Unit A Reproduction
Unit A Reproduction
Unit A Reproduction
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
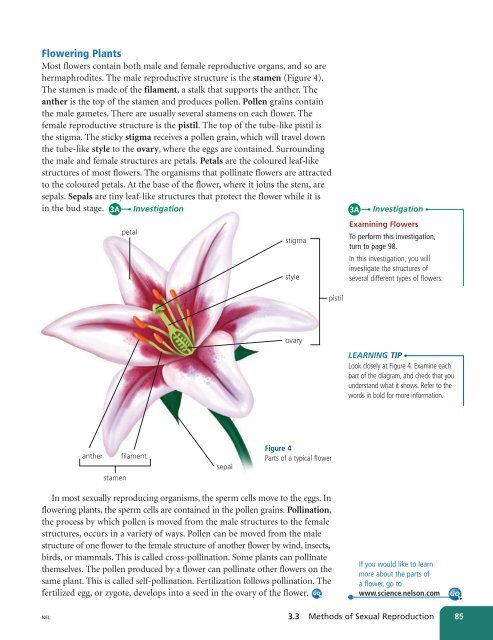
Flowering Plants<br />
Most flowers contain both male and female reproductive organs, and so are<br />
hermaphrodites. The male reproductive structure is the stamen (Figure 4).<br />
The stamen is made of the filament, a stalk that supports the anther. The<br />
anther is the top of the stamen and produces pollen. Pollen grains contain<br />
the male gametes. There are usually several stamens on each flower. The<br />
female reproductive structure is the pistil. The top of the tube-like pistil is<br />
the stigma. The sticky stigma receives a pollen grain, which will travel down<br />
the tube-like style to the ovary, where the eggs are contained. Surrounding<br />
the male and female structures are petals. Petals are the coloured leaf-like<br />
structures of most flowers. The organisms that pollinate flowers are attracted<br />
to the coloured petals. At the base of the flower, where it joins the stem, are<br />
sepals. Sepals are tiny leaf-like structures that protect the flower while it is<br />
in the bud stage.<br />
3A<br />
petal<br />
Investigation<br />
stigma<br />
style<br />
3A<br />
Investigation<br />
Examining Flowers<br />
To perform this investigation,<br />
turn to page 98.<br />
In this investigation, you will<br />
investigate the structures of<br />
several different types of flowers.<br />
pistil<br />
ovary<br />
LEARNING TIP<br />
Look closely at Figure 4. Examine each<br />
part of the diagram, and check that you<br />
understand what it shows. Refer to the<br />
words in bold for more information.<br />
anther<br />
stamen<br />
filament<br />
sepal<br />
Figure 4<br />
Parts of a typical flower<br />
In most sexually reproducing organisms, the sperm cells move to the eggs. In<br />
flowering plants, the sperm cells are contained in the pollen grains. Pollination,<br />
the process by which pollen is moved from the male structures to the female<br />
structures, occurs in a variety of ways. Pollen can be moved from the male<br />
structure of one flower to the female structure of another flower by wind, insects,<br />
birds, or mammals. This is called cross-pollination. Some plants can pollinate<br />
themselves. The pollen produced by a flower can pollinate other flowers on the<br />
same plant. This is called self-pollination. Fertilization follows pollination. The<br />
fertilized egg, or zygote, develops into a seed in the ovary of the flower. GO<br />
If you would like to learn<br />
more about the parts of<br />
a flower, go to<br />
www.science.nelson.com<br />
GO<br />
NEL<br />
3.3 Methods of Sexual <strong>Reproduction</strong> 85