Women in Latin America and the Caribbean - Cepal
Women in Latin America and the Caribbean - Cepal
Women in Latin America and the Caribbean - Cepal
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
33<br />
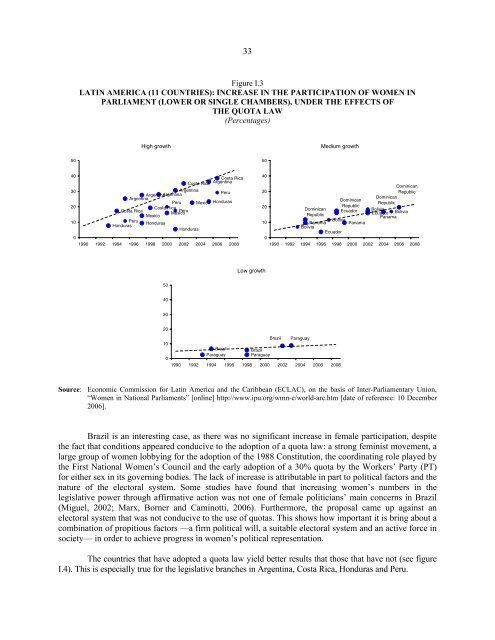
Figure I.3<br />
LATIN AMERICA (11 COUNTRIES): INCREASE IN THE PARTICIPATION OF WOMEN IN<br />
PARLIAMENT (LOWER OR SINGLE CHAMBERS), UNDER THE EFFECTS OF<br />
THE QUOTA LAW<br />
(Percentages)<br />
High growth<br />
Medium growth<br />
50<br />
50<br />
40<br />
Costa Rica<br />
Costa Rica Argent<strong>in</strong>a<br />
30<br />
Argent<strong>in</strong>a Argent<strong>in</strong>aArgent<strong>in</strong>aArgent<strong>in</strong>a Peru<br />
Peru Mexico Honduras<br />
20<br />
Costa Rica<br />
Costa Rica<br />
Peru<br />
Mexico<br />
Mexico<br />
10<br />
Peru<br />
Honduras<br />
Honduras<br />
Honduras<br />
0<br />
1990 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008<br />
40<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
Dom<strong>in</strong>ican<br />
Republic<br />
Dom<strong>in</strong>ican Ecuador<br />
Republic<br />
Bolivia<br />
Panama<br />
Panama<br />
Bolivia<br />
Ecuador<br />
Dom<strong>in</strong>ican<br />
Republic<br />
Dom<strong>in</strong>ican<br />
Republic<br />
Bolivia<br />
Ecuador Bolivia<br />
Panama<br />
0<br />
1990 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008<br />
Low growth<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
20<br />
Brazil Paraguay<br />
10<br />
Brazil<br />
Brazil<br />
0<br />
Paraguay<br />
Paraguay<br />
1990 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008<br />
Source: Economic Commission for Lat<strong>in</strong> <strong>America</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>Caribbean</strong> (ECLAC), on <strong>the</strong> basis of Inter-Parliamentary Union,<br />
“<strong>Women</strong> <strong>in</strong> National Parliaments” [onl<strong>in</strong>e] http://www.ipu.org/wmn-e/world-arc.htm [date of reference: 10 December<br />
2006].<br />
Brazil is an <strong>in</strong>terest<strong>in</strong>g case, as <strong>the</strong>re was no significant <strong>in</strong>crease <strong>in</strong> female participation, despite<br />
<strong>the</strong> fact that conditions appeared conducive to <strong>the</strong> adoption of a quota law: a strong fem<strong>in</strong>ist movement, a<br />
large group of women lobby<strong>in</strong>g for <strong>the</strong> adoption of <strong>the</strong> 1988 Constitution, <strong>the</strong> coord<strong>in</strong>at<strong>in</strong>g role played by<br />
<strong>the</strong> First National <strong>Women</strong>’s Council <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> early adoption of a 30% quota by <strong>the</strong> Workers’ Party (PT)<br />
for ei<strong>the</strong>r sex <strong>in</strong> its govern<strong>in</strong>g bodies. The lack of <strong>in</strong>crease is attributable <strong>in</strong> part to political factors <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
nature of <strong>the</strong> electoral system. Some studies have found that <strong>in</strong>creas<strong>in</strong>g women’s numbers <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
legislative power through affirmative action was not one of female politicians’ ma<strong>in</strong> concerns <strong>in</strong> Brazil<br />
(Miguel, 2002; Marx, Borner <strong>and</strong> Cam<strong>in</strong>otti, 2006). Fur<strong>the</strong>rmore, <strong>the</strong> proposal came up aga<strong>in</strong>st an<br />
electoral system that was not conducive to <strong>the</strong> use of quotas. This shows how important it is br<strong>in</strong>g about a<br />
comb<strong>in</strong>ation of propitious factors —a firm political will, a suitable electoral system <strong>and</strong> an active force <strong>in</strong><br />
society— <strong>in</strong> order to achieve progress <strong>in</strong> women’s political representation.<br />
The countries that have adopted a quota law yield better results that those that have not (see figure<br />
I.4). This is especially true for <strong>the</strong> legislative branches <strong>in</strong> Argent<strong>in</strong>a, Costa Rica, Honduras <strong>and</strong> Peru.