Unit A Reproduction
Unit A Reproduction
Unit A Reproduction
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
CHAPTER<br />
4<br />
Review<br />
Human <strong>Reproduction</strong><br />
Key Ideas<br />
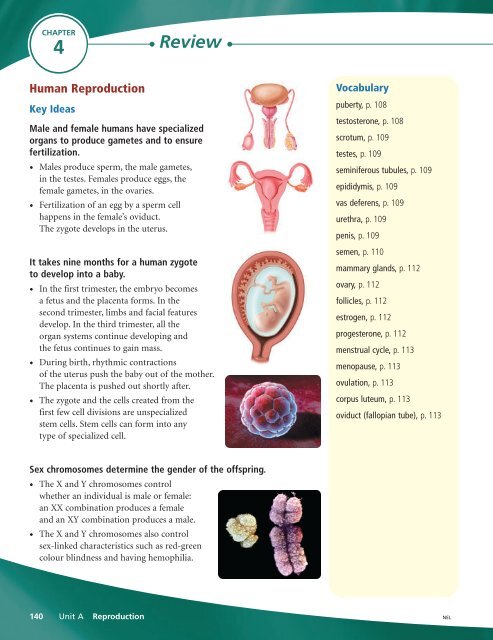
Male and female humans have specialized<br />
organs to produce gametes and to ensure<br />
fertilization.<br />
• Males produce sperm, the male gametes,<br />
in the testes. Females produce eggs, the<br />
female gametes, in the ovaries.<br />
• Fertilization of an egg by a sperm cell<br />
happens in the female’s oviduct.<br />
The zygote develops in the uterus.<br />
It takes nine months for a human zygote<br />
to develop into a baby.<br />
• In the first trimester, the embryo becomes<br />
a fetus and the placenta forms. In the<br />
second trimester, limbs and facial features<br />
develop. In the third trimester, all the<br />
organ systems continue developing and<br />
the fetus continues to gain mass.<br />
• During birth, rhythmic contractions<br />
of the uterus push the baby out of the mother.<br />
The placenta is pushed out shortly after.<br />
• The zygote and the cells created from the<br />
first few cell divisions are unspecialized<br />
stem cells. Stem cells can form into any<br />
type of specialized cell.<br />
Vocabulary<br />
puberty, p. 108<br />
testosterone, p. 108<br />
scrotum, p. 109<br />
testes, p. 109<br />
seminiferous tubules, p. 109<br />
epididymis, p. 109<br />
vas deferens, p. 109<br />
urethra, p. 109<br />
penis, p. 109<br />
semen, p. 110<br />
mammary glands, p. 112<br />
ovary, p. 112<br />
follicles, p. 112<br />
estrogen, p. 112<br />
progesterone, p. 112<br />
menstrual cycle, p. 113<br />
menopause, p. 113<br />
ovulation, p. 113<br />
corpus luteum, p. 113<br />
oviduct (fallopian tube), p. 113<br />
Sex chromosomes determine the gender of the offspring.<br />
• The X and Y chromosomes control<br />
whether an individual is male or female:<br />
an XX combination produces a female<br />
and an XY combination produces a male.<br />
• The X and Y chromosomes also control<br />
sex-linked characteristics such as red-green<br />
colour blindness and having hemophilia.<br />
140 <strong>Unit</strong> A <strong>Reproduction</strong><br />
NEL