114<br />
luteal phase, p. 114<br />
embryonic development, p. 115<br />
amniotic fluid, p. 117<br />
labour, p. 119<br />
differentiation, p. 120<br />
stem cells, p. 120<br />
karyotype, p. 123<br />
sex-linked characteristics, p. 125<br />
nondisjunction, p. 127<br />
Down syndrome, p. 127<br />
Turner syndrome, p. 128<br />
Klinefelter syndrome, p. 128<br />
ultrasound, p. 130<br />
amniocentesis, p. 130<br />
miscarriage, p. 130<br />
surrogate mother, p.135<br />
NEL<br />
Chapter 4 Review 141