Unit A Reproduction
Unit A Reproduction
Unit A Reproduction
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
amniotic<br />
fluid<br />
placenta<br />
umbilical<br />
cord<br />
fetus<br />
uterus<br />
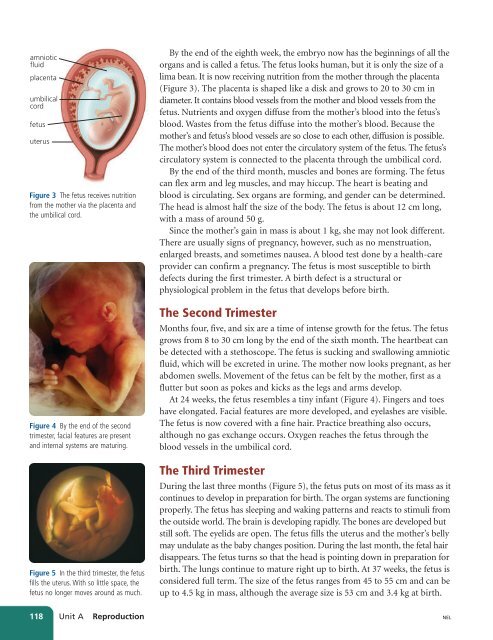
Figure 3 The fetus receives nutrition<br />
from the mother via the placenta and<br />
the umbilical cord.<br />
Figure 4 By the end of the second<br />
trimester, facial features are present<br />
and internal systems are maturing.<br />
Figure 5 In the third trimester, the fetus<br />
fills the uterus. With so little space, the<br />
fetus no longer moves around as much.<br />
By the end of the eighth week, the embryo now has the beginnings of all the<br />
organs and is called a fetus. The fetus looks human, but it is only the size of a<br />
lima bean. It is now receiving nutrition from the mother through the placenta<br />
(Figure 3). The placenta is shaped like a disk and grows to 20 to 30 cm in<br />
diameter. It contains blood vessels from the mother and blood vessels from the<br />
fetus. Nutrients and oxygen diffuse from the mother’s blood into the fetus’s<br />
blood. Wastes from the fetus diffuse into the mother’s blood. Because the<br />
mother’s and fetus’s blood vessels are so close to each other, diffusion is possible.<br />
The mother’s blood does not enter the circulatory system of the fetus. The fetus’s<br />
circulatory system is connected to the placenta through the umbilical cord.<br />
By the end of the third month, muscles and bones are forming. The fetus<br />
can flex arm and leg muscles, and may hiccup. The heart is beating and<br />
blood is circulating. Sex organs are forming, and gender can be determined.<br />
The head is almost half the size of the body. The fetus is about 12 cm long,<br />
with a mass of around 50 g.<br />
Since the mother’s gain in mass is about 1 kg, she may not look different.<br />
There are usually signs of pregnancy, however, such as no menstruation,<br />
enlarged breasts, and sometimes nausea. A blood test done by a health-care<br />
provider can confirm a pregnancy. The fetus is most susceptible to birth<br />
defects during the first trimester. A birth defect is a structural or<br />
physiological problem in the fetus that develops before birth.<br />
The Second Trimester<br />
Months four, five, and six are a time of intense growth for the fetus. The fetus<br />
grows from 8 to 30 cm long by the end of the sixth month. The heartbeat can<br />
be detected with a stethoscope. The fetus is sucking and swallowing amniotic<br />
fluid, which will be excreted in urine. The mother now looks pregnant, as her<br />
abdomen swells. Movement of the fetus can be felt by the mother, first as a<br />
flutter but soon as pokes and kicks as the legs and arms develop.<br />
At 24 weeks, the fetus resembles a tiny infant (Figure 4). Fingers and toes<br />
have elongated. Facial features are more developed, and eyelashes are visible.<br />
The fetus is now covered with a fine hair. Practice breathing also occurs,<br />
although no gas exchange occurs. Oxygen reaches the fetus through the<br />
blood vessels in the umbilical cord.<br />
The Third Trimester<br />
During the last three months (Figure 5), the fetus puts on most of its mass as it<br />
continues to develop in preparation for birth. The organ systems are functioning<br />
properly. The fetus has sleeping and waking patterns and reacts to stimuli from<br />
the outside world. The brain is developing rapidly. The bones are developed but<br />
still soft. The eyelids are open. The fetus fills the uterus and the mother’s belly<br />
may undulate as the baby changes position. During the last month, the fetal hair<br />
disappears. The fetus turns so that the head is pointing down in preparation for<br />
birth. The lungs continue to mature right up to birth. At 37 weeks, the fetus is<br />
considered full term. The size of the fetus ranges from 45 to 55 cm and can be<br />
up to 4.5 kg in mass, although the average size is 53 cm and 3.4 kg at birth.<br />
118 <strong>Unit</strong> A <strong>Reproduction</strong><br />
NEL